
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{2}=k\left(k\in Z\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3k\\y=2k\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mà \(x.y^2=96\)
\(\Rightarrow3k.4k^2=96\)
\(\Rightarrow12k^3=96\)
\(\Rightarrow k^3=8\)
\(\Rightarrow k=2\)
a. Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{2}=k\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3k\\y=2k\end{matrix}\right.\)
mà x . y2 = 96
hay \(3k.\left(2k\right)^2=96\)
\(\Rightarrow3k.4.k^2=96\)
\(\Rightarrow12.k^3=96\)
\(\Rightarrow k^3=8=2^3\)
\(\Rightarrow k=2\)
Với k = 2 \(\Rightarrow\begin{matrix}x=3.2=6\\y=2.2=4\end{matrix}\)
Vậy........
b. Áp dụng t/c dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{2x}{6}=\dfrac{4y}{20}=\dfrac{2x+4y}{6+20}=\dfrac{28}{26}=\dfrac{14}{13}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{14}{13}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3.14}{13}=\dfrac{42}{13}\\\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{14}{13}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{5.14}{13}=\dfrac{70}{13}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...........

1/ a, Ta có :
\(x-2y+3z=35\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{2y}{8}=\dfrac{3z}{15}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{2y}{8}=\dfrac{3z}{15}=\dfrac{x-2y+3z}{3-8+15}=\dfrac{35}{10}=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{7}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{21}{2}\\\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{7}{2}\Leftrightarrow y=14\\\dfrac{z}{5}=\dfrac{7}{2}\Leftrightarrow z=\dfrac{35}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ..

Theo đề bài ta có :
\(\dfrac{x-y}{3}=\dfrac{x+y}{13}\)
Áp dụng t/c dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x-y}{3}=\dfrac{x+y}{13}=\dfrac{x-y+x+y}{3+13}=\dfrac{2x}{16}=\dfrac{x}{8}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{xy}{200}\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x}{xy}=\dfrac{8}{200}\Rightarrow\) \(\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{25}\) \(\Rightarrow y=25\)
Thay y = 25 vào biểu thức ta có :
\(\dfrac{x-25}{3}=\dfrac{x+25}{13}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(13x-325=3x+75\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13x-3x=75+325\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x=400\)
\(\Rightarrow x=40\)
Vậy \(x=40\) ; \(y=25\)

a, \(\left[x\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)-\left(x^2+1\right)\right]x^2-1\)
\(=\left[x\left(x^2-16\right)-\left(x^2+1\right)\right]x^2-1\)
\(=\left[x^3-16x-x^2-1\right]x^2-1\)
\(=x^5-16x^3-x^4-x^2-1\)
b, \(\left(y-3\right)y+3y^2+9-y^2+2\left(y^2-2\right)\)
\(=y^2-3y+3y^2+9-y^2+2y^2-4\)
\(=5y^2-3y+5\)
c, \(\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2x^2-xy+y^2\right)\)
\(=x^5-x^2y+xy^2+x^4y-xy^2+y^3\)
d, \(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}xy+\dfrac{3}{4}y\right).\dfrac{1}{2}xy-\dfrac{3}{4}y\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}x^2y^2+\dfrac{3}{8}xy^2-\dfrac{3}{4}y\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}y.\left(x^2y+\dfrac{3}{2}xy-3\right)\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!!!

a) \(\dfrac{x^3}{8}=\dfrac{y^3}{64}=\dfrac{z^3}{216}\)
Từ \(\dfrac{x^3}{8}=\dfrac{y^3}{64}=\dfrac{z^3}{216}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x^3}{2^3}=\dfrac{y^3}{4^3}=\dfrac{z^3}{6^3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{2^2}=\dfrac{y^2}{4^2}=\dfrac{z^2}{6^2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{4}=\dfrac{y^2}{16}=\dfrac{z^2}{36}\)
Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta có:
\(\dfrac{x^2}{4}=\dfrac{y^2}{16}=\dfrac{z^2}{36}=\dfrac{x^2+y^2+z^2}{4+16+36}=\dfrac{14}{56}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{4}\Rightarrow x^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot4\Rightarrow x^2=1\Rightarrow x=1\)
\(\dfrac{y^2}{16}=\dfrac{1}{4}\Rightarrow y^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot16\Rightarrow y^2=4\Rightarrow y=2\)
\(\dfrac{z^2}{36}=\dfrac{1}{4}\Rightarrow z^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot36\Rightarrow z^2=9\Rightarrow z^2=3\)
Xin lỗi mình chỉ làm được câu a)

Đặt k = 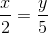 . Ta có x = 2k, y = 5k
. Ta có x = 2k, y = 5k
Từ xy=10. suy ra 2k.5k = 10 => 10 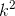 = 10 =>
= 10 => 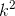 = 1 => k = ± 1
= 1 => k = ± 1
Với k = 1 ta được 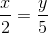 = 1 suy ra x = 2, y = 5
= 1 suy ra x = 2, y = 5
Với k = -1 ta được 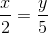 = -1 suy ra x = -2, y = -5
= -1 suy ra x = -2, y = -5
Gọi \(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=k\)
Với \(\dfrac{x}{2}=k\Rightarrow x=2k\); \(\dfrac{y}{5}=k\Rightarrow y=5k\)
Theo đề bài,ta còn có:
\(xy=10\)
hay 2k.5k=10
10k2 =10
\(\Rightarrow k=\pm1\)
Với k=1 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=1\Rightarrow x=2;y=5\)
Với k=-1 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=-1\Rightarrow x=-2;y=-5\)

Bài 1:
1)
\(\dfrac{3x+2}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{5x-3}{3}\)
<=> 3(3x + 2) = 4(5x - 3)
<=> 9x + 6 = 20x - 12
<=> 6 +12 = 20x - 9x
<=> 11x = 18
<=> x = \(\dfrac{18}{11}\)
Vậy: x = \(\dfrac{18}{11}\)
2)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{3x+2}\)= \(\dfrac{1}{5}\)
<=> 5(x - 1) = 3x + 2
<=> 5x - 5 = 3x + 2
<=> 5x - 3x = 2 +5
<=> 2x = 7
<=> x = \(\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy : x = \(\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Bài 1 :
1) Ta có :
\(\dfrac{3x+2}{4}=\dfrac{5x-3}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow4\cdot\left(5x-3\right)=3\cdot\left(3x+2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow20x-12=9x+6\\ \Leftrightarrow20x-18=9x\\ \Leftrightarrow20x-9x=18\\ \Leftrightarrow11x=18\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{11}\\ Vậy.,...\)
2) Ta có :
\(\dfrac{x-1}{3x+2}=\dfrac{1}{5}\Leftrightarrow5\cdot\left(x-1\right)=3x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow5x-5=3x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow5x-3x-5=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-5=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=7\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Vậy ....
Bài 2 ;
1) Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{x+y}{3+4}=\dfrac{21}{7}=3\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\cdot3=9\\y=3\cdot4=12\end{matrix}\right.\\ Vậy...\)
2) Ta có : \(3x=5y\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{3}\)
Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{3}=\dfrac{x-y}{5-3}=\dfrac{-16}{2}=-8\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\cdot5=-40\\y=-8\cdot3=-24\end{matrix}\right.\\ Vậy....\)
3) Ta có : \(4x=7y\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{7}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{x^2}{7^2}=\dfrac{y^2}{4^2}=\dfrac{x\cdot y}{7\cdot4}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{7}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{112}{28}=4\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\cdot7=28\\y=4\cdot4=16\end{matrix}\right.\\ Vậy...\)

Ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+xy+\dfrac{y^2}{3}=2019\\z^2+\dfrac{y^2}{3}=1011\\x^2+xz+z^2=1008\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x^2+xy+\dfrac{y^2}{3}=z^2+\dfrac{y^2}{3}+x^2+xz+z^2\)
\(\Rightarrow xy=2z^2+xz\Leftrightarrow xy+xz=2z^2+2xz\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(y+z\right)=2z\left(x+z\right)\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2z}{x}=\dfrac{y+z}{x+z}\left(đpcm\right)\)
xy = 96 => x = 96/y => 2/x = y/48
=> y/48 = 3/y => y = 12 hoặc -12
=> x = 8 hoặc -8
\(\dfrac{2}{x}=\dfrac{3}{y}\) và x.y =96
\(=>\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{3}=k\)
=> x = 2k và y = 3k
Thay vào x.y = 96
(2k . 3k) = 96
\(6k^2=96\)
\(k^2=96:6\)
\(k^2=16\)
\(k=-4\) hoặc \(+4\)
Với k = - 4 => x = 2 . ( - 4 ) = - 8
y = 3 . ( - 4) = - 12
Với k = 4 => x = 2 . 4 = 8
y = 3 . 4 = 12