
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)(x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)
=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5
=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25
=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x
=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x
c) tự làm, đkxđ: x≠1;x≠−1

a) \(\frac{5x}{2x+4}\)
Để pt được xác định thì 2x + 4 ≠ 0
2 (x + 2) ≠ 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2\ne0\\x+2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2\ne0\\x\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x ≠ -2 thì pt trên được xác định.
b) \(\frac{x-1}{x^2-1}\)
Để pt được xác định thì x2 - 1 ≠ 0
=> x2 ≠ 1
=> x ≠ \(\pm1\)
Vậy x ≠ \(\pm1\) thì pt được xác định.

Bài 1:
\(\left(\frac{1}{2x-1}-\frac{1}{2x+1}\right):\frac{4}{10x-5}\)
\(=\left(\frac{2x+1}{4x^2-1}-\frac{2x-1}{4x^2-1}\right)\cdot\frac{10x-5}{4}\)
\(=\frac{2}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\cdot\frac{5\left(2x-1\right)}{4}\)
\(=\frac{5}{2\left(2x+1\right)}\)
Bài 2:
a)Đk:\(2x^2+2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x\ne0\\x\ne-1\end{array}\right.\)
b)\(A=\frac{5x+5}{2x^2+2x}=\frac{5\left(x+1\right)}{2x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{5}{2x}\)
Phân thức A=1 nghĩ là \(\frac{5}{2x}=1\Rightarrow5=2x\Rightarrow x=\frac{5}{2}\)

a, \(ĐKXĐ:x^3+8\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne-2\)
b, \(C=\frac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}=\frac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=\frac{2}{x+2}\)
c, \(\left|2x+1\right|=3\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+1=3\\2x+1=-3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-2\left(ktm\right)\end{cases}\Rightarrow x=1}\)
thay vào ta được : \(C=\frac{2}{1+2}=\frac{2}{3}\)
\(\frac{x}{x+2}=2\Leftrightarrow x=2x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-4\left(tm\right)\)

a) phân thức xác định khi \(x^3+8\ne0\Leftrightarrow x^3\ne-8\Leftrightarrow x\ne-2\)
b)\(\frac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}=\frac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=\frac{2}{x+2}\)
c) \(\frac{2}{x+2}=\frac{2}{2+2}=\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\)
d)\(\frac{2}{x+2}=2\Leftrightarrow x+2=1\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)

Câu a :
Để biểu thức được xác định khi \(x+2\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne-2\)
Câu b :
\(\dfrac{x^2+4x+4}{x+2}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x+2}=x+2\)
Câu c :
Để phân thức bằng 1 thì \(x+2=1\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Câu d :
Để biểu thức bằng 0 thì \(\left(x+2\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2\) ( không thõa mãng )
Nên ko có giá trị x nào hết
a) ĐKXĐ : x+2≠0 ⇒x ≠ -2
b) \(\dfrac{x^{2^{ }}+4x+4}{x+2}\)= \(\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{x+2}\)= x+2
c) x+2= 1
⇒ x = -1
d) có x = -2 thì giá trị của phân thức = 0

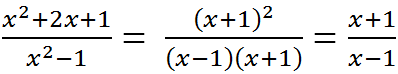
Phân thức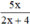 xác định
xác định
⇔ 2x + 4 ≠ 0
⇔ 2x ≠ -4
⇔ x ≠ -2
Vậy với mọi x ≠ -2 thì phân thức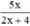 xác định.
xác định.