Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bạn bạn nhân phân phối (3x-1)(x-2) và (3x-1)(7x-10)
Sau đó chuyển vế sao cho về phương trình bậc 2
Sau đó giải pt bậc hai là ra
Ta có : (3x -1 ) . ( x + 2 ) = ( 3x-1 ) .( 7x - 10)
<=>3.x2 + 6x -x -2 = 21x2 -30x - 7x +10
<=> 3x2 + 5x -2 = 21x2 -37x + 10
<=> 3x2 +5x - 3 - 21x2 +37x -10 = 0
<=> -18x2 + 42x -12 = 0
<=> 3x2 -7x +2 = 0
<=> 3x2 -x -6x + 2 = 0
<=> x. ( 3x -1 ) -2.(3x -1 ) = 0
<=> (3x -1 ) . ( x - 2 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}}\)
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
Tập nghiệm của phương trình là : { \(\frac{1}{3}\); 2}

( 3x - 1)( x + 2) = ( 3x - 1)(7x - 10)
<=>( 3x - 1)( x + 2) - ( 3x - 1)(7x - 10) = 0
<=> ( 3x - 1)( x + 2 - 7x + 10) = 0
<=>( 3x - 1)( -6x + 12) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\-6x+12=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy.....
\(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)=\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-10\right)\)
\(3x^2+5x-2=21x^2-37x+10\)
\(3x^2+5x-2-21x^2+37x-10=0\)
\(-18x^2+42x-12=0\)
\(-6\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(-6\ne0\)
\(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x=1\\x=2\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)

a) \(2x^3 + 6x^2 = x^2 +3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x+3\right)=x\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(2x^2-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right).x\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
S = \(\left\{-3;0;\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
b) \((3x-1) (x^2 +2 ) = (3x-1) (7x - 10)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)-\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+2-7x+10\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2-7x+12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\x-3=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=3\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
S = \(\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};3;4\right\}\)


a)\(2x^3=x^2+2x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^3-x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2\left(2x-1\right)-\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\pm1\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
b)\(\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=\left(3x-1\right)\left(7x-x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)-6x\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x^2+2-6x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x-1=0\\\Delta_{x^2-6x+2=0}=\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot2=28\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x_{2,3}=\frac{6\pm\sqrt{28}}{2}\end{cases}}\)

b: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7x+10}{x+1}\left(x^2-x-2-2x^2+3x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(7x+10\right)\left(-x^2+2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(7x+10\right)\left(x^2-2x-3\right)=0\)
=>(7x+10)(x-3)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{10}{7};3\right\}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{2x^2+7x-6x-21}+\dfrac{1}{2x+7}-\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2x+7\right)}-\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow26x+91+x^2-9-12x-14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+14x+68=0\)
hay \(x\in\varnothing\)
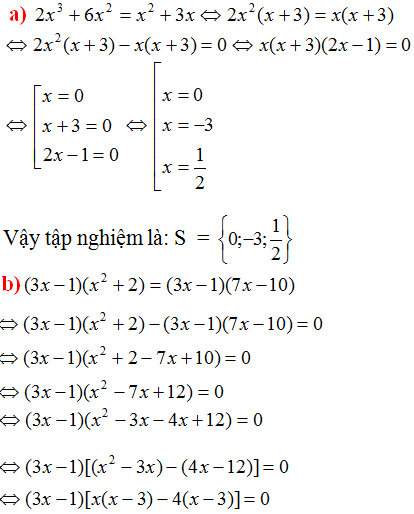
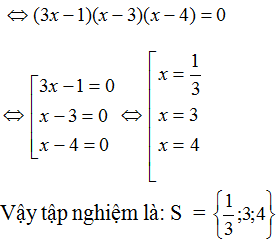
(3x – 1)(x2 + 2) = (3x – 1)(7x – 10)
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2) – (3x – 1)(7x – 10) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 + 2 – 7x + 10) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 – 7x + 12) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x2 – 4x – 3x + 12) = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)[(x2 – 4x) – (3x - 12)] = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)[x(x – 4) – 3(x – 4)] = 0
⇔ (3x – 1)(x – 3)(x – 4) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 4 = 0
+ 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 1/3.
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x – 4 = 0 ⇔ x = 4.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là