
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) \(\dfrac{x}{3}-\dfrac{2x+1}{2}=\dfrac{x}{6}-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x}{6}-\dfrac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{6}=\dfrac{x}{6}=\dfrac{6x}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3\left(2x+1\right)=x-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6x-3=x-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-6x-x+6x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
\(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{2+x}{5}-0,5x=\dfrac{1-2x}{4}+0,25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(2+x\right)}{20}-\dfrac{10x}{20}=\dfrac{5\left(1-2x\right)}{20}+\dfrac{5}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(2+x\right)-10x=5\left(1-2x\right)+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8+4x-10x=5-10x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-10x+10x=5+5-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x\right)^2-\left(2x-3\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x-2x+3\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+2x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\\left(3-\dfrac{3}{2}x\right)\left(\dfrac{5}{2}x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{\dfrac{6}{5}\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\\left(3x+4\right)^2-\left(2x\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\\left(5x+4\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=12\\\left(5x-x+12\right)\left(5x+x-12\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=12\\\left(4x+12\right)\left(6x-12\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay \(x\in\varnothing\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(2,5x-1,5x-5\right)\left(2,5x+1,5x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(x-5\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-\dfrac{5}{4};5\right\}\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{2}{3}\\\left(3x-2-2x\right)\left(3x-2+2x\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{2}{3}\\\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
hay x=2
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(-3,5x-1,5x-5\right)\left(-3,5x+1,5x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-\dfrac{10}{3}\\\left(-5x-5\right)\left(-2x+5\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-1;\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{1}{3}\\\left(3x-1-x-15\right)\left(3x-1+x+15\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{1}{3}\\\left(2x-16\right)\left(4x+14\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=0,5x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=8\\\left(0,5x-4-x+2\right)\left(0,5x-4+x-2\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=8\\\left(-0,5x-2\right)\left(1,5x-6\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)

Đặt \(y=x^2-2x+3=\left(x-1\right)^2+2\ge2\), ta có:
\(x^2-2x+3=\frac{6}{x^2-2x+4}\Leftrightarrow y=\frac{6}{y+1}\Leftrightarrow y\left(y+1\right)=6\Leftrightarrow y^2+y-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(y-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=2\\y=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)

a, \(1-\frac{2x-1}{9}=3-\frac{3x-3}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{108-12\cdot\left(2x-1\right)}{108}=\frac{108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)}{108}\)
\(\Rightarrow108-12\cdot\left(x-1\right)=108\cdot3-9\cdot\left(3x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow108-24x+12=324-27x+27\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=231\)
\(\Rightarrow x=77\)
c,\(\frac{3}{4x-20}+\frac{15}{50-2x^2}+\frac{7}{6x+30}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+15\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(6x+30\right)+7\cdot\left(4x-20\right)\cdot\left(50-2x^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow900x+4500-36x^3-180x^2+360x^2+1800x-1800x-9000+1400x-56x^3-7000+280x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-92x^3+460x^2+2300x-11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow92x^3-460x^2-2300x+11500=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=5\end{cases}}\)
a) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta được: 2.3 + 3 < 9 <=> 9 < 9 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình2x + 3 < 9
b) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: -4.3 > 2.3 + 5 => -12 > 11 (khẳng định sai)
Vậy x = 3 không là nghiệm của bất phương trình -4x > 2x + 5
c) Thay x = 3 vào bất phương trình ta có: 5 - 3 > 3.3 -12 => 2 > -3 (khẳng định đúng)
Vậy x = 3 là nghiệm của bất phương trình 5 - x > 3x - 12

Câu 1a : tự kết luận nhé
\(2\left(x+3\right)=5x-4\Leftrightarrow2x+6=5x-4\Leftrightarrow-3x=-10\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{10}{3}\)
Câu 1b : \(\frac{1}{x-3}-\frac{2}{x+3}=\frac{5-2x}{x^2-9}\)ĐK : \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3-2x+6=5-2x\Leftrightarrow-x+9=5-2x\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
c, \(\frac{x+1}{2}\ge\frac{2x-2}{3}\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+1}{2}-\frac{2x-2}{3}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x+3-4x+8}{6}\ge0\Rightarrow-x+11\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\le11\)vì 6 >= 0
1) 2(x + 3) = 5x - 4
<=> 2x + 6 = 5x - 4
<=> 3x = 10
<=> x = 10/3
Vậy x = 10/3 là nghiệm phương trình
b) ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne\pm3\)
\(\frac{1}{x-3}-\frac{2}{x+3}=\frac{5-2x}{x^2-9}\)
=> \(\frac{x+3-2\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{5-2x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
=> x + 3 - 2(x - 3) = 5 - 2x
<=> -x + 9 = 5 - 2x
<=> x = -4 (tm)
Vậy x = -4 là nghiệm phương trình
c) \(\frac{x+1}{2}\ge\frac{2x-2}{3}\)
<=> \(6.\frac{x+1}{2}\ge6.\frac{2x-2}{3}\)
<=> 3(x + 1) \(\ge\)2(2x - 2)
<=> 3x + 3 \(\ge\)4x - 4
<=> 7 \(\ge\)x
<=> x \(\le7\)
Vậy x \(\le\)7 là nghiệm của bất phương trình
Biểu diễn
-----------------------|-----------]|-/-/-/-/-/-/>
0 7

| 2x – 1| = 3 (1)
Ta có | 2x – 1| = 2x – 1 khi 2x – 1 ≥ 0 hay x ≥ 1/2
| 2x – 1| = – (2x – 1) khi 2x – 1 < 0 hay x <1/2
Vậy để giải phương trình (1), ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
* Phương trình 2x – 1 = 3 với điều kiện x ≥ 1/2
Ta có 2x – 1 = 3
<=> 2x = 3 + 1
<=> x = 2 (TMĐK)
* Phương trình – (2x – 1) = 3 với điều kiện x <1/2
Ta có – 2x + 1 = 3
<=> – 2x = 3 – 1
<=> x = -1 (TMĐK)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là : S = { – 1; 2 }
| 2x - 1 | = 3
=> 2x - 1 = 3 hoặc 2x - 1 = -3
2x = 3 + 1 2x = -3 + 1
2x = 4 2x = -2
x = 2 x = -1
Vậy x = 2 hoăc x = -1

\(2|3-2x|-3x=13\)
* Nếu \(3-2x\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x\le3\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow|3-2x|=3-2x\)
\(2\left(3-2x\right)-3x=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-4x-3x=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)( thỏa mãn )
* Nếu \(3-2x< 0\Leftrightarrow2x>3\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{3}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow|3-2x|=-3+2x\)
\(2\left(-3+2x\right)-3x=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6+4x-3x=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=19\) ( thỏa mãn )
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-1;19\right\}\)

\(\frac{2x}{5}+\frac{3-2x}{3}\ge\frac{3x+2}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\frac{12x}{30}+\frac{10\left(3-2x\right)}{30}\ge\frac{15\left(3x+2\right)}{30}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)12x + 30 - 20x \(\ge\) 45x + 30
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 12x - 20x - 45x \(\ge\) -30 + 30
\(\Leftrightarrow\)- 53x \(\ge\)0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x \(\le\)0
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm là : x \(\le0\)
b) \(1-\frac{2x-5}{6}>\frac{3-x}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\frac{12}{12}-\frac{2\left(2x-5\right)}{12}>\frac{3\left(3-x\right)}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 12 - 4x + 10 > 9 - 3x
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-4x + 3x > -12 - 10 + 9
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-x > -13
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x < 13
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm là : x < 13
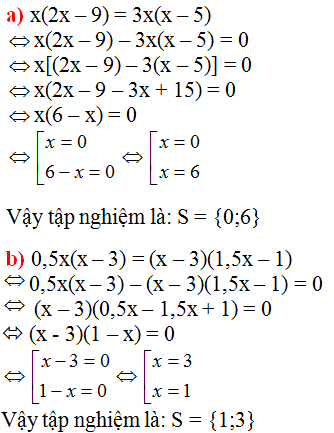
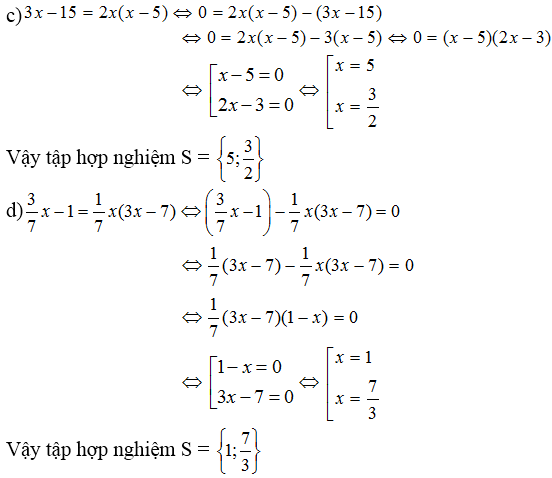
Ta có: |0,5x| = 0,5x khi 0,5x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 0
|0,5x| = -0,5x khi 0,5x < 0 ⇔ x < 0
Ta có: 0,5x = 3 – 2x ⇔ 0,5x + 2x = 3 ⇔ 2,5x = 3 ⇔ x = 1,2
Giá trị x = 1,2 thỏa mãn điều kiện x ≥ 0 nên 1,2 là nghiệm của phương trình.
-0,5x = 3 – 2x ⇔ -0,5x + 2x = 3 ⇔ 1,5x = 3 ⇔ x = 2
Giá trị x = 2 không thỏa mãn điều kiện x < 0 nên loại.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {1,2}