
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

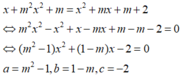

a: \(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3x+7=0\)
a=4; b=-3; c=7
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{5}x^2-x^2+5x-3-3x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\cdot\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)+2x+1=0\)
\(a=\sqrt{5}-1;b=2;c=1\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow mx^2-x^2-3x+mx+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(m-1\right)+x\left(m-3\right)+5=0\)
a=m-1; b=m-3; c=5
d: \(\Leftrightarrow m^2x^2-x^2+x+m-mx-m-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(m^2-1\right)+x\left(1-m\right)-2=0\)
\(a=m^2-1;b=1-m;c=-2\)

a) 5x2 + 2x = 4 – x ⇔ 5x2 + 3x – 4 = 0; a = 5, b = 3, c = -4
b) x2 + 2x – 7 = 3x +
⇔
x2 – x -
= 0, a =
, b = -1, c = -
c) 2x2 + x - √3 = √3 . x + 1 ⇔ 2x2 + (1 - √3)x – 1 - √3 = 0
Với a = 2, b = 1 - √3, c = -1 - √3
d) 2x2 + m2 = 2(m – 1)x ⇔ 2x2 - 2(m – 1)x + m2 = 0; a = 2, b = - 2(m – 1), c = m2

a) Thay m vào phương trình, ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}\sqrt{2}\times x+4y=10-\sqrt{2}\\x+\sqrt{2}\times y=6\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\sqrt{2}x+4y=10-\sqrt{2}\\x=6-\sqrt{2}y\end{cases}}\)
Thay giá trị đã có của x vào phương trình
\(\sqrt{2}\times\left(6-\sqrt{2}y\right)+4y=10-\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow y=5-\frac{7\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
Thay giá trị của y vào phương trình:
\(x=6-\sqrt{2}\times\left(5-\frac{7\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x=13-5\sqrt{2}\)

với m = 0 \Rightarrow ∫y=104x=4∫x=4y=104
với m khác 0 \Rightarrow ∫x+my=4mx+4y=10−m∫mx+4y=10−mx+my=4
\Leftrightarrow ∫y=5m+2x=−m+8m+2∫x=−m+8m+2y=5m+2
b. vì x >0 , y>0 \Rightarrow ∫y=5m+2>0x=−m+8m+2>0∫x=−m+8m+2>0y=5m+2>0
\Rightarrow ∫−m+8>0m+2>0∫m+2>0−m+8>0
\Rightarrow ∫m<8m>−2∫m>−2m<8
\Rightarrow -2<m<8
\Rightarrow m ={ -1;0;1;2;3;4;5;6;7}
c, y = −m+8m+2−m+8m+2 = -1 + 10m+210m+2
hệ có nghiệm x.y nguyên dương \Leftrightarrow m+2 là ước nguyên dương của 5
\Leftrightarrow m+2 = 1 ; 5
m+2 = 1 \Rightarrow m = -1
m+2 = 5 \Rightarrow m =3

Lời giải:
a)
\(3x^2-5x+1=2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-5x+1-2x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-7x+4=0\) (\(a=3; b=-7; c=4)\)
b)
\(\frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3=3x+\frac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3-3x-\frac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-7x-\frac{10}{3}=0(a=\frac{3}{5};b=-7; c=\frac{-10}{3})\)
c)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+x-5-\sqrt{3}x-\sqrt{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+(1-\sqrt{3})x-(5+\sqrt{2})=0\)
(\(a=-\sqrt{3}; b=1-\sqrt{3}; c=-(5+\sqrt{2}))\)
d)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5(m+1)x+m^2-2=0\)
(\(a=1;b=-5(m+1); c=m^2-2)\)

a) phương trình có a.c=3.(-8)=-24<0
vì a.c <0 nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm
b) phương trình có \(a.c=2004.\left(-1185\sqrt{5}\right)< 0\)
vì a.c<0 nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm
c) phương trình có \(a.c=3\sqrt{2}.\left(\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{3}\right)=6-3\sqrt{6}< 0\)
vì a.c<o nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm
d)phương trình có a.c=2010.(-m2)=-2010m2<0
vì a.c<0 nên phuong trình có 2 nghiệm

Lời giải
a)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=7\\b=-2\\c=3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta'=1-21=-20< 0\Rightarrow\left(a\right)VoN_0\)
(b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=5\\b=2\sqrt{10}\\c=2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta'=10-10=0\Rightarrow\left(b\right)\) có một nghiệm kép
(c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=7\\c=\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\Delta=49-4.\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{2}{3}=49-\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{143}{3}>0\) có hai nghiệm phân biệt
(d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1,7\\b=-1,2\\c=-2,1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Delta'=0,6^2+2,1.1,7>0\) pt có hai nghiệm phân biệt