
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{x^2-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-1^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{x-3}\)
Vậy đã biến đổi phân thức đó thành một phân thức bằng nó và có tử bằng với đa thức \(A=x-1\)

1.a) (3x+1)2-4(x-2)2= (3x+1)2-[2(x-2)]2=[(3x+1)-2(x-2)][(3x+1)+2(x-2)]=(x+3)(5x-1)
b) (a2+b2-5)2-4(ab+2)2= (a2+b2-5)2-[2(ab+2)]2 = (a2+b2-5-2ab-4)(a2+b2-5+2ab+4)=[(a-b)2-9][(a+b)2-1]
2. 3x2+9x-30=3x2-6x+15x-30=3x(x-2)+15(x-2)=3(x+5)(x-2)
b. x3-5x2-14x=x3+2x2-7x2-14x=x2(x+2)-7x(x+2)=(x2-7x)(x+2)
a) \(\left(3x+1\right)^2-4\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left[2.\left(x-2\right)\right]^2\)
\(=\left(3x+1\right)^2-\left(2x-4\right)^2\)
\(=\left[3x+1-2x+4\right].\left[3x+1+2x-4\right]\)
\(=\left(x+5\right)\left(5x-3\right)\)
b) \(\left(a^2+b^2-5\right)^2-4\left(ab+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(a^2+b^2-5\right)^2-\left[2.\left(ab+2\right)\right]^2\)
\(=\left(a^2+b^2-5\right)^2-\left(2ab+4\right)^2\)
\(=\left(a^2+b^2-5-2ab-4\right)\left(a^2+b^2-5+2ab+4\right)\)
\(=\left[\left(a-b\right)^2-9\right].\left[\left(a+b\right)^2-1\right]\)
\(=\left[\left(a-b-3\right)\left(a-b+3\right)\right].\left[\left(a+b-1\right)\left(a+b+1\right)\right]\)
a) \(3x^2+9x-30\)
\(=3\left(x^2+3x-10\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2-2x+5x-10\right)\)
\(=3.\left[x\left(x-2\right)+5.\left(x-2\right)\right]\)
\(=3.\left[\left(x+5\right)\left(x-2\right)\right]\)
b) \(x^3-5x^2-14x\)
\(=x\left(x^2-5x-14\right)\)
\(=x\left(x^2+2x-7x-14\right)\)
\(=x.\left[x\left(x+2\right)-7.\left(x+2\right)\right]\)
\(=x.\left[\left(x-7\right)\left(x+2\right)\right]\)

a) Để phân thức trên xác định \(\Leftrightarrow x^3-8\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne2\)
b) \(\frac{3x^2+6x+12}{x^3-8}\)
\(=\frac{3\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3}{x-2}\)

a) Phân thức 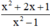 xác định
xác định
⇔ x2 – 1 ≠ 0
⇔ (x – 1)(x + 1) ≠ 0
⇔ x – 1 ≠ 0 và x + 1 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ ±1
Vậy phân thức xác định với mọi x ≠ ±1
b) Với x ≠ ±1, ta có:
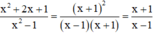
c) + Với x = 2, bạn Thắng tính giá trị biểu thức đúng.
+ Với x = -1, phân thức 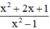 không xác định nên không thể tính giá trị biểu thức nên bạn Thắng tính sai.
không xác định nên không thể tính giá trị biểu thức nên bạn Thắng tính sai.
+ Để tính giá trị của phân thức bằng cách tính giá trị của phân thức rút gọn, ta phải đảm bảo giá trị của biến thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.

2.1
a) Áp dụng định lý Bezout:
\(P\left(x\right)⋮2x+3\)
\(\Rightarrow P\left(\frac{-3}{2}\right)=0\)
hay \(6.\frac{-27}{8}-7.\frac{9}{4}-16.\frac{-3}{2}+m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-81}{4}-\frac{63}{4}+24+m=0\)
\(\Rightarrow m=12\)
Vậy m = 12

`a^2 + ab + 2a + 2b = a(a+2) + b(a+2) = (a+b)(a+2)`