Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) ta có :
\(\Delta'=1^2-\left(-1-m\right)\left(m^2-1\right)=1-\left(-m^2+1-m^3+m\right)=1+m^2-1+m^3-m=m^3+m^2-m=m\left(m^2+m-1\right)\)để phương trình có nghiệm thì \(\Delta\ge0\)
hay \(m\left(m^2+m-1\right)\ge0\)
=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge0\\m^2+m-1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge0\\\left(m+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{5}{4}\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge0\\\left(m+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\\m+\dfrac{1}{2}\le-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}}\)

\(VT=\dfrac{1+cos2x}{cos2x}\times\dfrac{1+cos4x}{sin4x}\) (*)
Ta có: theo công thức hạ bậc có: \(cos^2x=\dfrac{1+cos2x}{2}\Leftrightarrow1+cos2x=2cos^2x\) (1)
Ta có: \(cos2x=1-sin^2x\Rightarrow cos4x=1-2sin^22x\) (2)
Tương Tự có \(sin2x=2sinx\times cosx\Rightarrow sin4x=2sin2x\times cos2x\) (3)
Thay (1),(2),(3) vào (*) ta được: \(VT=\dfrac{2cos^2x}{cos2x}\times\dfrac{1+\left(1-2sin^22x\right)}{2sin2x\times cos2x}\)
\(VT=\dfrac{2cos^2x\times2\left(1-sin^22x\right)}{cos^22x\times2sin2x}\) mà \(1-sin^22x=cos^22x\)
\(\Rightarrow VT=\dfrac{2cos^2x\times cos^22x}{cos^22x\times2sinx\times cosx}=\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}=tanx\left(đpcm\right)\)
đoạn cuối nhầm nha \(VT=\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}=cotx\left(đpcm\right)\)

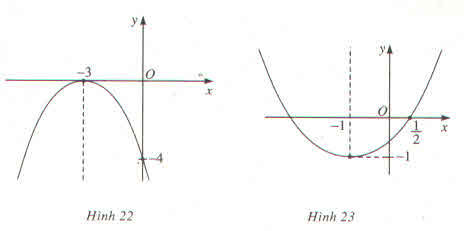
Hình 22
y=ax^2 +bx+c thỏa mãn hệ
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\left(0\right)=-4\Rightarrow c=-4\\y\left(-3\right)=9a-3b-4=0\\y\left(-6\right)=36a-6b-4=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
(3) -(2) nhân 2
\(36a-18a-4+8=-4\Rightarrow18a=-8\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{-8}{18}=\dfrac{-4}{9}\)
Thế vào (2) -4-3b-4=0 => b=-8/3
Vậy pa ra bo; cho hình 22 là
\(y=-\dfrac{4}{9}x^2-\dfrac{8}{3}x-4\)

Theo bài ra :
\(\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\left(3-x\right)>0\)
<=> \(\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(3-x\right)>0\)
Đặt \(\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(3-x\right)=A\)
Ta có bảng xét dấu :
| \(-\infty\) | -5 | -1 | 1 | 3 | \(+\infty\) | ||||
| (x+5) | - | 0 | + | + | + | + | |||
| x2-1 | + | + | 0 | - | 0 | + | + | ||
| 3-x | + | + | + | + | 0 | - | |||
| A | - (loại) | 0 (loại) | +(t.m) | 0(loại) | -(loại) | 0(loại) | +(t.m) | 0(loại) | -(loại) |
Từ bảng xét dấu trên suy ra :
\(A>0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-5< x< -1\\1< x< 3\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Ta thấy đường thẳng \(y=ax+b\) đi qua hai điểm \(\left(0;3\right)\) và \(\left(1;0\right)\). Vậy ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3=b\\0=a+b\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-3\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đường thẳng có phương trình là \(y=-3x+3\)
b) \(y=-4x\)
c) \(y=x-2\)

C1:
\(A=\dfrac{10^{50}+2}{10^{50}-1}=\dfrac{10^{50}-1}{10^{50}-1}+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-1}=1+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-1}\\ B=\dfrac{10^{50}}{10^{50}-3}=\dfrac{10^{50}-3}{10^{50}-3}+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-3}=1+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-3}\\ \text{Vì }10^{50}-3< 10^{50}-1\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-3}>\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-1}\Rightarrow1+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-3}>1+\dfrac{3}{10^{50}-1}\Leftrightarrow B>A\)
Vậy \(B>A\)
C2: Áp dụng \(\dfrac{a}{b}>1\Rightarrow\dfrac{a}{b}>\dfrac{a+n}{b+n}\left(n>0\right)\)
Dễ thấy
\(B=\dfrac{10^{50}}{10^{50}-3}>1\\ \Rightarrow B=\dfrac{10^{50}}{10^{50}-3}>\dfrac{10^{50}+2}{10^{50}-3+2}=\dfrac{10^{50}+2}{10^{50}-1}=A\)
Vậy \(B>A\)

1: ĐKXĐ: \(x^3-6x^2+11x-6< >0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-x^2-5x^2+5x+6x-6\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-5x+6\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\ne0\)
hay \(x\notin\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)
2; ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-2x>=0\\x+1< >-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =\dfrac{3}{2}\\x< >-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
3: ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2< >0\\x-1< >0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< >-2\\x< >1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in R\)

a) \(16x^2-\left(4x-5\right)^2=15\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(16x^2-\left(16x^2-40x+25\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(16x^2-16x^2+40x-25=15\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(40x-25=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(40x=40\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=1\) vậy \(x=1\)
b) \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(4x^2+12x+9-4\left(x^2-1\right)=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(4x^2+12x+9-4x^2+4=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(12x+13=49\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(12x=36\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=\dfrac{36}{12}=3\)vậy \(x=3\)
c) \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)+\left(1-2x\right)^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(4x^2-1+1-4x+4x^2=18\)\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(8x^2-4x=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(8x^2-4x-18=0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(-2\right)^2-8.\left(-18\right)=4+144=148>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(x_1=\dfrac{2+\sqrt{148}}{8}=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{37}}{4}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{148}}{8}=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)
vậy \(x=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{37}}{4};x=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)
Giải:
a) \(16x^2-\left(4x-5\right)^2=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2-16x^2-40x+25=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-40x+25=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-40x=15-25=-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{10}{-40}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b) \(\left(2x+3\right)^2-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-4\left(x^2-1^2\right)=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+12x+9-4x^2+4=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+9+4=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=49-9-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{36}{12}=3\)
Vậy \(x=3\)
c) \(\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)+\left(1-2x\right)^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-1+1-4x+4x^2=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x^2-4x=18\)
Mình chỉ làm được đến đây thôi, hình như là đề bị sai bạn nhé!
Chúc bạn học tốt!
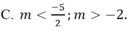
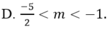

Đáp án: D