Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

2: ĐKXĐ: x<>1
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
f'(x)=0
=>x^2-2x=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-2\sqrt{2}\cdot x^2+8x-1\)
=>\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-2\sqrt{2}\cdot2x+8=x^2-4\sqrt{2}\cdot x+8=\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
f'(x)=0
=>\(\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\)
=>\(x-2\sqrt{2}=0\)
=>\(x=2\sqrt{2}\)


Để hàm số có đạo hàm tại x=0 phải thỏa mãn 2 điều kiện, đó là hàm số liên tục tại x=0 và có đạo hàm bên trái bằng đạo hàm bên phải
Để hàm số liên tục tại x=0 \(\Leftrightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}=f\left(0\right)\Leftrightarrow2=2\left(tm\right)\)
\(f'\left(0^+\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{f\left(x\right)-f\left(0\right)}{x-0}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{mx^2+2x+2-2}{x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{x\left(mx+2\right)}{x}=2\)
\(f'\left(0^-\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\dfrac{f\left(x\right)-f\left(0\right)}{x-0}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\dfrac{nx+2-2}{x}=n\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\in R\\n=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(0^+\right)=f\left(0^-\right)\Leftrightarrow n=2\)

\(f\left(x\right)=-x^3-2x^2+mx-3\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=-3x^2-4x+m\)
\(f'\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow-3x^2-4x+m>0\Leftrightarrow m>3x^2+4x\)(đúng với mọi \(x\in\left(0,1\right)\))
suy ra \(m\ge max\left(3x^2+4x\right)\)với \(x\in\left[0,1\right]\).
Xét hàm \(g\left(x\right)=3x^2+4x\)với \(x\in\left[0,1\right]\).
\(g'\left(x\right)=6x+4\)
\(g'\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow6x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{2}{3}\notin\left[0,1\right]\).
\(g\left(0\right)=0,g\left(1\right)=7\)
suy ra \(g_{max}=7\)
do đó \(m\ge7\).
Mà \(m\)nguyên, \(m\in\left[-2021,2021\right]\)nên có tổng cộng: \(2021-7+1=2015\)giá trị của \(m\)thỏa mãn.

1. Áp dụng quy tắc L'Hopital
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{f\left(0\right)-f\left(x\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}}{-f'\left(0\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{6}\)
2.
\(g'\left(x\right)=2x.f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=1\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2 pt cuối đều vô nghiệm nên \(g'\left(x\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{x^2+x-6}{x-2}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}{x-2}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}\left(x+3\right)=5\\ f\left(2\right)=5\\ \rightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow2}f\left(x\right)=f\left(2\right)\)
Suy ra f(x) liên tục tại x = 2.
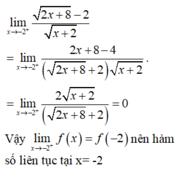
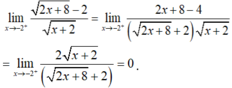
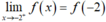 nên hàm số liên tục tại x = -2
nên hàm số liên tục tại x = -2
Chọn A.
Vậy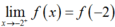 nên hàm số liên tục tại x = -2.
nên hàm số liên tục tại x = -2.