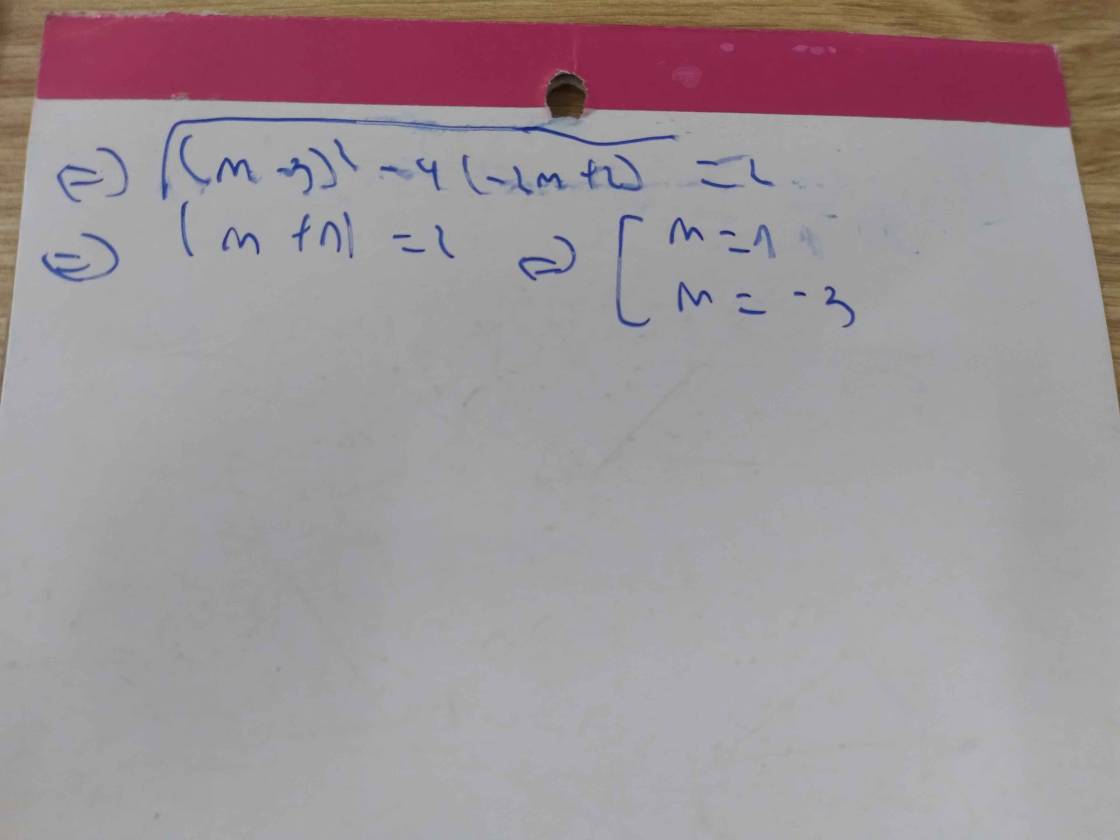Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a. PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt dương `<=> {(\Delta'=(m+1)^2-m^2>0),(S=2m+2>0),(P=m^2>0):} <=> {(m>-1/2),(m>-1),(forall m \ne 0):} <=> m>-1/2`
b. Viet: `{(x_1+x_2=2m+2),(x_1x_2=m^2):}`
Theo đề: `(x_1-m)+x_2=3m`
`<=> x_1-m+x_2=3m`
`<=>x_1+x_2=4m`
`<=> 2m+2=4m`
`<=>m=1` (TM)
Vậy `m=1`.

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiê pb thì:
$\Delta'=1-(m-3)>0\Leftrightarrow m< 4$
Áp dụng định lý Viet: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2=2\\ x_1x_2=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó:
\(x_1^2-2x_2+x_1x_2=-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2(2-x_1)+x_1(2-x_1)=-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1=-2\Leftrightarrow x_2=2-x_1=4\)
$m-3=x_1x_2=(-2).4=-8$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-5$ (tm)

b/ Ta có: x1 + x2 = 2m + 2
x1x2 = m - 4
M = x1(1 - x2) + x2(1 - x1) = x1 - x1x2 + x2 - x1x2 = (x1 + x2) - 2x1x2 = (2m + 2) - 2.(m - 4) = 10
Vậy không phụ thuộc vào m

\(x^2-x+1-m=0\left(1\right)\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm }x_1,x_2\\ \Leftrightarrow\Delta=1-4\left(1-m\right)\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m-3\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\\ \text{Vi-ét: }\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=1-m\end{matrix}\right.\\ \text{Ta có }5\left(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}\right)-x_1x_2+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5\cdot\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}-x_1x_2+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{1-m}+m-1+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{1-m}+m+3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5+\left(1-m\right)\left(m+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+4m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)\left(m+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\left(n\right)\\m=-4\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy $m=2$

dạ mình cám ơn ạ nma cho mình hỏi chút cái chỗ 2x1+x2=3 và x1+x2= gì v ạ