
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Xét (O) có
\(\widehat{BAD}\) là góc nội tiếp chắn \(\stackrel\frown{BD}\)
\(\widehat{CAD}\) là góc nội tiếp chắn \(\stackrel\frown{CD}\)
mà \(\widehat{BAD}=\widehat{CAD}\)(AD là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{BAC}\))
nên \(\stackrel\frown{BD}=\stackrel\frown{CD}\)
hay BD=CD
Ta có: OB=OC(=R)
nên O nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(Tính chất đường trung trực của một đoạn thẳng)(1)
Ta có: BD=CD(cmt)
nên D nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(Tính chất đường trung trực của một đoạn thẳng)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra OD là đường trung trực của BC
hay OD\(\perp\)BC(đpcm)

1.2 với \(x\ge0,x\in Z\)
A=\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\in Z< =>\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left(\pm1;\pm3\right)\)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=1=>\sqrt{x}=-1\)(vô lí)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-1=>\sqrt{x}=-3\)(vô lí
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=3=>x=1\)(TM)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-3=\sqrt{x}=-5\)(vô lí)
vậy x=1 thì A\(\in Z\)

Gọi vận tốc của ô tô là x
=>Vận tốc xe máy là x-10
Theo đề, ta có: 120/(x-10)-120/x=1
=>(120x-120x+1200)/x(x-10)=1
=>x^2-10x=1200
=>x^2-10x-1200=0
=>x=40


\(1,ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3x-6}+x-2-\left(\sqrt{2x-3}-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{3x-6}}+\left(x-2\right)-\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{3x-6}}-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x>2\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2x-3}+1}>-\dfrac{2}{1+1}=-1\left(3x-6\ne0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1\right)>0-1+1=0\left(vn\right)\)
Vậy \(x=2\)
\(2,ĐK:x\ge-1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x+1}=a\\\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2=x^2+2\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow2a^2+2b^2-5ab=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(2a-b\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\b=2a\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(a=2b\Leftrightarrow x+1=4x^2-4x+4\left(vn\right)\)
Với \(b=2a\Leftrightarrow4x+4=x^2-x+1\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-3=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...

a: \(=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}\left(x\sqrt{2}+y\sqrt{5}\right)}{2\left(x\sqrt{2}+y\sqrt{5}\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
b: \(=\dfrac{a+\sqrt{a}-a-2}{\sqrt{a}+1}:\dfrac{a-\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{a}-4}{a-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-2\right)}{\sqrt{a}+1}\cdot\dfrac{a-1}{a-4}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}-1}{\sqrt{a}+2}\)

a: góc AEB=góc ADB=90 độ
=>AEDB nội tiếp đường tròn đường kính AB
=>I là trung điểm của AB
b: Gọi H là giao của AD và BE
ABDE nội tiếp
=>góc HDE=góc HBA
=>góc HDE=góc HMN
=>DE//MN

a:
ΔOBC cân tại O
mà OI là trung tuyến
nên OI vuông góc BC
góc CMO+góc CIO=180 độ
=>CIOM nội tiếp







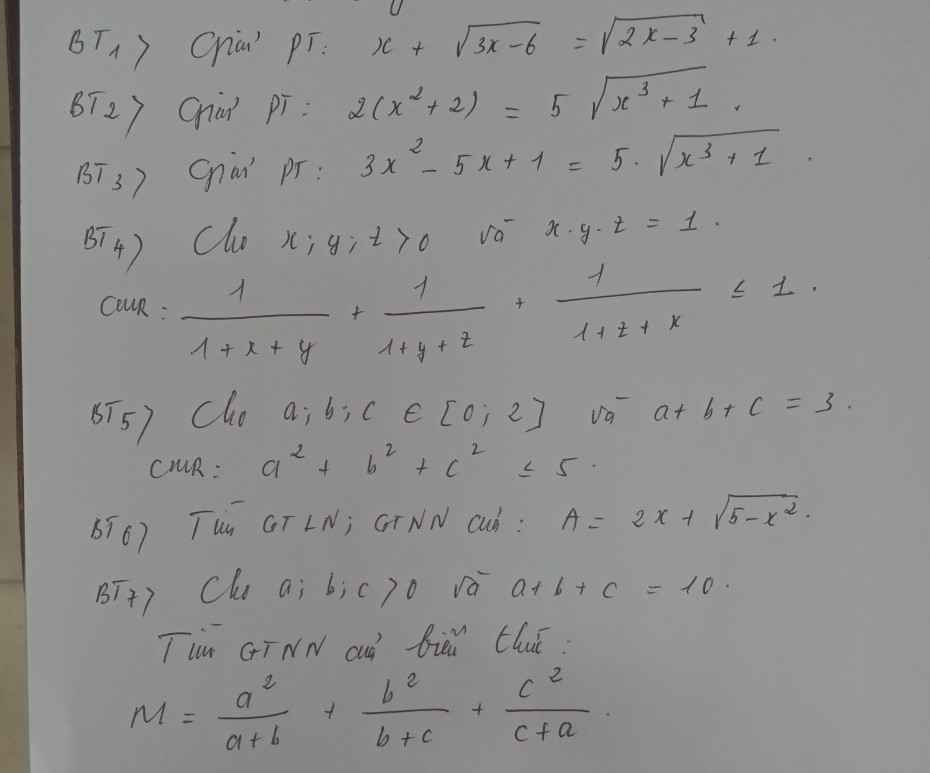
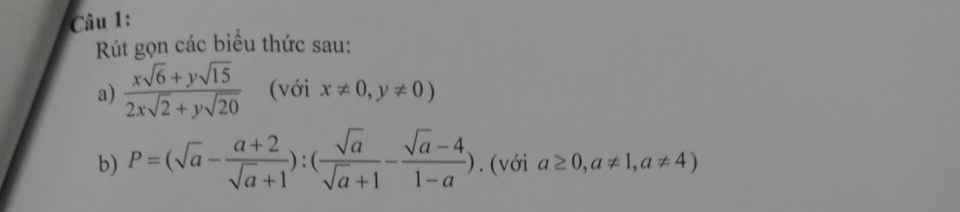


Ta có : x3 + y3 + 3(x2y + xy2) = 35 + 3.30
<=> (x + y)3 = 125
<=> x + y = 5 (1)
mà x2y + xy2 = 30
<=> xy(x + y) = 30
<=> xy = 6
Từ (1) => (x + y)2 = 25
<=> x2 + y2 + 2xy = 25
<=> x2 + y2 - 2xy = 1
<=> (x - y)2 = 1
<=> x - y = \(\pm1\)
Khi x - y = 1 ; x + y = 5 => x = 3 ; y = 2
Khi x - y = -1 ; x + y = 5 => x = 2 ; y = 3
8) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^2y+xy^2=30\\x^3+y^3=35\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}xy\left(x+y\right)=30\\\left(x+y\right)^3-3xy\left(x+y\right)=35\end{cases}}\)
Đặt xy = a ; x + y = b , hpt đã cho trở thành \(\hept{\begin{cases}ab=30\\b^3-3ab=35\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}ab=30\\b^3-90=35\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}ab=30\\b^3=125\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}ab=30\\b=5\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}a=6\\b=5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=5\\xy=6\end{cases}}\). Đến đây bạn giải pt x2 - Sx+ P = 0 với S = x + y và P = xy nhé , trong SGK có hd đấy:)
=> x = 2 ; y = 3 hoặc x = 3 ; y = 2