Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) x 2 - 7x + 5 = 0
Δ = 7 2 - 4.1.5 = 49 - 20 = 29 > 0
⇒ Phương trình đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
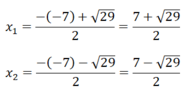
Vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm
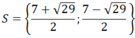

a)

Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất là (x; y) = (1; -3)

Từ hệ được x+y=1
a)Thay vào được x=1;y=0
b)Với mọi a
c)Thay vào x+y=1 tìm x;y
Thay ngược vào hệ tìm a
a) Khi a = 2 hệ phương trình đã cho tương đương với:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x+2x=3\left(1\right)\\2x-y=2\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}3x=3\\2x-y=2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\2x-2=y\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\2.1-2=0=y\end{cases}}\)
Do vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;0\right)\)
b) Ta có: \(x+y=\left(x+ax\right)-\left(ax-y\right)=3-2=1>0\forall a\)
c) Lấy (1) trừ (2),vế với vế,ta có: \(x+y=1\)
Thay vào,ta có: \(\sqrt{2}.y+y=1\Leftrightarrow y\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}+1}\Rightarrow x=1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}+1}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}+1}\)
Thay vào hệ phương trình ban đầu,ta có: \(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}+1}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}+1}.a=3\left(3\right)\\\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}+1}.a-\frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{2}+1}=2\left(4\right)\end{cases}}\)
Lấy (3) + (4),vế với vế,ta có: \(\frac{2\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}+1}.a=5\Leftrightarrow a=\frac{10+5\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
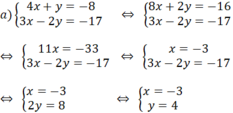
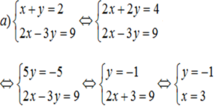
a) Khi a = 2, ta có hệ phương trình
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (x; y) = (7/5; 4/5)