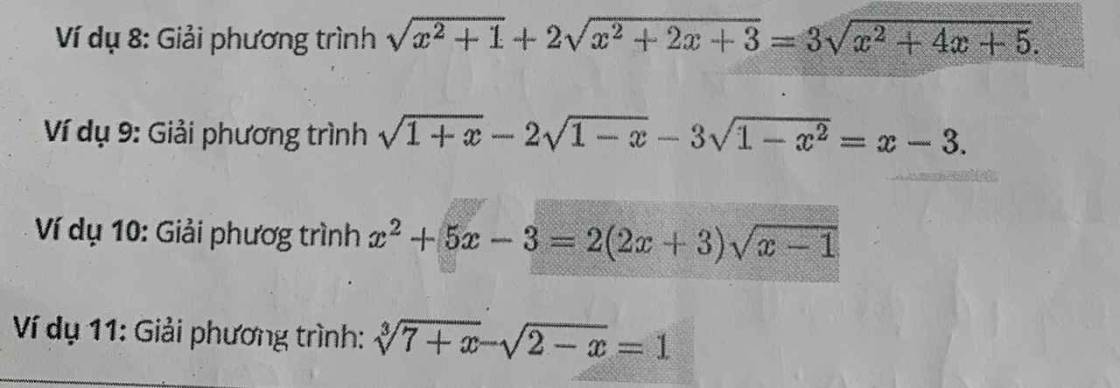Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


B1:
a, \(\dfrac{3x+7}{2+x-x^2}\ge5\)
<=> \(\dfrac{3x+7-5\left(2+x-x^2\right)}{2+x-x^2}\ge0\)
<=> \(\dfrac{5x^2+8x-3}{2+x-x^2}\ge0\)
\(5x^2+2x-3=0< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(-x^2+x+2=0< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Sau đó lập bảng xét dấu và kết luận
B2:
Vì \(\dfrac{\Pi}{2}< x< \Pi\) => \(\cos\alpha< 0\), \(\sin\alpha>0\)
\(\cos2\alpha=1-2\sin^2\alpha=1-2.\left(\dfrac{4}{5}\right)^2=\dfrac{-7}{25}\)\(\cos\alpha=-\sqrt{1-\sin^2\alpha}=-\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{4}{5}\right)^2}=\dfrac{-3}{5}\)\(\sin2\alpha=2\sin\alpha.\cos\alpha=2.\dfrac{4}{5}.\left(\dfrac{-3}{5}\right)=\dfrac{-24}{25}\)

8.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=a>0\\\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=x^2+1\)
Pt trở thành:
\(\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}+2a=3b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}=3b-2a\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=4a^2-12ab+9b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2-12ab+10b^2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\a=5b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\\\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=5\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+3=x^2+4x+5\\x^2+2x+3=25\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\24x^2+98x+122=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.
ĐKXĐ: \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{1-x}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2+2b^2=3-x=-\left(x-3\right)\)
Pt trở thành:
\(a-2b-3ab=-\left(a^2+2b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+a^2-3ab+2b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+\left(a-b\right)\left(a-2b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-b+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\a+1=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=2\sqrt{1-x}\\\sqrt{1+x}+1=\sqrt{1-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+x=4\left(1-x\right)\\x+2+2\sqrt{1+x}=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x=3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\-1-2x=2\sqrt{1+x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1-2x\ge0\\\left(-1-2x\right)^2=4\left(1+x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^2=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{\dfrac{3}{5};-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right\}\)



Xét (O) có
MA là tiếp tuyến
MB là tiếp tuyến
DO đó; OM là tia phân giác của góc AOB
Xét ΔOAM vuông tại A có
\(\tan\widehat{AOM}=\dfrac{AM}{AO}=\sqrt{3}\)
nên \(\widehat{AOM}=60^0\)
=>\(\widehat{AOB}=120^0\)

Ta thừa nhận định lý f(x) chia hết cho x-a thì f(a) =0 ( mình đang vội khỏi chứng minh nhé, nếu thắc mắc phiền bạn xem SGK 9 nha)
Thay 1 vào x, ta có
f(x) =14+12+a=0
2+a=0 suy ra a=-2



 mượn cái ngầu lòi của hai người này ới đấy đi học oln hahaha
mượn cái ngầu lòi của hai người này ới đấy đi học oln hahaha