Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\sqrt{2x+15}=32x^2+32x-20\)(1)
ĐK : \(x\ge-\dfrac{15}{2}\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x+15}-4=32x^2+32x-24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-1}{\sqrt{2x+15}+4}=\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x+15}+4}-\left(2x+3\right)\right)=0\)
Làm tiếp nhé!!

\(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x^2-8x+15\ge0\\x^2+2x-15\ge0\\4x^2-18x+18\ge0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge5\\x\le-5\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Với x = 8 thì (*) thỏa mãn \(\Rightarrow x=3\)là 1 nghiệm của bất phương trình.
\(\left(^∗\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-5\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\sqrt{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)}\le\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)\left(4x-6\right)}\)(1)
Với \(x\ge5\Rightarrow x-3\ge2>0\)hay \(x-3>0\)thì
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-5}+\sqrt{x+5}\le\sqrt{4x-6}\)\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2\sqrt{x^2-25}\le4x-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-25}\le x-3\Leftrightarrow x^2-25=x^2-6x+9\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{17}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow5\le x\le\frac{17}{3}\)
Với \(x\le-5\Leftrightarrow-x\ge5\Leftrightarrow3-x\ge8>0\)hay \(x\le-5\Leftrightarrow-x\ge5\Leftrightarrow3-x>0\)thì
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(5-x\right)\left(3-x\right)}+\sqrt{\left(-5-x\right)\left(3-x\right)}\)
\(\le\sqrt{\left(3-x\right)\left(4-6x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{5-x}+\sqrt{-x-5}\le\sqrt{6-4x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2\sqrt{\left(5-x\right)\left(-x-5\right)}\le6-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-25}\le3-x\Leftrightarrow x^2-25\le x^2-6x+9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{17}{3}\Rightarrow x\le-5\)
Từ đó suy ra tập nghiệm của bpt là \(x\in(-\infty;-5]\mu\left\{3\right\}\mu\left[5;\frac{17}{3}\right]\)

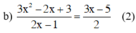
Điều kiện xác định: 2x – 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ 1/2.
Quy đồng và bỏ mẫu chung ta được:
Phương trình (2) ⇔ 2(3x2 – 2x + 3) = (2x – 1)(3x – 5)
⇔ 6x2 – 4x + 6 = 6x2 – 10x – 3x + 5
⇔ 9x = –1
⇔ x = –1/9 (thỏa mãn đkxđ)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = –1/9.

Trừ 2 vế ta được: (4x + 2)2 - (4y + 2)2 = 2y - 2x => (4x + 2 + 4y + 2).(4x + 2 - 4y - 2) + 2x - 2y = 0
=> (4x + 4y + 4).(4x - 4y) + 2.(x - y) = 0
=> 16.(x + y + 1).(x - y) + 2.(x - y) = 0
=> 8.(x + y + 1).(x - y) + 2.(x - y) = 0
=> (x - y). (8x + 8y + 8 + 2) = 0
=> (x - y).(8x + 8y + 10) = 0
=> (x - y).(4x + 4y + 5) = 0
\(\Rightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=y\\4x+4y+5=0\end{array}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=y\\x=\frac{-5-4y}{4}\end{array}\right.\)
Tới đây bạn chia ra 2 trường hợp giải nha
Lấy (2) trừ (1), ta có :
\(\left(4x-4y\right)\left(4x+4y+4\right)=2y-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-y\right)\left(8x+8y+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x-y=0\\8x+8y+9=0\end{array}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}y=x\\y=-\frac{8x+9}{8}\end{array}\right.\)
* Với \(y=x\), thay vào (1) ta có :
\(\left(4x+2\right)^2=2x+15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2+14x-11=0\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=-\frac{11}{8}\end{array}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2};\frac{1}{2}\right);\left(x;y\right)=\left(-\frac{11}{8};-\frac{11}{8}\right)\) là nghiệm của hệ phương trình
* Với \(y=-\frac{8x+9}{8}\), ta có :
\(\left(4x+2\right)^2=15-\frac{8x+9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow64x^2+72x-35=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-9\pm\sqrt{221}}{16}\)
Khi \(x=\frac{-9-\sqrt{221}}{16}\Rightarrow y=\frac{-9+\sqrt{221}}{16}\)
Khi \(x=\frac{-9+\sqrt{221}}{16};y=\frac{-9-\sqrt{221}}{16}\)
Hệ đã cho có 4 nghiệm :
\(\left(\frac{1}{2};\frac{1}{2}\right);\left(-\frac{11}{8};-\frac{11}{8}\right);\left(\frac{-9-\sqrt{221}}{16};\frac{-9+\sqrt{221}}{16}\right);\left(\frac{-9+\sqrt{221}}{16};\frac{-9-\sqrt{221}}{16}\right)\)

\(\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)=1\Rightarrow\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^x\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)^x=1\)
Đặt \(t=\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^x,t>0\Rightarrow\left(4-\sqrt{15}\right)^x=\frac{1}{t}\)
Bất phương trình đã cho trở thành :
\(t+\frac{1}{t}>8\Rightarrow t^2-8t+1>0\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}t>4+\sqrt{15}\\t< 4-\sqrt{15}\end{array}\right.\)
* \(t>4+\sqrt{15}\Rightarrow\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^x>4+\sqrt{15}\Rightarrow x>1\)
* \(t< 4-\sqrt{15}\Rightarrow\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^x< 4-\sqrt{15}\Rightarrow\left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^x< \left(4+\sqrt{15}\right)^{-1}\Rightarrow x< -1\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(S=\left(-\infty;-1\right)\cup\left(1;+\infty\right)\)


Đặt a = x ; b = y ; a ; b ≥ 0 ⇒ a 2 = x 2 ; b 2 = y 2
Khi đó hệ phương trình đã cho trở thành: a + b = 3 ( 1 ) 2 ( a 2 + b 2 ) = 9 ( 2 )
Từ (1) suy ra: b = 3 - a thay vào (2) ta được:
2 . a 2 + 3 - a 2 = 9 ⇔ 2 2 a 2 - 6 a + 9 = 9 ⇔ 4 a 2 - 12 a + 9 = 0 ⇔ a = 3 2
Với a = 3 2 ⇒ b = 3 2 .
Khi đó; x = 3 2 ; y = 3 2 ⇒ x = ± 3 2 ; y = ± 3 2
Suy ra, hệ phương trình đã cho có 4 nghiệm:
3 2 ; 3 2 ; 3 2 ; - 3 2 ; - 3 2 ; 3 2 ; - 3 2 ; - 3 2
Chọn C.