Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(7+2x=22-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x=15\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
b) \(8x-3=5x+12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\Leftrightarrow x=5\)
c) \(x-12+4x=25+2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=36\Leftrightarrow x=12\)
d) \(x+2x+3x-19=3x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=24\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
e) \(7-\left(2x+4\right)=-\left(x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=7\)
f) \(\left(x-1\right)-\left(2x-1\right)=9-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=9\) ( vô lí )

a) (x-1)(5x+3)=(3x-8)(x-1)
= (x-1)(5x+3)-(3x-8)(x-1)=0
=(x-1)[(5x+3)-(3x-8)]=0
=(x-1)(5x+3-3x+8)=0
=(x-1)(2x+11)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x-1=0 hoặc 2x+11=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x=1 hoặc x=\(\dfrac{-11}{2}\)
Vậy S={1;\(\dfrac{-11}{2}\)}
b) 3x(25x+15)-35(5x+3)=0
=3x.5(5x+3)-35(5x+3)=0
=15x(5x+3)-35(5x+3)=0
=(5x+3)(15x-35)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x+3=0 hoặc 15x-35=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x=\(\dfrac{-3}{5}\) hoặc x=\(\dfrac{7}{3}\)
Vậy S={\(\dfrac{-3}{5};\dfrac{7}{3}\)}
c) (2-3x)(x+11)=(3x-2)(2-5x)
=(2-3x)(x+11)-(3x-2)(2-5x)=0
=(3x-2)[(x+11)-(2-5x)]=0
=(3x-2)(x+11-2+5x)=0
=(3x-2)(6x+9)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 3x-2=0 hoặc 6x+9=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x=\(\dfrac{2}{3}\) hoặc x=\(\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
Vậy S={\(\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{-3}{2}\)}
d) (2x2+1)(4x-3)=(2x2+1)(x-12)
=(2x2+1)(4x-3)-(2x2+1)(x-12)=0
=(2x2+1)[(4x-3)-(x-12)=0
=(2x2+1)(4x-3-x+12)=0
=(2x2+1)(3x+9)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)2x2+1=0 hoặc 3x+9=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)hoặc x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) hoặc x=-3
Vậy S={\(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{-1}{2};-3\)}
e) (2x-1)2+(2-x)(2x-1)=0
=(2x-1)[(2x-1)+(2-x)=0
=(2x-1)(2x-1+2-x)=0
=(2x-1)(x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 2x-1=0 hoặc x+1=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) hoặc x=-1
Vậy S={\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\);-1}
f)(x+2)(3-4x)=x2+4x+4
=(x+2)(3-4x)=(x+2)2
=(x+2)(3-4x)-(x+2)2=0
=(x+2)[(3-4x)-(x+2)]=0
=(x+2)(3-4x-x-2)=0
=(x+2)(-5x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x+2=0 hoặc -5x+1=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x=-2 hoặc x=\(\dfrac{1}{5}\)
Vậy S={-2;\(\dfrac{1}{5}\)}

Bài 3:
a) \(\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).\left(3x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right).\left(2x-5\right).3.\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Vì \(3\ne0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\2x=5\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\frac{5}{2}\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{6;\frac{5}{2};-3\right\}.\)
b) \(2x.\left(x-3\right)+5.\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right).\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\2x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\frac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{3;-\frac{5}{2}\right\}.\)
c) \(\left(x^2-4\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2^2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\3x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập hợp nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{2;\frac{1}{3}\right\}.\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!

chẳng ai giải, thôi mình giải vậy!
a) Đặt \(y=x^2+4x+8\),phương trình có dạng:
\(t^2+3x\cdot t+2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2+xt+2xt+2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t+x\right)+2x\left(t+x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+t\right)\left(t+x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+x^2+4x+8\right)\left(x^2+4x+8+x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=-4\end{cases}}\)vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là:S={-2;-4}
b) nhân 2 vế của phương trình với 12 ta được:
\(\left(6x+7\right)^2\left(6x+8\right)\left(6x+6\right)=72\)
Đặt y=6x+7, ta được:\(y^2\left(y+1\right)\left(y-1\right)=72\)
giải tiếp ra ta sẽ được S={-2/3;-5/3}
c) \(\left(x-2\right)^4+\left(x-6\right)^4=82\)
S={3;5}
d)s={1}
e) S={1;-2;-1/2}
f) phương trình vô nghiệm

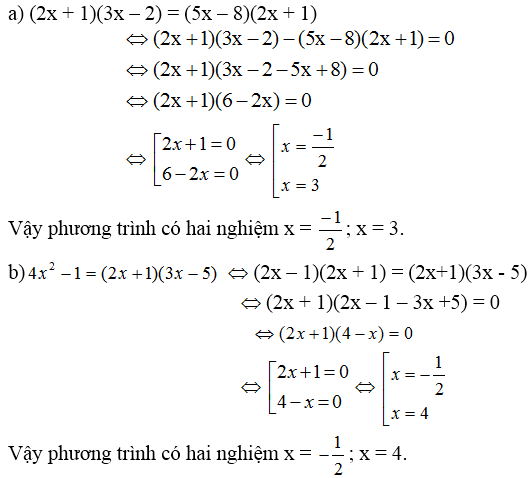
a)(2x+1)(3x-2)=(5x-8)(2x+1)
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2)-(5x-8)(2x+1)=0
⇔(2x+1)(3x-2-5x+8)=0
⇔(2x+1)(-2x+6)=0
⇔2x+1=0 hoặc -2x+6=0
1.2x+1=0⇔2x=-1⇔x=-1/2
2.-2x+6=0⇔-2x=-6⇔x=3
phương trình có 2 nghiệm x=-1/2 và x=3

1,
a,\(2x\left(3x^2-5x+3\right)\)
\(=6x^3-10x^2+6x\)
b,\(-2x\left(x^2+5x-3\right)\)
\(=-2x^3-10x^2+6x\)
c,\(-\dfrac{1}{2}x\left(2x^3-4x+3\right)\)
\(=-x^4+2x^2-\dfrac{3}{2}x\)
Bài 2:
a) \(\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-5-4\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-1\right)\left(x^2-9\right)\)
\(=2x^3-18x-x^2+9\)
b) \(-\left(5x-4\right)\left(2x+3\right)\)
\(=-\left(10x^2+15x-8x-12\right)\)
\(=-10x^2-7x+12\)
c) \(\left(2x-y\right)\left(4x^2-2xy+y^2\right)\)
\(=8x^3-y^3\)
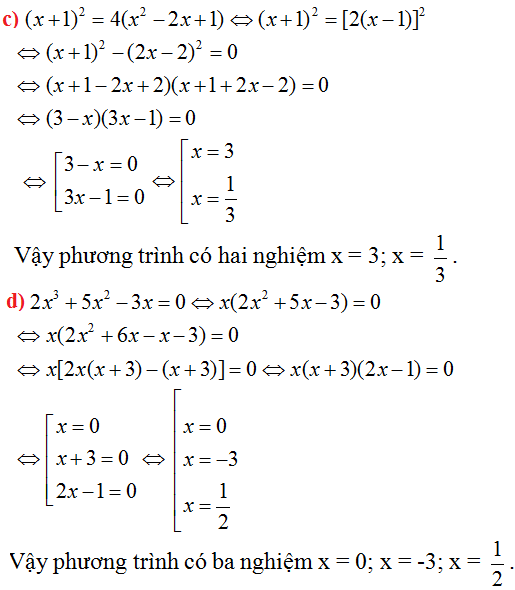
a)X= 3 b)X= 5 c)X= 12
d)X= 8 e)X= 7 f)X= ?