Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b: Để A là số nguyên thì \(2x+2⋮x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-4;-1;-5;1;-7\right\}\)

\(\frac{2x+3}{x-5}\)\(=\frac{2\left(x-5\right)+13}{x-5}\)
\(=\frac{2\left(x-5\right)}{x-5}+\frac{13}{x-5}\)
\(=2+\frac{13}{x-5}\)
để biểu thức trên có giá trị nguyên <=> \(\frac{13}{x-5}\)thuộc Z
mà \(x\)thuộc Z => \(x-5\)thuộc ước của \(13\)
=> \(x-5\)thuộc \(\left(1;-1;13;-13\right)\)
=>\(x\)thuộc \(\left(6;4;18;-8\right)\)
vậy ....
\(\frac{x^3-2x^2+4}{x-2}\) \(=\frac{x^2\left(x-2\right)+4}{x-2}\)
\(=x^2+\frac{4}{x-2}\)
để biểu thức trên đạt giá trị nguyên <=> \(\frac{4}{x-2}\) thuộc giá trị nguyên
mà \(x\) là số nguyên => \(x-2\)thuộc ước của \(4\)
=> \(x-2\) thuộc \(\left(1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right)\)
=> \(x\)thuộc \(\left(3;1;4;0;6;-2\right)\)
vậy...

a: \(A=\dfrac{x^2-2x+2x^2+4x-3x^2-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
a, \(\dfrac{x}{x+2}\) + \(\dfrac{2x}{x-2}\) -\(\dfrac{3x^2-4}{x^2-4}\)
= \(\dfrac{x}{x+2}+\dfrac{2x}{x-2}-\dfrac{3x^2+4}{x^2-4}\)
= \(\dfrac{x}{x+2}+\dfrac{2x}{x-2}-\dfrac{3x^2+4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)+2x\left(x+2\right)-3x^2-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{2x-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
Có vài bước mình làm tắc á nha :>

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1
b: \(P=\left(1-\dfrac{x+1}{x^2-x+1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x+1-x-1}{x^2-x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x+1}\)
c: P=2
=>x^2-2x=2x+2
=>x^2-4x-2=0
=>\(x=2\pm\sqrt{6}\)

a: Thay x=2/3 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{3\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}+2}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=\dfrac{2+2}{\dfrac{2}{3}}=4\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}=6\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2-x}-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x}\)
c: P=A:B
\(=\dfrac{3x+2}{x}:\dfrac{x-1}{x}=\dfrac{3x+2}{x}\cdot\dfrac{x}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x+2}{x-1}\)
Để P là số nguyên thì \(3x+2⋮x-1\)
=>\(3x-3+5⋮x-1\)
=>\(5⋮x-1\)
=>\(x-1\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{2;0;6;-4\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{2;6;-4\right\}\)
Thay x=2 vào P, ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{3\cdot2+2}{2-1}=\dfrac{8}{1}=8\)
Thay x=6 vào P, ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{3\cdot6+2}{6-1}=\dfrac{18+2}{5}=\dfrac{20}{5}=4\)
Thay x=-4 vào P, ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{3\cdot\left(-4\right)+2}{-4-1}=\dfrac{-12+2}{-5}=\dfrac{-10}{-5}=2\)
Vì 2<4<8
nên khi x=-4 thì P có giá trị nguyên nhỏ nhất
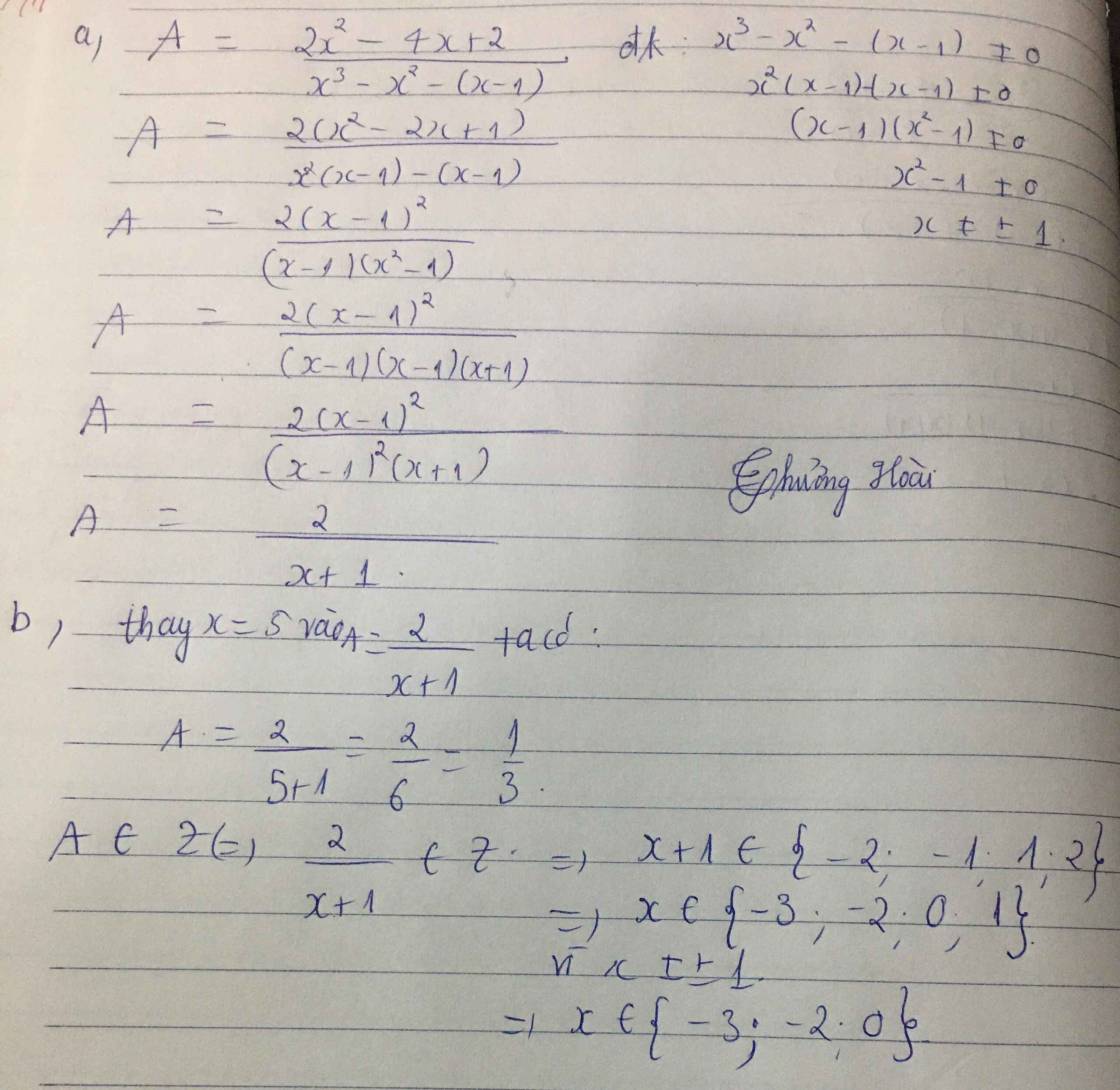


\(A=\dfrac{2x+2}{x+3}.\left(x\ne-3\right).\)
\(A=2+\dfrac{-4}{x+3}.\)
Để \(A\in Z.\Leftrightarrow2+\dfrac{-4}{x+3}\in Z.\Leftrightarrow x+3\inƯ\left(-4\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}.\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-2;-4;-1;-5;1;-7\right\}.\)