
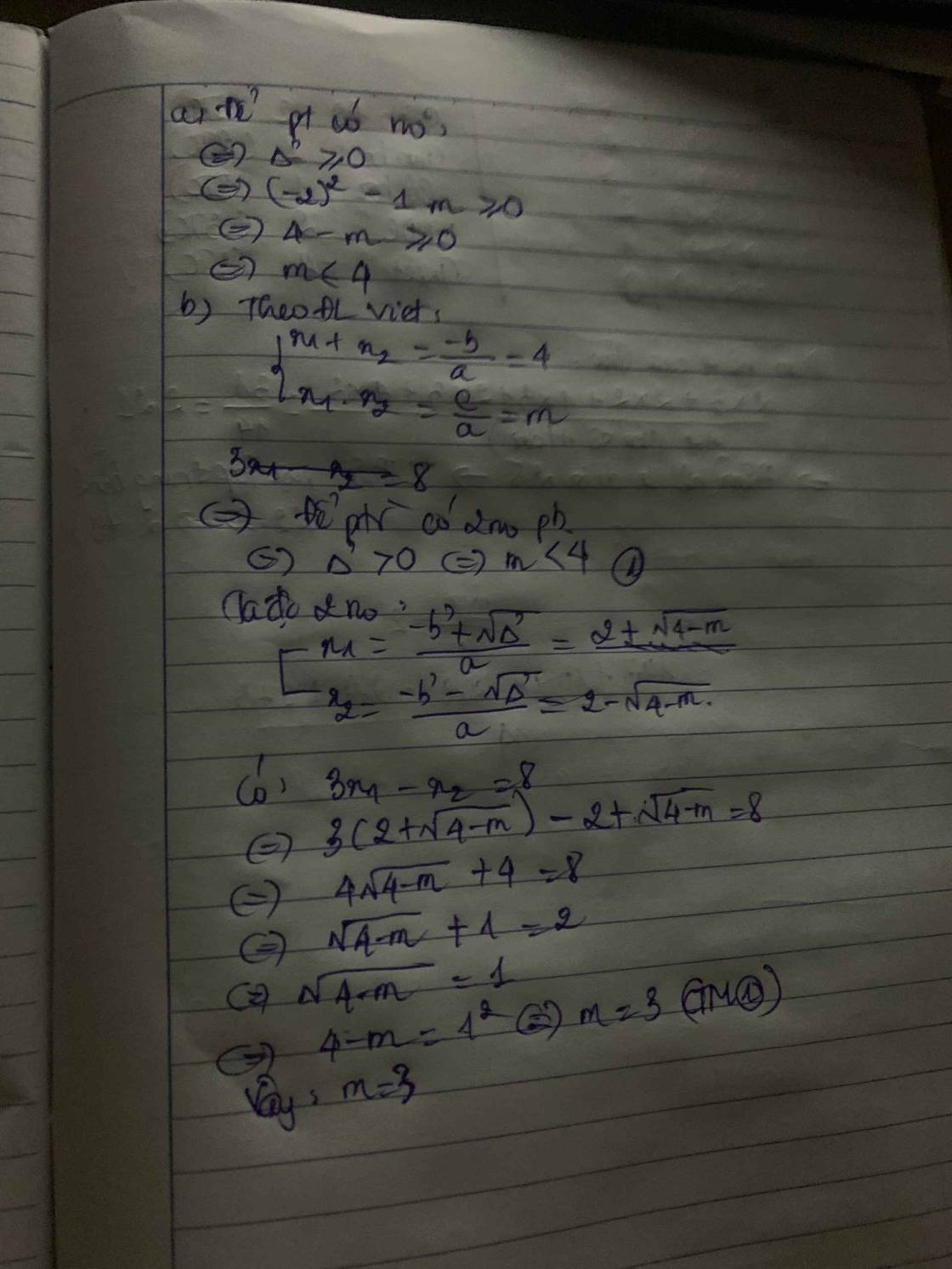
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

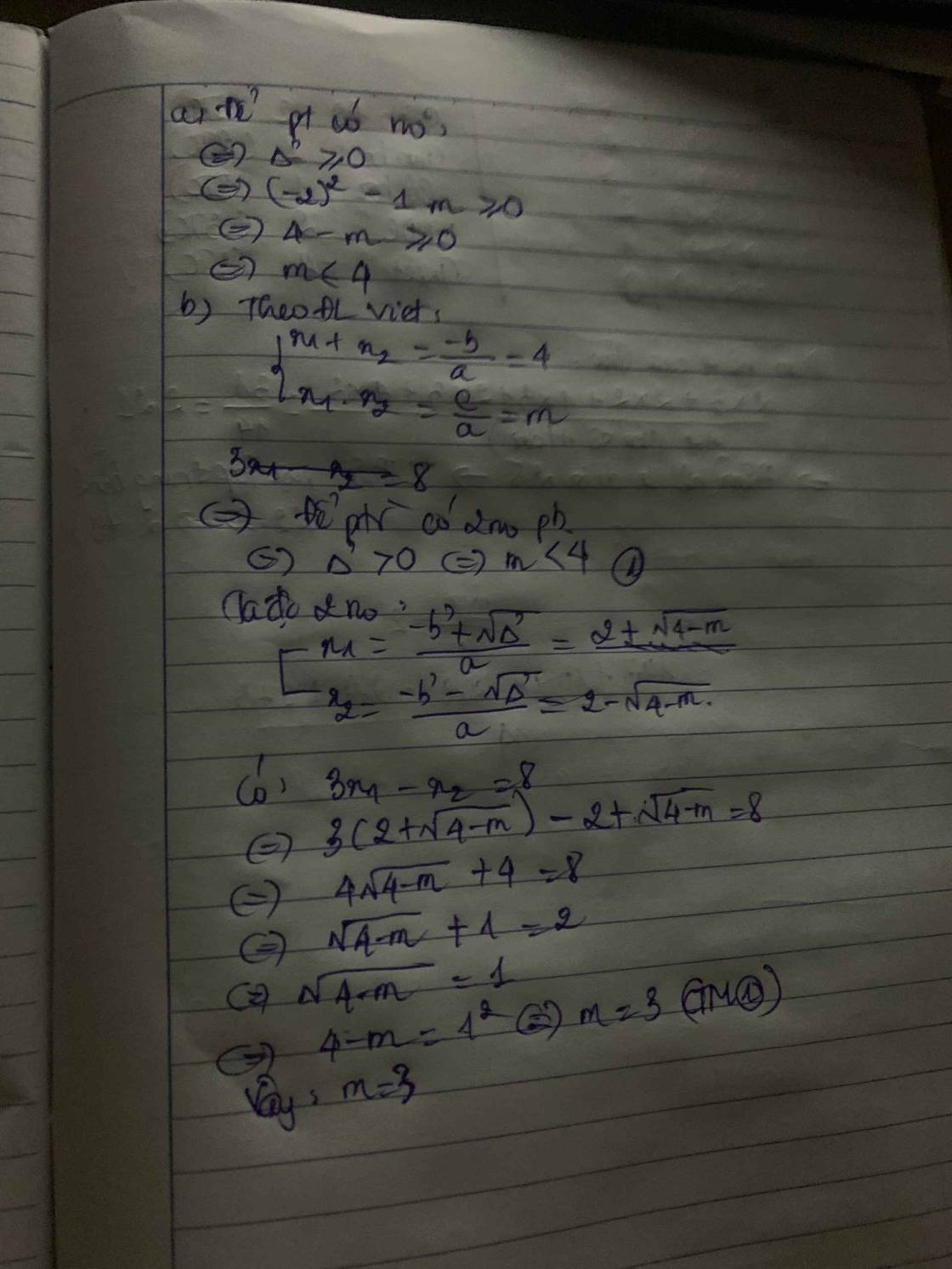

\(x^2+2\left(m+1\right)+4m-4=0\)
Theo Vi - ét, ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=-2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=4m-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(x_1^2+x_2^2+3x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2+3x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m+1\right)\right]^2+\left(4m-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m^2+2m+1\right)+4m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4+4m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+12m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m\left(m+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\text{Δ}=\left(2m-1\right)^2-8\left(m-1\right)\)
\(=4m^2-4m+1-8m+8\)
\(=4m^2-12m+9=\left(2m-3\right)^2\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì 2m-3<>0
hay m<>3/2
Theo đề, ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-2m+1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\2x_1+2x_2=-2m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\4x_1+4x_2=-4m+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x_1=-4m+13\\4x_2=3x_1-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-4m+13}{7}\\4x_2=\dfrac{-12m+36}{7}-\dfrac{77}{7}=\dfrac{-12m-41}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-4m+13}{7}\\x_2=\dfrac{-12m-41}{28}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo Vi-et, ta được: \(x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(4m-13\right)\left(12m+41\right)}{196}=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m-13\right)\left(12m+1\right)=98\left(m-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48m^2+4m-156m-13-98m+98=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48m^2-250+85=0\)
Đến đây bạn chỉ cần giải pt bậc hai là xong rồi
\(\Delta=\left(2m-1\right)^2-8\left(m-1\right)=4m^2-12m+10\)
\(=\left(2m-3\right)^2+1>0\)
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm pb
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}\left(1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(3x_1-4x_2=11\left(3\right)\)
Từ (1) ; (3) ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x_1+4x_2=2-4m\\3x_1-4x_2=11\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x_1=13-4m\\x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}-x_1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\\x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}-\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{7-14m-26+8m}{14}=\dfrac{-19-6m}{14}\)
Thay vào (2) ta được \(\left(\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\right)\left(\dfrac{-19-6m}{14}\right)=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=4,125\)

a) Thay x=-1 vào pt có:5+m=0 <=> m=-5
Thay m=-5 vào pt có:\(x^2-4x-5=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy nghiệm còn lại là 5
b) Để pt có hai nghiệm <=> \(\Delta\ge\) <=>\(16-4m\ge0\) <=>\(m\le4\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=4\\x_1x_2=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có \(\left(3x_1+1\right)\left(3x_2+1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x_1x_2+3\left(x_1+x_1\right)+1=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m+3.4+1=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-1\) (thỏa)
Vậy m=-1
a) `x=-1` là nghiệm `=> (-1)^2-4.(-1)+m=0 <=> m=-5`
`=>` PT: `x^2-4x-5=0 =>` Nghiệm còn lại là: `x=5`
b) PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt `<=> \Delta'>0 <=> 2^2-m>0 <=> m < 4`
Viet: `x_1+x_2=4`
`x_1x_2=m`
Theo đề: `(3x_1+1)(3x_2+1)=4`
`<=> 3x_1x_2+3(x_1+x_2)+1=4`
`<=> 3m+3.4+1=4`
`<=> m=-9`
Vậy `m=-9`.

A, ta có: \(\Delta’\)=m2-1
Vậy trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt <=> m2-1>0 => m>1
B,Phương trình có nghiệm kép khi: m2-1=0 => m=+- 1
Nghiem kép đó là: 0
\(x^2+2\left(m+1\right)x+2m+2=0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m+2\right)=m^2-1\)
a, Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì:
\(\Delta'>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< -1;m>1\)
b, Phương trinh có nghiệm kép khi:
\(\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le-1;m\ge1\)
Theo Viet ta có:
\(x_1+x_2=-2\left(m+1\right)\)
\(x_1x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+4m-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m=1\\m=-2\end{cases}}\)
So với điều kiện phương trình có nghiệm m=1 ; m =-2

Bài 1:
a, Thay m=-1 vào (1) ta có:
\(x^2-2\left(-1+1\right)x+\left(-1\right)^2+7=0\\
\Leftrightarrow x^2+1+7=0\\
\Leftrightarrow x^2+8=0\left(vô.lí\right)\)
Thay m=3 vào (1) ta có:
\(x^2-2\left(3+1\right)x+3^2+7=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2.4x+9+7=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-8x+16=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\)
b, Thay x=4 vào (1) ta có:
\(4^2-2\left(m+1\right).4+m^2+7=0\\ \Leftrightarrow16-8\left(m+1\right)+m^2+7=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2+23-8m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-8m+15=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m^2-3m\right)-\left(5m-15\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\left(m-3\right)-5\left(m-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)\left(m-5\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Delta'=\left[-\left(m+1\right)\right]^2-\left(m^2+7\right)=m^2+2m+1-m^2-7=2m-6\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta'\ge0\Leftrightarrow2m-6\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge3\)
Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m+2\\x_1x_2=m^2+7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2-2\left(m^2+7\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-2m^2-14=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2m^2+8m-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\left(ktm\right)\\m=-5\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1-x_2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(m^2+7\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-4m^2-28=0\\ \Leftrightarrow8m=28=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{7}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
Bài 2:
a,Thay m=-2 vào (1) ta có:
\(x^2-2x-\left(-2\right)^2-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-4-4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Delta'=\left(-m\right)^2-\left(-m^2-4\right)\ge0=m^2+m^2+4=2m^2+4>0\)
Suy ra pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\\x_1x_2=-m^2-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=20\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=20\\ \Leftrightarrow2^2-2\left(-m^2-4\right)=20\\ \Leftrightarrow4+2m^2+8-20=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2m^2-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\pm2\)
\(x_1^3+x_2^3=56\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^3-3x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=56\\ \Leftrightarrow2^3-3\left(-m^2-4\right).2=56\\ \Leftrightarrow8-6\left(-m^2-4\right)-56\\ =0\\ \Leftrightarrow8+6m^2+24-56=0\\ \Leftrightarrow6m^2-24=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\pm2\)
\(x_1-x_2=10\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=100\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2-100=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2^2-4\left(-m^2-4\right)-100=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4+4m^2+16-100=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2-80=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\pm2\sqrt{5}\)
cho pt: x^2 - 4x + m = 0(m là tham số) b) Tìm m để pt có nghiệm x1, x2 thỏa mãn: 1/x1^2 + 1/x2^3 = 2


a Khi m=-2 \(\Rightarrow x^2+\left(-2-2\right)x+-2+5=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+3=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\) b Theo hệ thức Vi-et có :
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2-m\\x_1x_2=m+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mà \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1^2+x_2^2=10\Rightarrow\left(2-m\right)^2-2\left(m+5\right)=10\Leftrightarrow m^2-4m+4-2m-10=10\Leftrightarrow m^2-6m-16=0\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-8m-16=0\Leftrightarrow\left(m+2\right)\left(m-8\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-2\\m=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
a) Thay m=-2 vào phương trình, ta được:
\(x^2-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-3x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-3\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Khi m=-2 thì phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là S={1;3}