Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+5=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^3-3x^2+5\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
BBT:
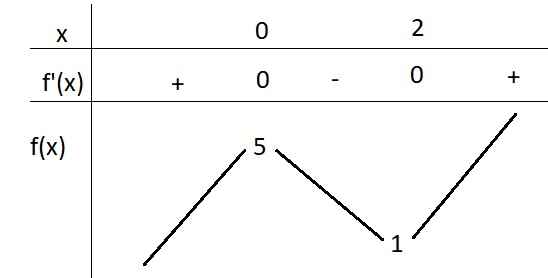
Từ BBT ta thấy \(y=m\) cắt \(y=f\left(x\right)\) tại 3 điểm khi \(1< m< 5\)

a.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+x+1\ge mx\) ; \(\forall x\ge0\) (1)
- Với \(x=0\) thỏa mãn
- Với \(x>0\)
(1) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\ge m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le\min\limits_{x>0}\left(x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\)
Xét \(f\left(x\right)=x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\) với \(x>0\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2x+3-\dfrac{1}{x^2}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2}=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Từ BBT ta thấy \(f\left(x\right)_{min}=f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{19}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\le\dfrac{19}{4}\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3.2^xlogx-12logx-2^x+4=0\left(1\right)\\5^x=m\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) và \(5^x\ge m\) (\(x>0\))
Xét (1):
\(\Leftrightarrow3logx\left(2^x-4\right)-\left(2^x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3logx-1\right)\left(2^x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=2\\x_2=\sqrt[3]{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(y=5^x\) đồng biến trên R nên (2) có tối đa 1 nghiệm
Để pt đã cho có đúng 2 nghiệm phân biệt ta có các TH sau:
TH1: (2) vô nghiệm \(\Rightarrow m\le0\) (ko có số nguyên dương nào)
TH2: (2) có nghiệm (khác với 2 nghiệm của (1)), đồng thời giá trị của m khiến cho đúng 1 nghiệm của (1) nằm ngoài miền xác định
(2) có nghiệm \(\Rightarrow m>0\Rightarrow x_3=log_5m\)
Do \(\sqrt[3]{10}>2\) nên bài toán thỏa mãn khi: \(x_1< x_3< x_2\)
\(\Rightarrow2< log_5m< \sqrt[3]{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow25< m< 5^{\sqrt[3]{10}}\) (hơn 32 chút xíu)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(32-26+1\) giá trị nguyên

Chép lại đề bài: ....
Đk: x\(\ge\)1
\(\sqrt[4]{x^2-1}=\sqrt[4]{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}
\) (1)
chia cả 2 vế cho (1): \(3.\sqrt[4]{\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}}+m.\sqrt[4]{\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}}=1\) (đk: x>1)
Đặt \(\sqrt[4]{\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}}=t\) (t>0) => 3t +\(\dfrac{m}{t}\)=1
<=> 3t2 -t+m=0 (2)
Đến đây ta biện luận nghiệm của pt (2) có nghiệm dương

Bài 1: Giải các phương trình
a)17x+15(x-1)=1-14(3x+1) b)2x(x+5)-(x-3)2 =x2+6 c)(4x+7)(x-5)-3x2=x(x-1) d) 6(x-3)+(x-1)

ĐKXĐ: \(-3\le x\le1\)
\(4+2\sqrt{-x^2-2x+3}=m+1-x^2-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+3+2\sqrt{-x^2-2x+3}=m\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{-x^2-2x+3}=t\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow-t^2+2t+6=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=-t^2+2t+6\) trên \(\left[0;2\right]\)
\(f'\left(t\right)=-2t+2=0\Rightarrow t=1\)
\(f\left(0\right)=6;f\left(1\right)=7;f\left(2\right)=6\Rightarrow6\le m\le7\)

Bài 1:
Đặt \(\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^x=a\) \((a>0)\)
PT tương đương với:
\(\left(\frac{9}{4}\right)^x-2.\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^x+m^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-2a+m^2=0\) (1)
-Trước tiên, để pt đầu tiên có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì (1) cũng phải có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(\rightarrow \) \(\Delta'=1-m^2>0\Leftrightarrow -1< m< 1\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Viete với \(a_1,a_2\) là nghiệm của (1) \(\left\{\begin{matrix} a_1+a_2=2\\ a_1a_2=m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
-Vì \(a\) luôn dương nên \(\left\{\begin{matrix} a_1+a_2>0\\ a_1a_2>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m^2>0 \Leftrightarrow m\neq 0\)
-Xét đk cuối cùng, để pt đầu tiên có hai nghiệm trái dấu, tức \(x<0\) hoặc $x>0$ thì \(a<1\) hoặc \(a>1\), hay \((a_1-1)(a_2-1)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a_1a_2-(a_1+a_2)+1< 0\Leftrightarrow m^2<1\Leftrightarrow -1< m< 1\)
Vậy \(-1< m< 1; m\neq 0\)
Bài 2:
Đặt \(2^x=a\Rightarrow \) \(4^x-2m.2^x+2m=0\) tương đương với:
\(a^2-2ma+2m=0\) (1)
Để pt đầu tiên có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì (1) cũng phải có hai nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Rightarrow \Delta'=m^2-2m>0\Leftrightarrow m< 0\) hoặc $m>2$
Áp dugnj hệ thức viete với $a_1,a_2$ là hai nghiệm của phương trình:
\(a_1a_2=2m\Leftrightarrow 2^{x_1}.2^{x_2}=2m\Leftrightarrow 2^{x_1+x_2}=2m\Leftrightarrow 8=2m\rightarrow m=4\)
(thỏa mãn)
Vậy \(m=4\)

\(m.3^{x^2-3x+2}+3^{4-x^2}=3^{6-3x}+m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m.3^{x^2-3x+2}+3^{6-3x-\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}=3^{6-3x}+m\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-3x+2=a\\6-3x=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(m.3^a+3^{b-a}=3^b+m\Leftrightarrow m\left(3^a-1\right)=3^b-3^{b-a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m.\left(3^a-1\right)=3^{b-a}\left(3^a-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3^a-1=0\\m=3^{b-a}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3^{x^2-3x+2}=1\\3^{4-x^2}=m\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\\3^{4-x^2}=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để pt có đúng 3 nghiệm thực thì \(3^{4-x^2}=m\) có nghiệm duy nhất hoặc có 1 nghiệm bằng 1 hoặc 2.
- Nếu \(x=1\Rightarrow m=3^3=27\)
- Nếu \(x=2\Rightarrow m=3^0=1\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=3^{4-x^2}\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=-2x.3^{4-x^2}.ln3\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến khi \(x< 0\), nghịch biến khi \(x>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất khi \(x=0\Rightarrow m=3^4=81\)
\(\Rightarrow m=\left\{1;27;81\right\}\)