Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, Hoành độ giao điểm tm pt
\(x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=0;x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Với x = 0 => y = 0
Với x = 1/2 => y = 1/4
Vậy (P) cắt (d) tại O(0;0) ; A(1/2;1/4)

a: Thay x=1 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot1=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Vậy: \(A\left(1;-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\) thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
b: Thay x=2 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot2=-5\)
=>B(2;-5) thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
Thay x=3 vào y=-5/2x, ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot3=-\dfrac{15}{2}\)<>7
=>\(C\left(3;7\right)\) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số y=-5/2x
Thay x=1 vào y=-5/2x, ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot1=-\dfrac{5}{2}\)<>5/2
=>\(D\left(1;\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\)
Thay x=0 vào \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\), ta được:
\(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot0=0\)<>4
=>E(0;4) không thuộc đồ thị hàm số \(y=-\dfrac{5}{2}x\)

Lời giải:
a.
b. Để $C(-2;m)$ thuộc $(P)$ thì:
$y_C=\frac{1}{2}x_C^2$
$\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{1}{2}(-2)^2=2$

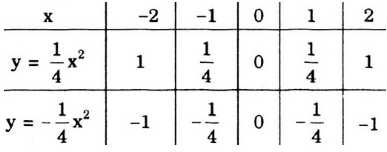
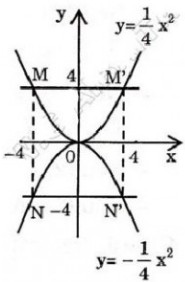
1/ \(\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}\hline x&-2&-1&0&1&2\\\hline y&2&0,5&0&0,5&2\\\hline\end{array}\)
\(\to\) Đồ thị hàm số đi qua điểm \( (-2;2);(-1;0,5);(0;0);(1;0,5);(2;2)\)
2/ \( C(2;m)\in (P)\)
\(\to m=\dfrac{1}{2}.2^2=2\)
Vậy \(m=2\)
2) Thay x=2 và y=m vào (P), ta được:
\(m=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot4=2\)

Bài 1:
a: Thay x=-2 và y=2 vào hàm số, ta được:
4a=2
hay a=1/2
Bài 2:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+5y=3\\4x-12y=20\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}17y=-17\\x-3y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\3y=x-5=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}=1\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{3}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)=\left(2;\dfrac{10}{3}\right)\)
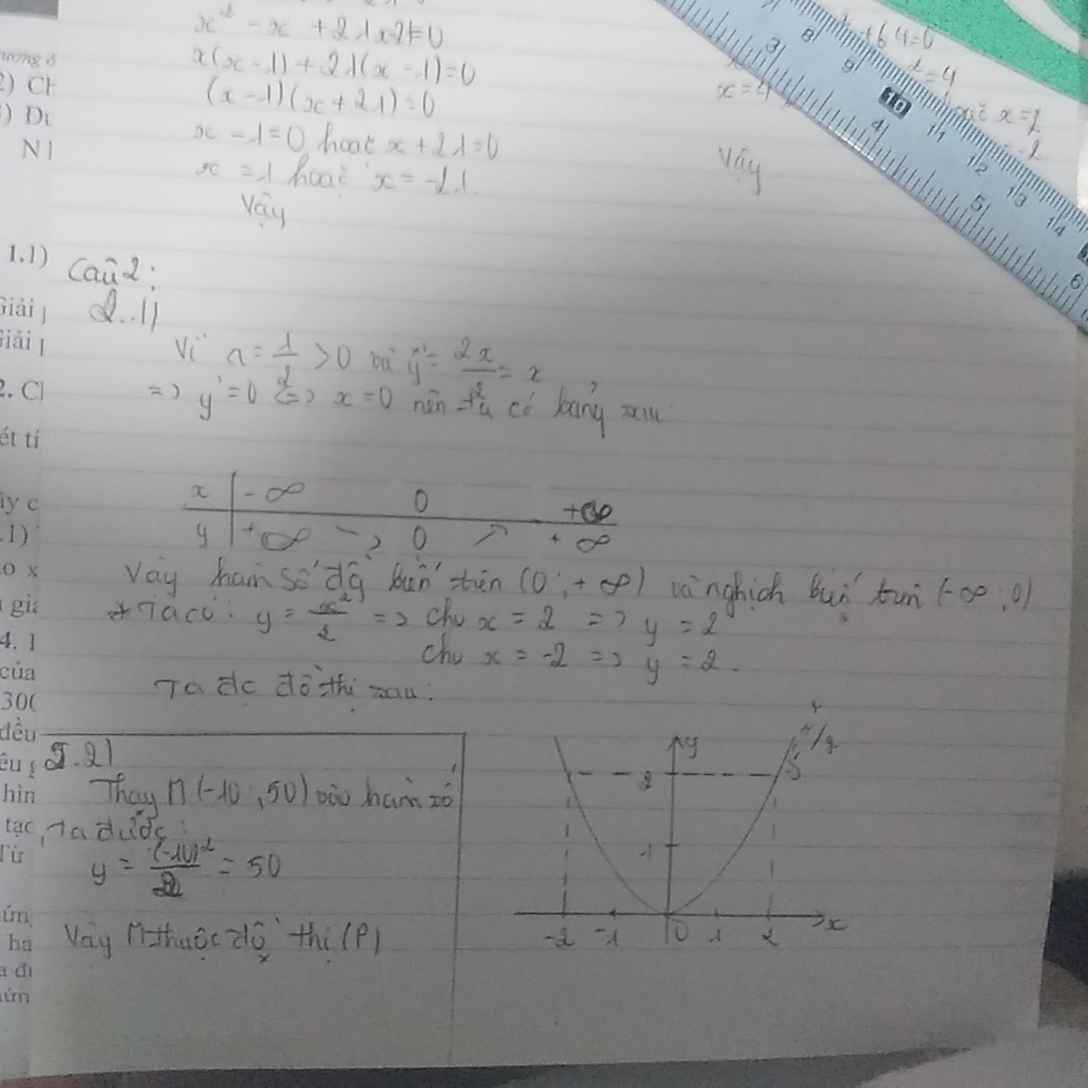

a: Đặt (P): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x^2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
b:
Thay x=-5 vào (P), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(-5\right)^2=\dfrac{25}{2}\)
=>\(M\left(-5;-\dfrac{25}{2}\right)\) không thuộc (P)
Thay \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\) vào (P), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{9}{4}=\dfrac{9}{8}\)
=>\(N\left(-\dfrac{3}{2};\dfrac{9}{8}\right)\) thuộc (P)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào (P), ta được:
\(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{8}\ne2\)
=>\(Q\left(\dfrac{1}{2};2\right)\) không thuộc (P)