Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=3x+1\\y=3x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\y=\dfrac{9}{5}+1=\dfrac{14}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a/ bạn tự làm
b/ \(\Rightarrow y=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=0\) giải PT tìm hoành độ x
c/ \(\Rightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=0+2=2\)
d/ \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=-x+2\) Giải PT tìm hoành độ x của C rồi thay vào d1 hoặc d2 để tìm tung độ y của C

\(b,\) Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;2\right)\)
Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng với trục hoành là
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B\left(2;0\right),C\left(-1;0\right)\)

\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(3x+2=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-4\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-2;-4\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm

a: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
3x-4=4x-6
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-4x=-6+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-2\)
hay x=2
Thay x=2 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(y=3\cdot2-4=2\)
b: Thay y=0 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(3x-4=0\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Thay x=0 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(y=3\cdot0-4=-4\)
Vậy: \(A\left(\dfrac{4}{3};0\right);B\left(0;-4\right)\)

1) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d_1\right):y=2x\\\left(d_2\right):y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
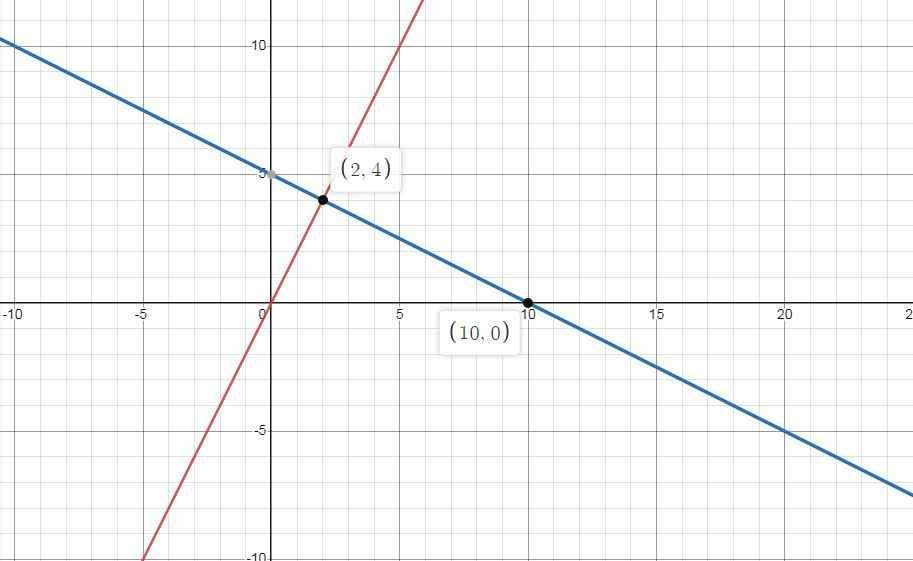
2) Theo đồ thi ta có :
\(\left(d_1\right)\cap\left(d_2\right)=A\left(2;4\right)\)
3) \(\left(d_2\right)\cap Ox=B\left(a;0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{2}a+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}a=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=10\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(d_2\right)\cap Ox=B\left(10;0\right)\)
4) \(OA=\sqrt[]{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(4-0\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{20}=2\sqrt[]{5}\)
\(OB=\sqrt[]{\left(10-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{10^2}=10\)
\(AB=\sqrt[]{\left(10-2\right)^2+\left(0-4\right)^2}=\sqrt[]{80}=4\sqrt[]{5}\)
Ta thấy :
\(OA^2+AB^2=20+80=OB^2=100\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta OAB\) vuông tại A
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OAB}=90^o\)
\(sin\widehat{AOB}=\dfrac{AB}{OB}=\dfrac{4\sqrt[]{5}}{10}=\dfrac{2\sqrt[]{5}}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{AOB}\sim63,43^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OBA}=90^o-63,43^o=26,57^o\)
5) Chu vi \(\Delta OAB\) :
\(AB+OA+OB=4\sqrt[]{5}+2\sqrt[]{5}+10=10\sqrt[]{5}+10=10\left(\sqrt[]{5}+1\right)\left(đvmd\right)\)
Diện tích \(\Delta OAB\) :
\(\dfrac{1}{2}AB.OA=\dfrac{1}{2}.4\sqrt[]{5}.2\sqrt[]{5}=20\left(đvdt\right)\)

b) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (D1) và (d2) là:
-x+4=x-4
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-8\)
hay x=4
Thay x=4 vào (d1), ta được:
y=-4+4=0
Thay x=0 vào (d1), ta được:
\(y=-0+4=4\)
Thay x=0 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=0-4=-4\)
Vậy: A(0;4); B(0;-4); C(4;0)

(d1): y = 1/2x + 2
và (d2): y = -x + 2
1. Vẽ (d1) và (d2) trên cùng một hệ trục tọa độ Oxy.
(d1) là đường thẳng đi qua hai điểm (0; 2) và (-4; 0)
(d2) là đường thẳng đi qua hai điểm (0; 2) và (2;0)
2. Tính chu vi và diện tích của tam giác ABC
(d1) và (d2) cùng cắt nhau tại một điểm trên trục tung có tung độ bằng 2
Áp dụng định lý Pi ta go cho các tam giác AOC và BOC vuông ở O ta được:
\(AC=\sqrt{4^2+2^2}=\sqrt{20}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{2^2+2^2}=\sqrt{8}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác ABC : AC + BC + AB= 2√5 + 2√2 + 6
≈ 13,30
Diện tích tam giác ABC
\(\frac{1}{2}.OC.AB=\frac{1}{2}.2.6=6CM^2\)
NHÉ THAK NHÌU
a:
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-2:\dfrac{2}{3}=-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=2x+2\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{4}{3}x=0\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-3;0); B(-1;0); C(0;2)