
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a: \(=\dfrac{2x+x-2-x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
b: x^2-x-6=0
=>(x-3)(x+2)=0
=>x=3(nhận) hoặc x=-2(loại)
Khi x=3 thì \(E=\dfrac{2}{3+2}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
c: Để E nguyên thì \(x+2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{-1;-3;0;-4\right\}\)

Bài 2:
Ta có: \(3n^3+10n^2-5⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n^3+n^2+9n^2+3n-3n-1-4⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n\in\left\{0;-3;3\right\}\)
hay \(n\in\left\{0;-1;1\right\}\)

\(\dfrac{x^3-27}{x^2-9}\left(x\ne\pm3\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3-3^3}{x^2-3^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+3x+9}{x+3}\)

\(x^2+2x+1=x^2+2\cdot1x+1^2=\left(x+1\right)^2\)
\(4x^2+12x+9=\left(2x\right)^2+2\cdot3\cdot2x+3^2=\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
\(\dfrac{4}{9}a^2-\dfrac{4}{3}a+1=\left(\dfrac{2}{3}a\right)^2-2\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot1a+1^2=\left(\dfrac{2}{3}a-1\right)^2\)
\(a^2+5a+\dfrac{25}{4}=a^2+2\cdot2,5a+2,5^2=\left(2,5+a\right)^2\)

c: Gọi bốn số nguyên liên tiếp là x;x+1;x+2;x+3
Ta có: \(x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)\left(x^2+3x+2\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x\right)^2+2\left(x^2+3x\right)+1\)
\(=\left(x^2+3x+1\right)^2\)
\(d,M=\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)-2\left(x-2y\right)+1+9\\ M=\left(x-2y\right)^2-2\left(x-2y\right)+1+9\\ M=\left(x-2y+1\right)^2+9\ge9\\ M_{min}=9\Leftrightarrow x=2y-1\)

Bài 1:
a) (2x+5)(x-6)=2x2+5x-12x-30=2x2-7x-30
b) (2x-1)(x2-4x+3)=2x3-8x2+6x-x2+4x-3=2x3-9x2+10x-3
c) x2-2x-(x-7)(x+2)=x2-2x-x2+7x-2x+14=3x+14
d) 3x-(x+2)(x+4)=3x-x2-2x-4x-8=-x2-3x-8
Bài 2:
a) 2(x+1)=x-1
⇒2x+2=x-1
⇒2x+2-x+1=0
⇒x+3=0
⇒x=-3
b) x(x+2)-x2=1
⇒x2+2x-x2=1
⇒2x=1
⇒x=0,5
c) 3x(x-2)=(3x-1)(x-1)-5
⇒3x2-6x=3x2-x-3x+1-5
⇒3x2-6x-3x2+x+3x-1+5=0
⇒-2x+4=0
⇒-2x=-4
⇒x=2
d) 6(x-1)(x-2)-6x(x+3)=2x
⇒6(x2-x-2x+2)-6x2-18x-2x=0
⇒6x2-6x-12x+12-6x2-18x-2x=0
⇒-38x+12=0
⇒-38x=-12
⇒x=\(\dfrac{6}{19}\)


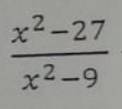




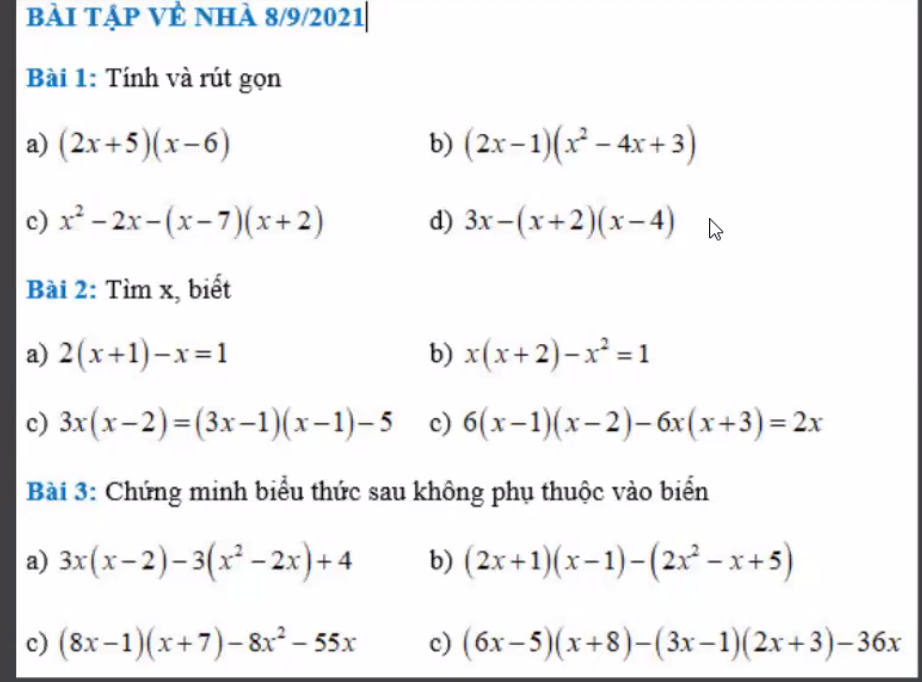
b, xét tam giác vuông BIM và tam giác vuông MKA có :
BM=MA (GT) , góc IMB= góc MAK (đồng vị)
\(\Rightarrow\)tam giác BIM=tam giác MKA (ch.gn)
\(\Rightarrow\)IM=KA (hai cạnh tương ứng) mà IM=OK(hình chữ nhật ở câu a,)
\(\Rightarrow\)OK=KA=IM=\(\frac{AO}{2}\)=2(cm)
(câu c, tí nữa mình làm cho)
c, vì M là trung điểm của AB nên M di chuyển trên AB