Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)\le5x^2-7\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
hay x<=4
b: \(\dfrac{6x+1}{18}+\dfrac{x+3}{12}>=\dfrac{5x+3}{6}+\dfrac{12-5x}{9}\)
=>2(6x+1)+3(x+3)>=6(5x+3)+4(12-5x)
=>12x+2+3x+9>=30x+18+48-20x
=>15x+11>=10x+66
=>5x>=55
hay x>=11

1.
a) \(x\left(x+4\right)+x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(x\left(x-3\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bài 1:
a, \(x\left(x+4\right)+x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+4\right)+\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=-4\) hoặc \(x=-1\)
b, \(x\left(x-3\right)+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=3\) hoặc \(x=-2\)

a)
A = \(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^3}{x+3}\) (đkxđ: x \(\ne\)\(\pm\)3)
= \(\left(\dfrac{x}{x+3}-1\right).\dfrac{x+3}{3x^2}\)
= \(\dfrac{x-x-3}{x+3}.\dfrac{x+3}{3x^2}\)
= -x2
b) Thay x = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào A, ta có:
A = -\(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
= -\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
c) Để A < 0 thì -x2 < 0
mà -x2 \(\le\) 0 \(\forall\)x
\(\Rightarrow\) Với mọi x (x\(\ne\)0) thì A < 0

Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\neq \pm 3\)
a)
Ta có \(P=\frac{2x(3-x)}{(x+3)(3-x)}-\frac{x(x+3)}{(x+3)(3-x)}+\frac{6x}{(3-x)(3+x)}\)
\(=\frac{2x(3-x)-x(x+3)+6x}{(3-x)(3+x)}=\frac{9x-3x^2}{(3-x)(3+x)}=\frac{3x(3-x)}{(3-x)(3+x)}=\frac{3x}{3+x}\)
b) Tại $x=\frac{3}{4}$
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{3.\frac{3}{4}}{3+\frac{3}{4}}=\frac{3}{5}\)

\(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-3;2\)
\(\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{x^2+x-6}-\frac{1}{x-2}=\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{1}{x-2}\)
\(=\frac{x^2+4x+4}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{x+3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2+4x+4-5-x-3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x^2+3x-4}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{\left(x+4\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(x^2-9=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(vì:x\ne-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{7}{15}\)
\(P\inℤ\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x-4⋮x^2+5x+6\Leftrightarrow2x+10⋮x^2+5x+6\Leftrightarrow12⋮x^2+5xx+6\)
\(................\left(dễ\right)\)
P/s: shitbo sai rồi nha bạn!Nếu không tin thì thay x = 3 vào P ban đầu và giá trị P sau khi rút gọn sẽ thấy sự khác biệt =)
ĐK: \(x\ne-3;x\ne2\)
a) \(P=\frac{x+2}{x+3}-\frac{5}{x^2+x-6}-\frac{1}{x-2}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-4}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x+3}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{x-4}{x-2}\)
b) \(x^2-9=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=9\Leftrightarrow x=\pm3\)
Thay vào điều kiện,tìm loại x = -3 .Tìm được x =3
Ta có: \(P=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{3-4}{3-2}=-1\)
c)Ta có: \(P=\frac{x-4}{x-2}=\frac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\frac{2}{x-2}\)
Để P có giá trị nguyên thì \(\frac{2}{x-2}\) nguyên hay \(x-2\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
Suy ra \(x=\left\{0;1;3;4\right\}\)

Lời giải của bạn Nhật Linh đúng rồi, tuy nhiên cần thêm điều kiện để A có nghĩa: \(x\ne\pm2\)


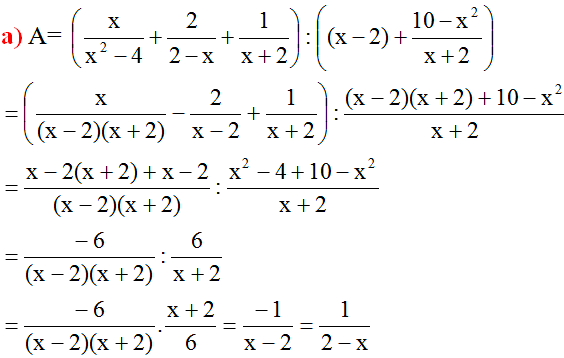
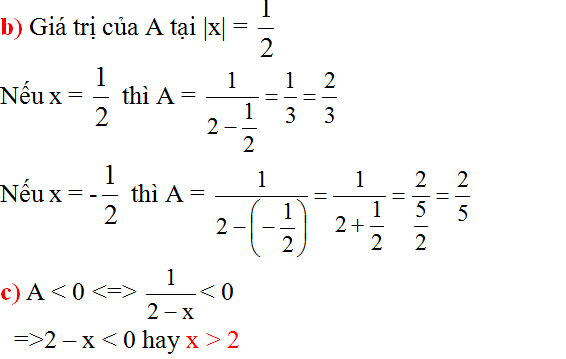
1/ a, \(A=\dfrac{3}{2x+6}-\dfrac{x-6}{2x^2+6x}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x-6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x-x+6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x+6}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x+3\right)}{2x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Vậy \(A=x\)
b/ Khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{2}}=2\)
Vậy...
2/a,
\(A=\dfrac{5x+2}{3x^2+2x}+\dfrac{-2}{3x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+2}{x\left(3x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+2-2x}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+2}{x\left(3x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
Vậy....
b/ Với \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{3}}=3\)
Vậy..