Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(MCO_3-^{t^o}\rightarrow MO+CO_2\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=0,1\left(mol\right);n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố Ba => \(n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố C =>\(n_{CO_2}=n_{BaCO_3}+n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn khối lượng => \(m_B=m_{muối}-m_{CO_2}=20-0,2.44=11,2\left(g\right)\)
Theo PT ta có : \(n_{MCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(M_{MCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\)
=> M + 60 =100
=> M=40 (Ca)
=> CT muối : CaCO3

a. Đặt CT muối: \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=\dfrac{200.17,1}{171.100}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{29,55}{197}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
`@` TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,15}=140\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=80\) ( loại )
`@` TH2: Ba(OH)2 hết
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,2 ( mol )
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15+0,1=0,25\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,25}=84\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=24\) `->` R là Mg
\(n_{MgO}=0,25.\left(24+16\right)=10\left(g\right)\)
b.\(n_{MgCO_3}=\dfrac{4,2}{84}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{HCl}=0,05.3=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_{HCl}=50.1,15=57,5\left(g\right)\)
\(MgCO_3+2HCl\rightarrow MgCl_2+CO_2+H_2O\)
0,05 < 0,15 ( mol )
0,05 0,1 0,05 0,05 ( mol )
\(m_{ddspứ}=4,2+57,5-0,05.44=59,5\left(g\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%m_{MgCl_2}=\dfrac{0,05.95}{59,5}.100=7,98\%\\\%m_{HCl\left(dư\right)}=\dfrac{\left(0,15-0,1\right).36,5}{59,5}.100=3,06\%\end{matrix}\right.\)

a)
$MCO_3 \xrightarrow{t^o} MO + CO_2$
$CO_2 + Ba(OH)_2 \to BaCO_3 + H_2O$
$CO_2 + Ba(OH)_2 \to Ba(HCO_3)_2$
b)
$n_{Ba(OH)_2} = 0,15(mol) ; n_{BaCO_3} = \dfrac{19,7}{197} = 0,1(mol)$
$n_{Ba(HCO_3)_2} = n_{Ba(OH)_2} - n_{BaCO_3} = 0,05(mol)$
$n_{CO_2} = n_{BaCO_3} + 2n_{Ba(HCO_3)_2} = 0,2(mol)$
$n_{MCO_3} = n_{CO_2} = 0,2(mol)$
$m_A = m_{MCO_3} - m_{CO_2} = 20 - 0,2.44 = 11,2(gam)$
c)
$M_{MCO_3} = M + 60 = \dfrac{20}{0,2} = 100$
$\Rightarrow M = 40(Canxi)$
Vậy CTHH : $CaCO_3$

Giả sử kim loại hóa trị II là A.
Ta có: nBa(OH)2 = 0,1 (mol)
nBaCO3 = 0,05 (mol)
\(ACO_3\underrightarrow{t^o}AO+CO_2\)
- TH1: Ba(OH)2 dư.
PT: \(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3+H_2O\)
Theo PT: \(n_{ACO_3}=n_{CO_2}=n_{BaCO_3}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M_{ACO_3}=\dfrac{15}{0,05}=300\left(g/mol\right)\Rightarrow M_A=240\left(g/mol\right)\)
→ Không có chất nào thỏa mãn.
- TH2: Ba(OH)2 hết.
PT: \(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3+H_2O\)
______0,05_____0,05_____0,05 (mol)
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
___0,05_____0,1 (mol)
⇒ nCO2 = 0,05 + 0,1 = 0,15 (mol)
Theo PT: \(n_{ACO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow M_A=\dfrac{15}{0,15}=100\left(g/mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow M_A=40\left(g/mol\right)\)
→ A là Ca.
Vậy: CTHH cần tìm là CaCO3

3. CuO +H2SO4 -->CuSO4 +H2O
nCuO=64/80=0,8(mol)
theo PTHH :nCuO =nH2SO4=nCuSO4=0,8(mol)
=>mddH2SO4 20%=0,8.98.100/20=392(g)
mCuSO4=0,8.160=128(g)
mdd sau phản ứng =64 +392=456(g)
mH2O=456 -128=328(g)
giả sử có a g CuSO4.5H2O tách ra
trong 250g CuSO4 tách ra có 160g CuSO4 và 90g H2O tách ra
=> trong a g CuSO4.5H2O tách ra có : 160a/250 g CuSO4 và 90a/250 g H2O tách ra
=>mCuSO4(còn lại)=128 -160a/250 (g)
mH2O (còn lại)=328 -90a/250 (g)
=>\(\dfrac{128-\dfrac{160a}{250}}{328-\dfrac{90a}{250}}.100=25\)
=>a=83,63(g)

a) Hãy xác định công thức của một loại oxit sắt, biết rằng khi cho 32 gam oxit sắt này tác dụng hoàn toàn với khí cacbon oxit thì thu được 22,4 gam chất rắn. Biết khối lượng mol phân tử của oxit sắt là 160 gam/mol.
b) Chất khí sinh ra được hấp thụ hoàn toàn bằng nước vôi trong dư. Tính khối lượng kết tủa thu được.
Giải
a) Gọi CTHH của oxit sắt là: FexOy
PTHH: : FexOy + yCO ------> xFe + yCO2
Số mol Fe là

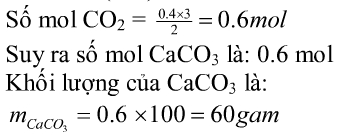
a/
mFe=22,4g
=> mO = 32-22,4=9,6g
Gọi công thức oxit sắt: FexOy
x:y=(22,4:56):(9,6:16)=2:3
=> CT: Fe2O3.
b/
nO=nC=nCO2=(9,6:16)=0,6mol
nCaCO3 =nCO2=0,6mol
=> mCaCO3 =0,6.100=60g

nNaOH= 0,35 mol
NaOH + CO2 -> NaHCO3 (1)
a a a
2NaOH + CO2 -> Na2CO3 + H2O (2)
2b b b
đặt nCO2(1)= a mol nCO2(2)=b mol
theo đề bài ta có hệ pt
a+2b=0,35 => a=0,05
84a+106b=20,1 b=0,15
nCO2= 0,05+0,15= 0,2 mol
gọi M là KL cần tìm
MCO3 -> MO + CO2
0,2 0,2
MMCO3= 16,2/0,2=81 g/mol
Cho mình hỏi bạn có chép sai đề không, theo mình nghĩ khối lượng muối ban đầu là 16,8g mới ra kim loại Mg =)))


Đặt CT muối \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=15.0,01=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{19,7}{197}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
`@`TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1) \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,1}=200\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=140\) \((g/mol)\) (loại )
`@`TH2: Tạo ra 2 muối
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 ( mol )
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=0,1+0,1=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=40\) \((g/mol)\) `->` R là Canxi ( Ca )
\(m_{CaO}=0,2\left(40+16\right)=11,2\left(g\right)\)