
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) Vì x=25 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ nên Thay x=25 vào biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{x+1}\), ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{25}-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{5-2}{25+1}=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
Vậy: Khi x=25 thì \(A=\dfrac{3}{26}\)
2) Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{x-\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-5\sqrt{x}+6+2x+8\sqrt{x}-6}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)

3:
b: x1^2+x2^2=12
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2=12
=>(2m+2)^2-4m=12
=>4m^2+4m+4=12
=>m^2+m+1=3
=>(m+2)(m-1)=0
=>m=1;m=-2
2:
b: =>|x1|-|x2|=m+3-|-1|=m+2
=>x1^2+x2^2-2|x1x2|=m+2
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2-2|x1x2|=m+2
=>(2m)^2-2(-1)-2|-1|=m+2
=>4m^2-m-2=0
=>m=(1+căn 33)/8; m=(1-căn 33)/8

ĐKXĐ: x>0; x ≠ 1
P = \(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}+4\sqrt{x}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right)\)
= \(\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1-x+2\sqrt{x}-1+4x\sqrt{x}-4\sqrt{x}}{x-1}.\dfrac{x-1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
= \(\dfrac{4x\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}\)= 4x
Vậy P = 4x với x > 0; x ≠ 1

a) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x^2=\left(m+2\right)x-2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\left(m+2\right)x+2m=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(m+2\right)^2-8m=m^2+4m+4-8m=m^2-4m+4=\left(m-2\right)^2\)
Để (d) và (P) cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)^2>0\)
mà \(\left(m-2\right)^2\ge0\)
nên \(m-2\ne0\)
hay \(m\ne2\)
Vậy: Để (d) và (P) cắt nhau tại hai điểm phân biệt thì \(m\ne2\)

a: góc ASB=1/2*180=90 độ=góc ABM
b: ON vuông góc AS
BS vuông góc SA
=>ON//BS
c: góc OIM+góc OBM=180 độ
=>OIMB nội tiếp


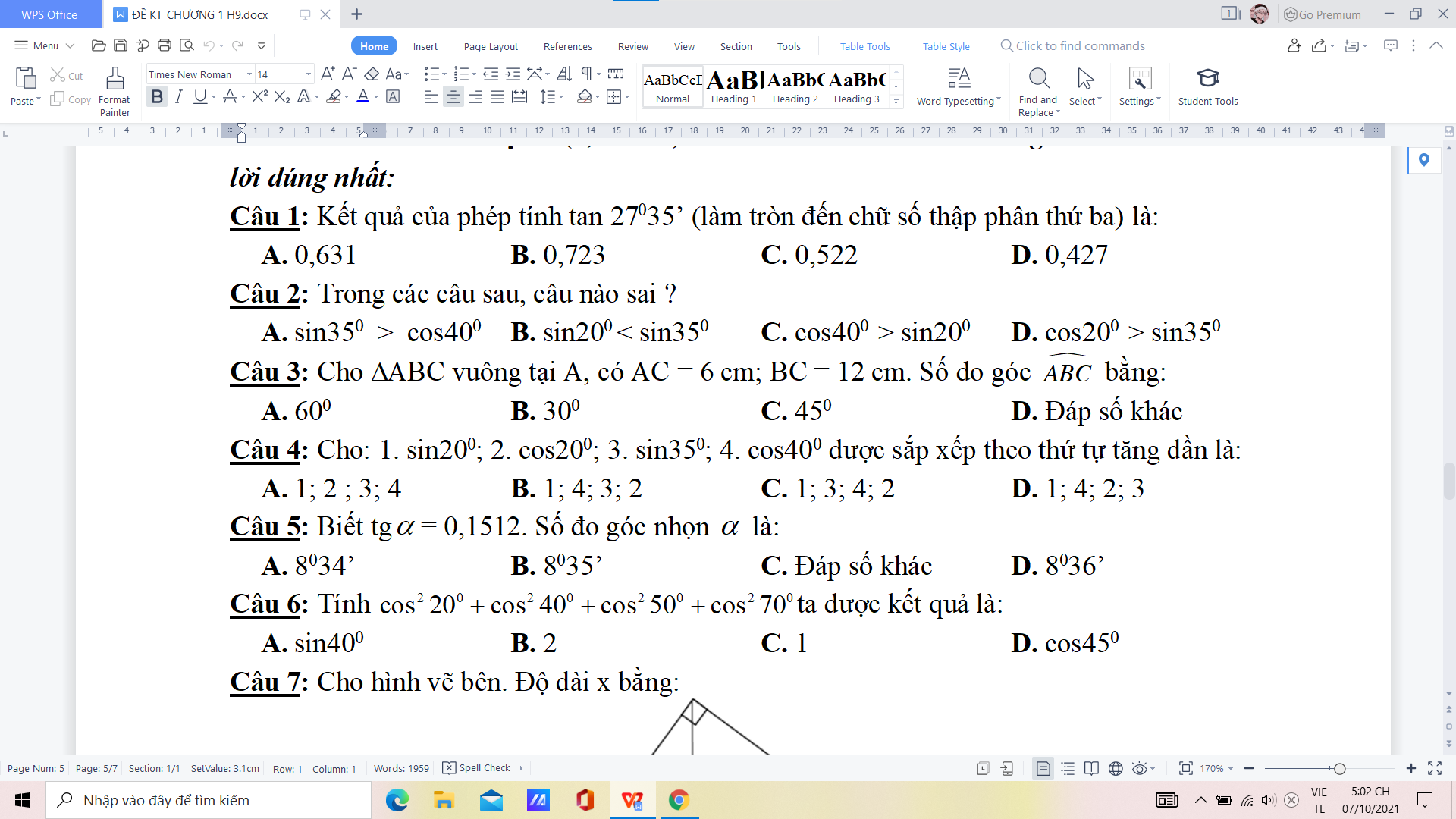
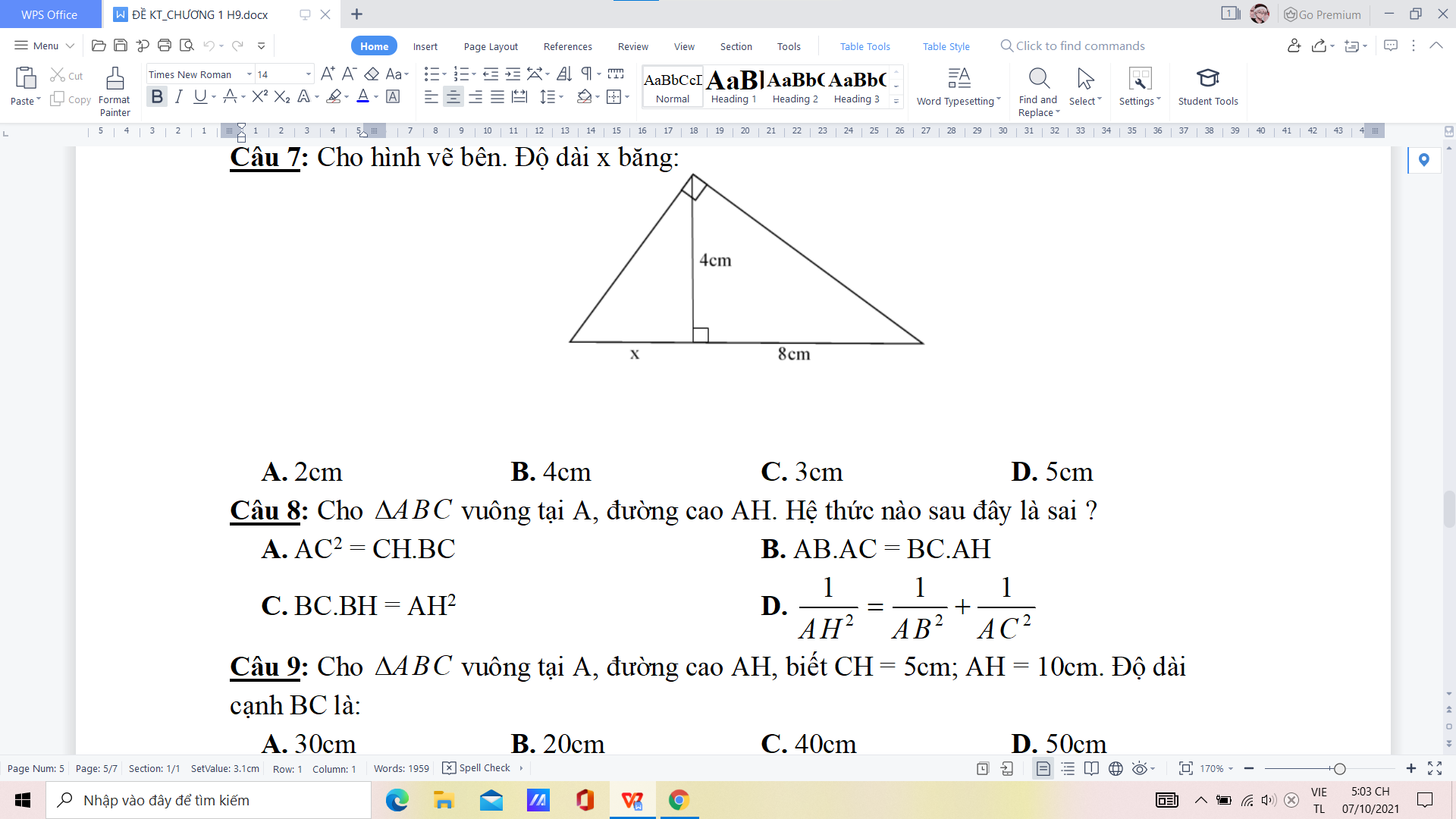
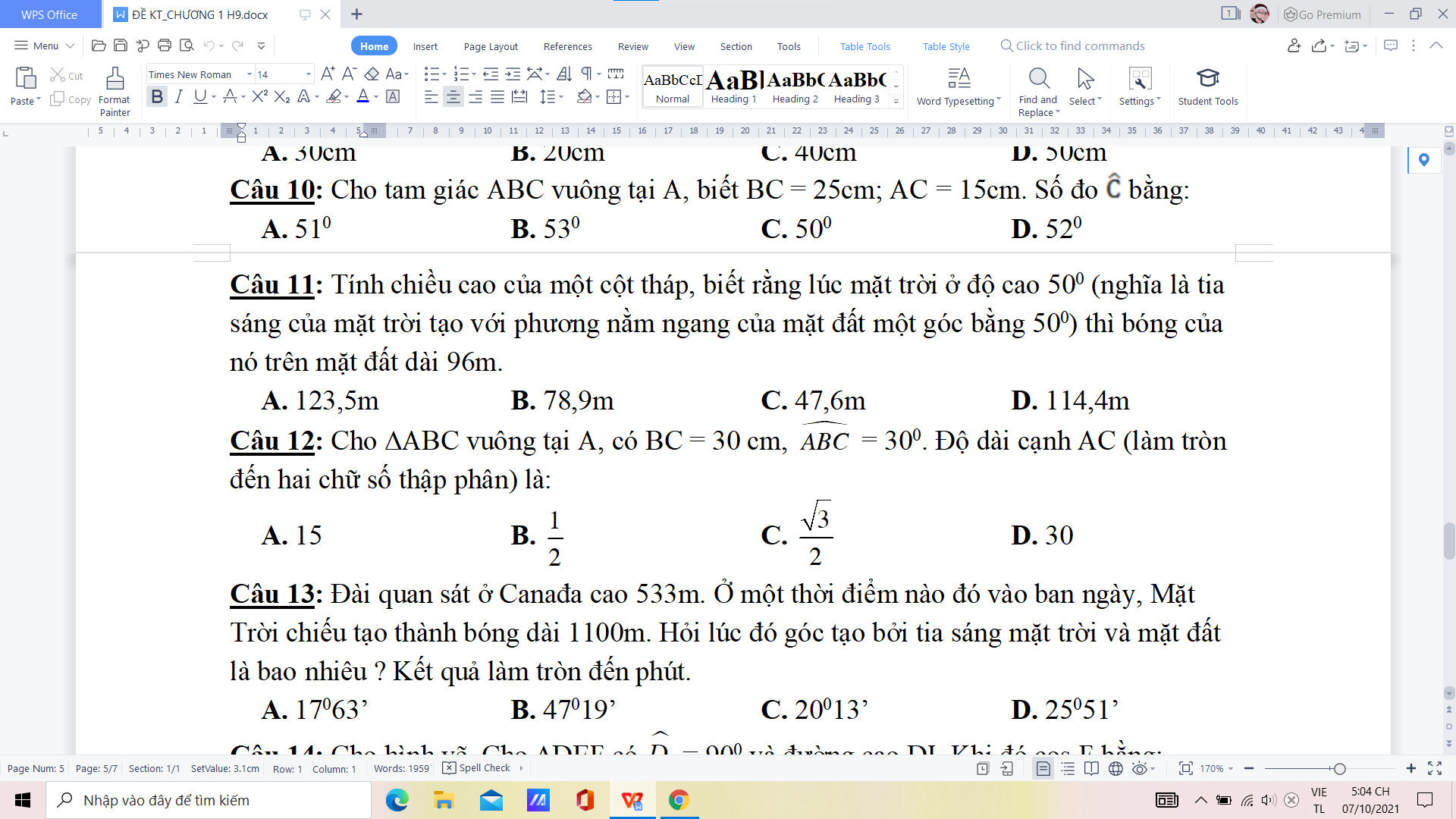
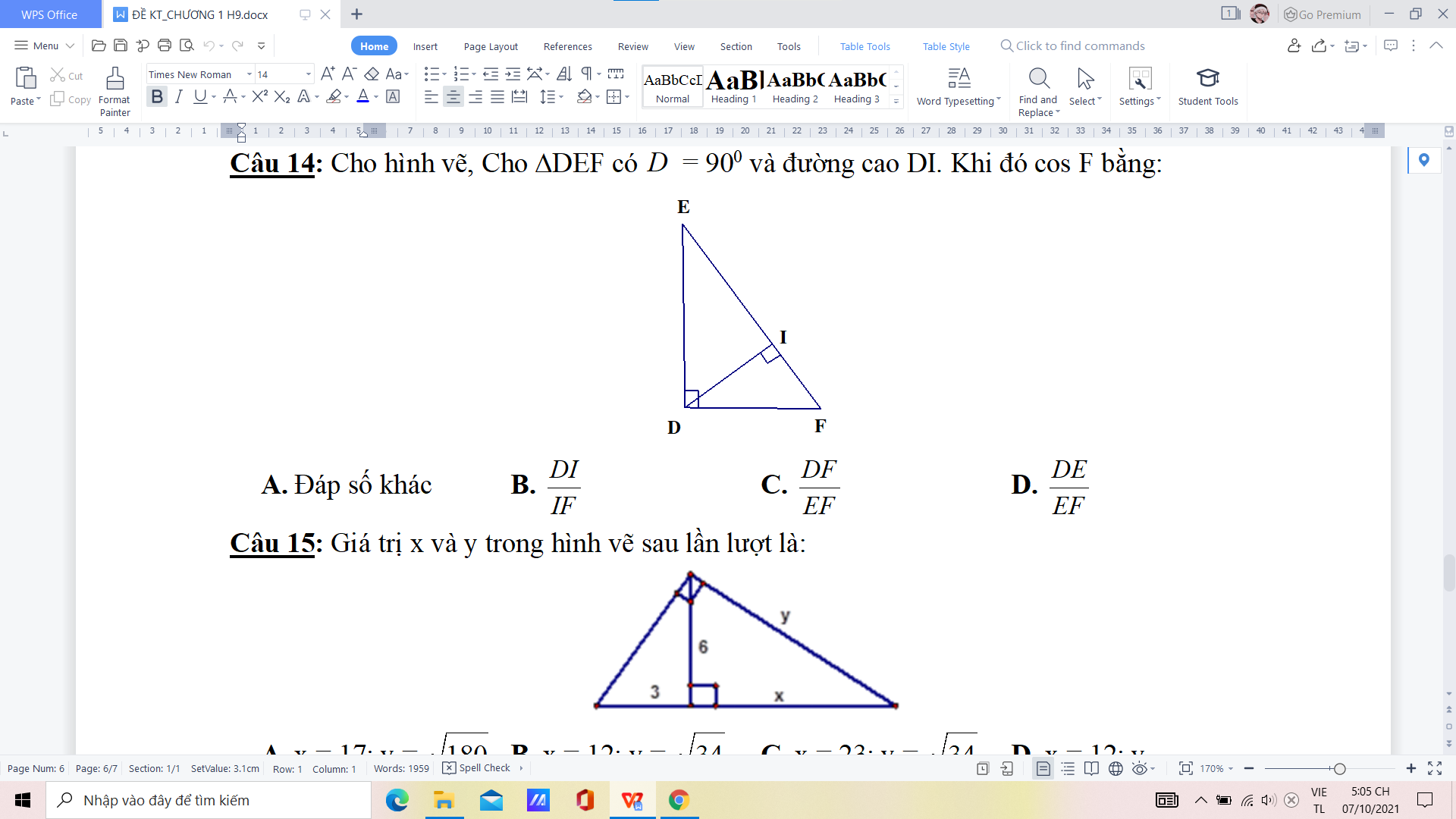
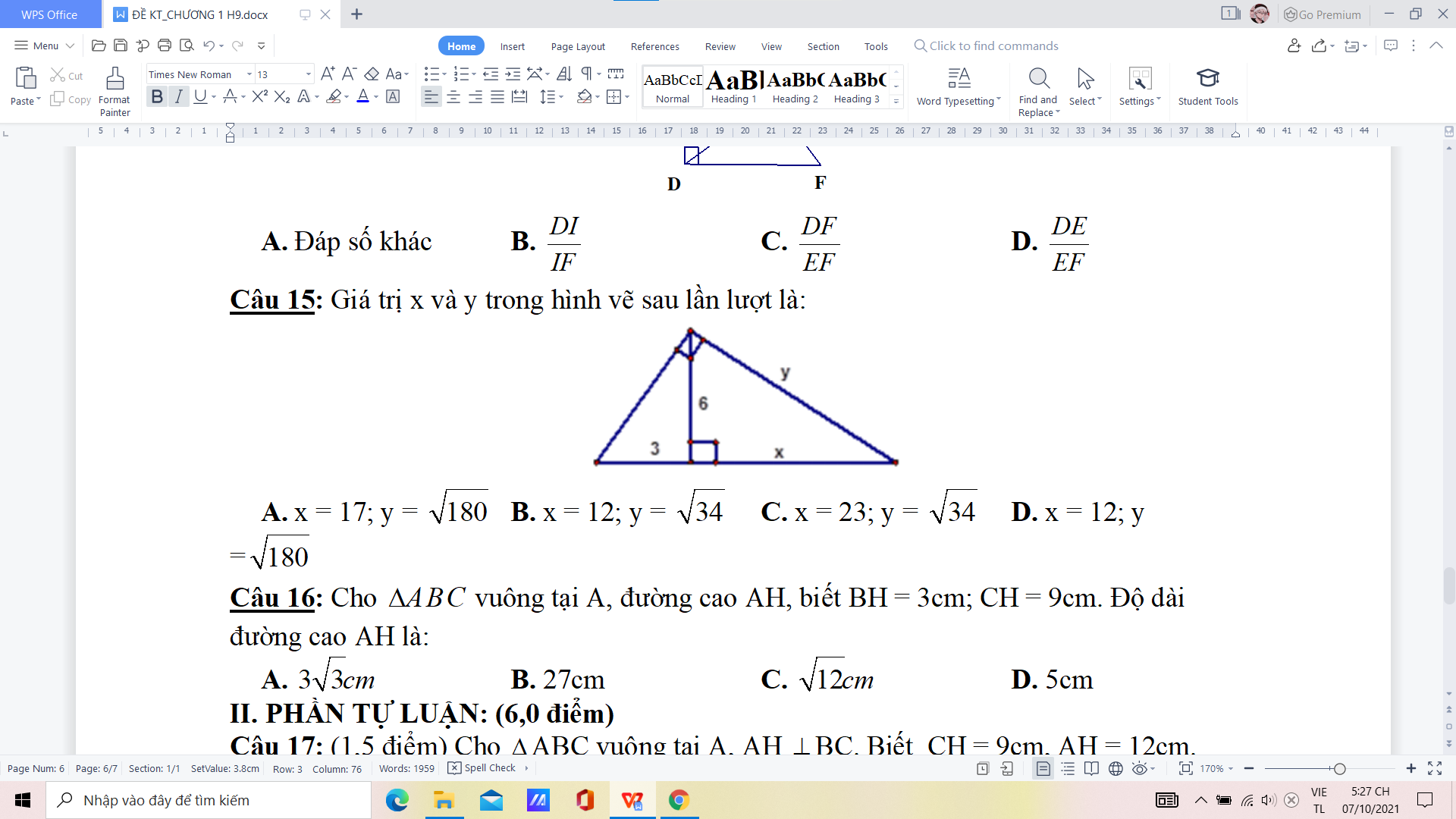
 làm nhanh hộ mình ạ
làm nhanh hộ mình ạ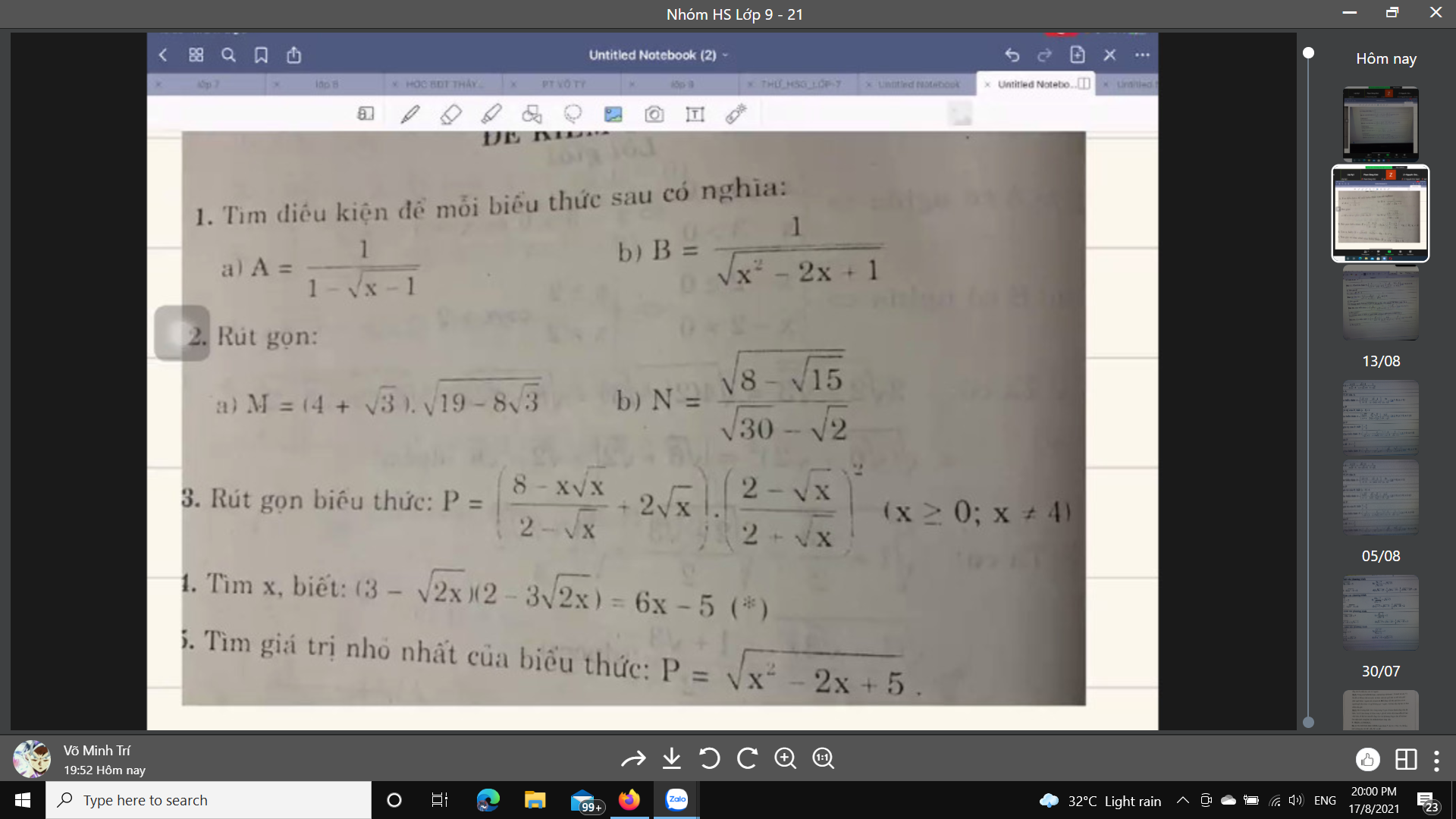






4. Ta có : 2M = \(\frac{2\sqrt{x}+4}{2\sqrt{x}-3}=\frac{2\sqrt{x}-3+7}{2\sqrt{x}-3}=1+\frac{7}{2\sqrt{x}-3}\)
Để M nguyên dương thì \(\frac{7}{2\sqrt{x}-3}\)nguyên dương
=> \(2\sqrt{x}-3\in\left\{1;7\right\}\)
=> \(x\in\left\{\sqrt{2};\sqrt{5}\right\}\)
Mà x\(\in\)Z; x\(\ge\)0
=> Không có giá trị x nguyên thỏa mãn nào để M nguyên dương
5. \(C=\frac{2\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\frac{2\sqrt{x}-4+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}=2+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
Để C nguyên thì \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)nguyên
=> \(\sqrt{x}-2\in\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
=> \(x\in\left\{1;\sqrt{3}\right\}\)
Mà x nguyên và C cần đạt GTNN nên x = 1
Vậy minC = 1 <=> x = 1
6. \(D=\frac{x-3}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\frac{x+\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}-1-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)-\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\sqrt{x}-1-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Để D nguyên thì \(\sqrt{x}\)nguyên; \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)nguyên
=> \(\sqrt{x}+1\in\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\)
Mà \(\sqrt{x}+1\ge1\)=> \(\sqrt{x}\in\left\{0;1\right\}\)(tm \(\sqrt{x}\)nguyên)
=> x\(\in\){ 0 ; 1 } . Mà x khác 1
=> x = 0
Vậy D nguyên khi x = 0