Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
Vận tốc cano khi dòng nước lặng là: $25-2=23$ (km/h)
Bài 2:
Đổi 1 giờ 48 phút = 1,8 giờ
Độ dài quãng đường AB: $1,8\times 25=45$ (km)
Vận tốc ngược dòng là: $25-2,5-2,5=20$ (km/h)
Cano ngược dòng từ B về A hết:
$45:20=2,25$ giờ = 2 giờ 15 phút.

Bài 1:
a.
$a^3-a^2c+a^2b-abc=a^2(a-c)+ab(a-c)$
$=(a-c)(a^2+ab)=(a-c)a(a+b)=a(a-c)(a+b)$
b.
$(x^2+1)^2-4x^2=(x^2+1)^2-(2x)^2=(x^2+1-2x)(x^2+1+2x)$
$=(x-1)^2(x+1)^2$
c.
$x^2-10x-9y^2+25=(x^2-10x+25)-9y^2$
$=(x-5)^2-(3y)^2=(x-5-3y)(x-5+3y)$
d.
$4x^2-36x+56=4(x^2-9x+14)=4(x^2-2x-7x+14)$
$=4[x(x-2)-7(x-2)]=4(x-2)(x-7)$
Bài 2:
a. $(3x+4)^2-(3x-1)(3x+1)=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-[(3x)^2-1]=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-(3x)^2=48$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4-3x)(3x+4+3x)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(6x+4)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x+4=12$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x=8$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$
b. $x^2-4x+4=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-2-9)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-11)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x-11=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=11$
c.
$x^2-25=3x-15$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)=3(x-5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-5=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=5$ hoặc $x=-2$

Bài 3:
Gọi x(m) là chiều rộng của mảnh đất(Điều kiện: x>0)
Chiều dài của mảnh đất là: x+5(m)
Theo đề, ta có phương trình:
2x+5=25
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=20\)
hay x=10(thỏa ĐK)
Vậy: Diện tích của mảnh đất là 150m2

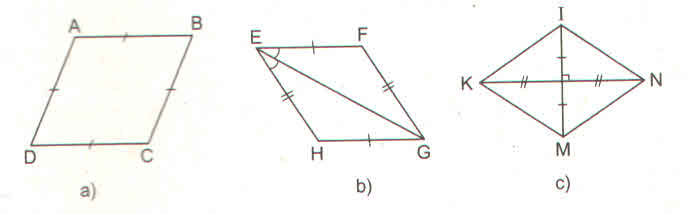
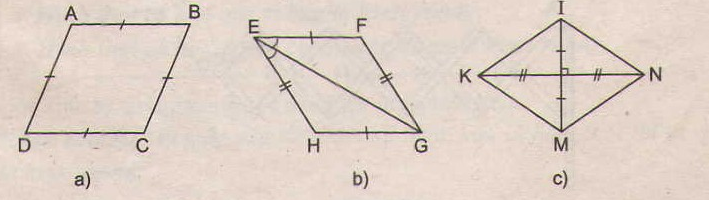
73. Tìm các hình thoi trên hình 102.
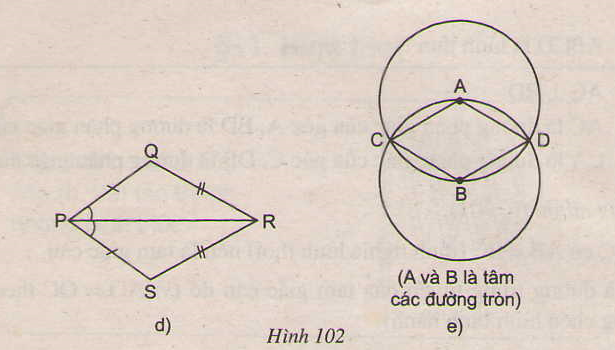
Bài giải:
Các tứ giác ở hình 39 a, b, c, e là hình thoi.
- Ở hình 102a, ABCD là hình thoi (theo định nghĩa)
- Ở hình 102b, EFGH là hình thoi (theo dấu hiệu nhận biết 4)
- Ở hình 102c, KINM là hình thoi (theo dấu hiệu nhận biết 3)
-Ở hình 102e, ADBC là hình thoi (theo định nghĩa, vì AC = AD = AB = BD = BC)
Tứ giác trên hình 102d không là hình thoi.
Các tứ giác ở hình 39 a, b, c, e là hình thoi.
- Ở hình 102a, ABCD là hình thoi (theo định nghĩa)
- Ở hình 102b, EFGH là hình thoi (theo dấu hiệu nhận biết 4)
- Ở hình 102c, KINM là hình thoi (theo dấu hiệu nhận biết 3)
-Ở hình 102e, ADBC là hình thoi (theo định nghĩa, vì AC = AD = AB = BD = BC)
Tứ giác trên hình 102d không là hình thoi.

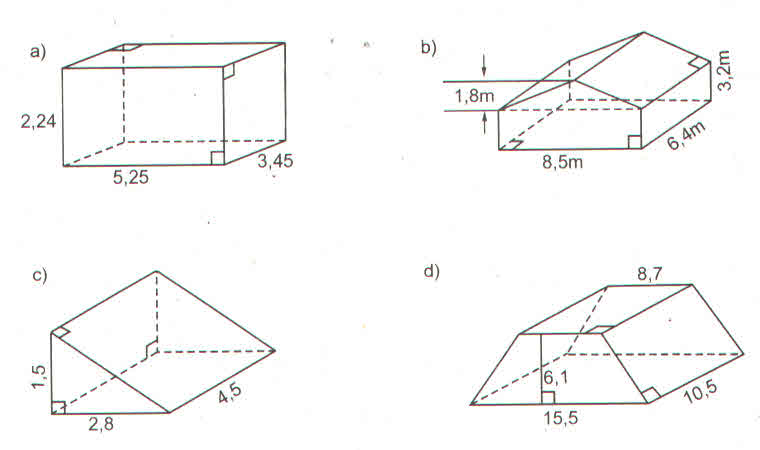
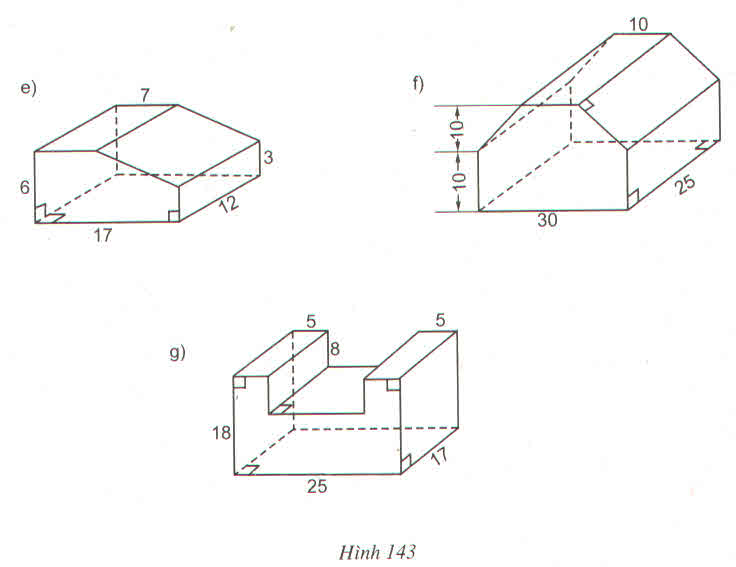
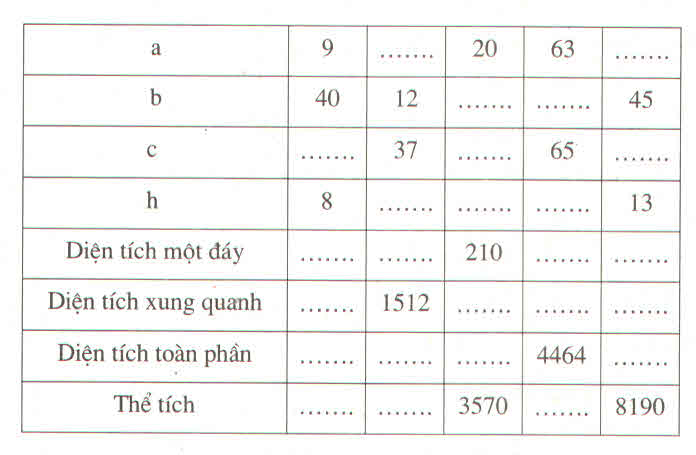
| a | 9 | 35 | 20 | 63 | 28 |
| b | 40 | 12 | 21 | 16 | 45 |
| c | 41 | 37 | 29 | 65 | 53 |
| h | 8 | 18 | 17 | 24 | 13 |
| Diện tích 1 đáy | 180 | 210 | 210 | 504 | 630 |
| Diện tích xung quanh | 720 | 1512 | 1190 | 3456 | 1638 |
| Diện tích toàn phần | 1080 | 1932 | 1610 | 4464 | 2898 |
| Thể tích | 1440 | 3780 | 3570 | 12096 | 8190 |

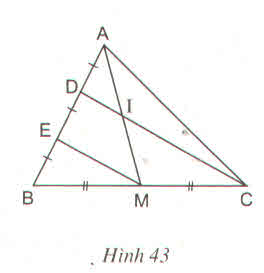
∆BDC có BE = ED và BM = MC
nên EM // DC
==> DI // EM
∆AEM có AD = DE và DI // EM
==> AI = IM.

Giải:
∆A'B'C' ∽ ∆A"B"C" theo tỉ số đồng dạng K1 = A′B′A"B"A′B′A"B"
∆A"B"C" ∽∆ ABC theo tỉ số đồng dạng k2 = A"B"ABA"B"AB
Theo tính chất 3 thì ∆A'B'C' ∽ ∆ABC.
Theo tỉ số K= A′B′ABA′B′AB = A′B′.A"B"A′B′.ABA′B′.A"B"A′B′.AB = A′B′A"B"A′B′A"B".A"B"ABA"B"AB
vậy K= K1.k2