
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




\(\left(d\right):\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{b}=1\)\(\left(1\right)\)
Thế \(x=a,y=0\)vào phương trình \(\left(1\right)\)thỏa mãn nên \(A\left(a,0\right)\)thuộc \(\left(d\right)\).
Thế \(x=0,y=b\)vào phương trình \(\left(1\right)\)thỏa mãn nên \(B\left(0,b\right)\)thuộc \(\left(d\right)\).
Do đó ta có đpcm.

Bài 2:
a: Để hai đồ thị song song thì 2m-1=m+2
hay m=3

Bài 5:
\(K=\sqrt{5x-9+6\sqrt{5x-9}+9}+\sqrt{5x-9-6\sqrt{5x-9}+9}\\ K=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5x-9}+3\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{5x-9}-3\right)^2}\\ K=\left|\sqrt{5x-9}+3\right|+\left|3-\sqrt{5x-9}\right|\\ K\ge\left|\sqrt{5x-9}+3+3-\sqrt{5x-9}\right|=6\\ K_{min}=6\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{5x-9}+3\right)\left(3-\sqrt{5x-9}\right)\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow-3\le\sqrt{5x-9}\le3\\ \Leftrightarrow0\le5x-9\le9\\ \Leftrightarrow9\le5x\le18\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9}{5}\le x\le\dfrac{18}{5}\)

a: Khi m=1 thì hệ sẽ là x+y=1 và x-y=2
=>x=1,5; y=0,5
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-y\\m\left(1-y\right)-y=2m\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-y\\m-my-y=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=1-y và y(-m-1)=m
=>x=1-y và y=-m/m+1
=>x=1+m/m+1=2m+1/m+1 và y=-m/m+1
Để x,y nguyên thì 2m+1 chia hết cho m+1 và -m chia hết cho m+1
=>\(m+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(m\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)

A=\(\dfrac{1-\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}.\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)^2}{1-\sqrt{x}}\)=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}}\)


 ai giúp mình giải câu này với ạ, mình cám ơn mn nhiều
ai giúp mình giải câu này với ạ, mình cám ơn mn nhiều

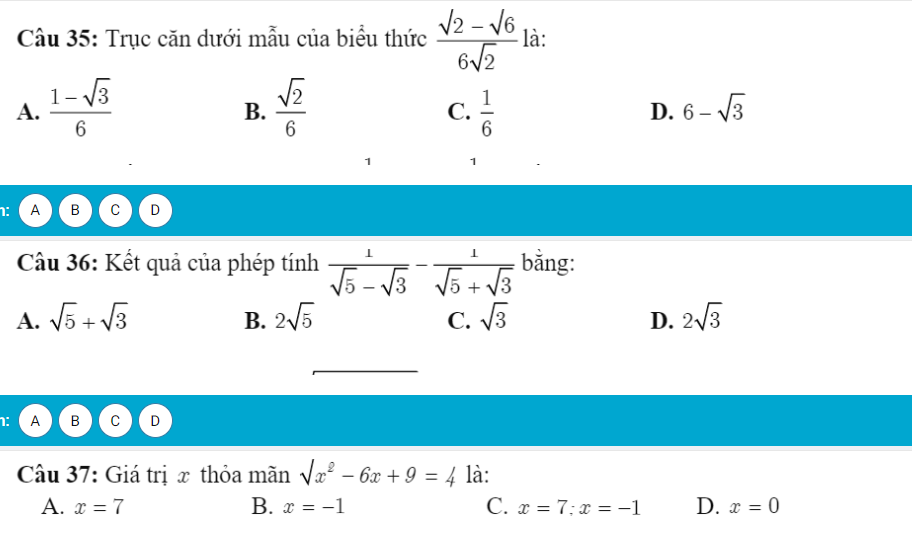
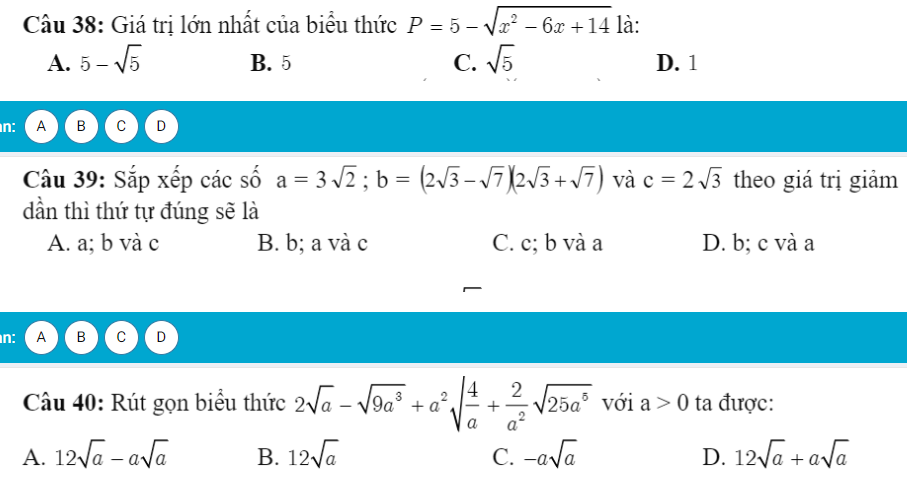



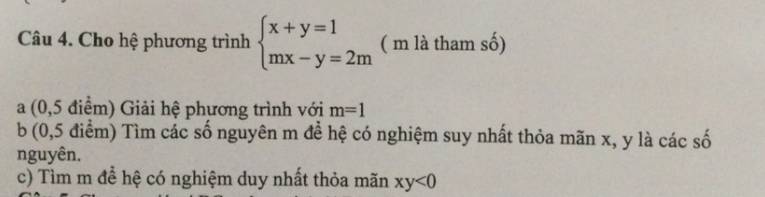


1) Phương trình đó có vô số nghiệm khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}m^2-1=0\\m+1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow m=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Chọn A
2) Phương trình đó có nghiệm duy nhất khi \(m^2-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\pm1\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Chọn D.