
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


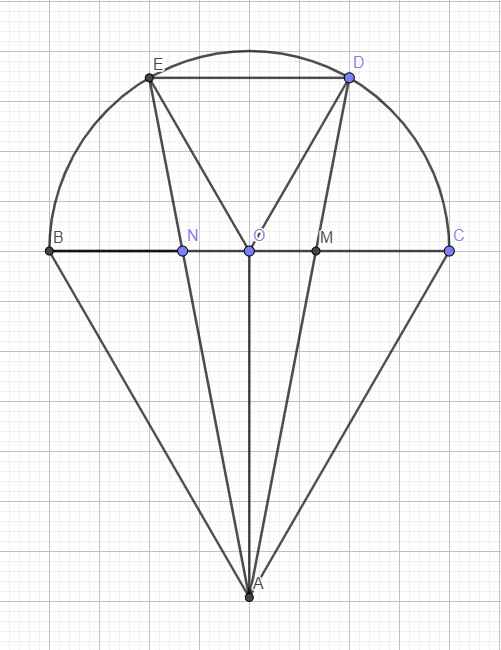
Gọi O là tâm đường tròn \(\Rightarrow\) O là trung điểm BC
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{ED}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow\widehat{BOE}=\widehat{EOD}=\widehat{DOC}=\dfrac{180^0}{3}=60^0\)
Mà \(OD=OE=R\Rightarrow\Delta ODE\) đều
\(\Rightarrow ED=R\)
\(BN=NM=MC=\dfrac{2R}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{NM}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow ED||BC\)
Áp dụng định lý talet:
\(\dfrac{AN}{AE}=\dfrac{MN}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{OB-BN}{BN}=\dfrac{R-\dfrac{2R}{3}}{\dfrac{2R}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) và \(\widehat{ENO}=\widehat{ANB}\) (đối đỉnh)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ENO\sim ANB\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{NBA}=\widehat{NOE}=60^0\)
Hoàn toàn tương tự, ta có \(\Delta MDO\sim\Delta MAC\Rightarrow\widehat{MCA}=\widehat{MOD}=60^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\) đều


Lời giải:
a) $MA,MB$ là tiếp tuyến của $(O)$ nên $MA\perp OA, MB\perp OB$
$\Rightarrow \widehat{MAO}=\widehat{MBO}=90^0$
Tứ giác $MAOB$ có tổng 2 góc đối $\widehat{MAO}+\widehat{MBO}=90^0+90^0=180^0$ nên là tứ giác nội tiếp.
b) Xét tam giác $MAC$ và $MDA$ có:
$\widehat{M}$ chung
$\widehat{MAC}=\widehat{MDA}$ (tính chất góc tạo bởi tiếp tuyến và dây cung bằng góc nội tiếp chắn cung đó)
$\Rightarrow \triangle MAC\sim \triangle MDA$ (g.g)
$\Rightarrow \frac{MA}{MD}=\frac{MC}{MA}\Rightarrow MA^2=MC.MD$
c) Dễ thấy $AB\perp MO$ tại $H$.
Xét tam giác $AMO$ vuông tại $A$ có đường cao $AH$, áp dụng định lý hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông:
$MA^2=MH.MO$
Kết hợp kết quả phần b suy ra $MH.MO=MC.MD$
$\Rightarrow CHOD$ là tứ giác nội tiếp.
d) Vận dụng giả thiết $AD\parallel MB$ và tính chất góc tạo bởi tiếp tuyến- dây cung ta có:
$\widehat{MCB}=180^0-\widehat{CMB}-\widehat{CBM}$
$=180^0-\widehat{CDA}-\widehat{CDB}$
$=180^0-\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{ACB}$ (do $ACBD$ là tứ giác nội tiếp)
** Khuyên chân thành các bạn muốn nâng cao xác suất được hỗ trợ thì nên chịu khó gõ đề bằng công thức toán. Chụp hình như này đọc bài rất nản, đặc biệt là hình xoay ngược đọc mỏi cổ lém.



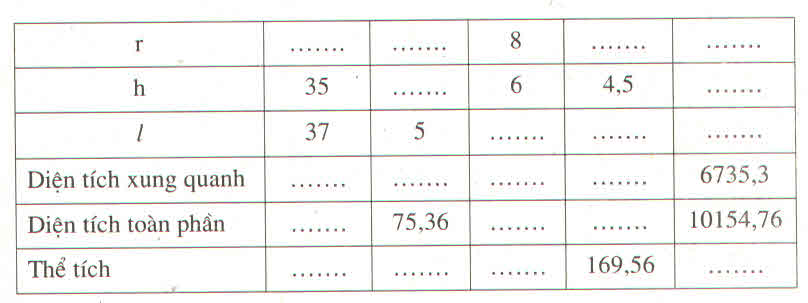
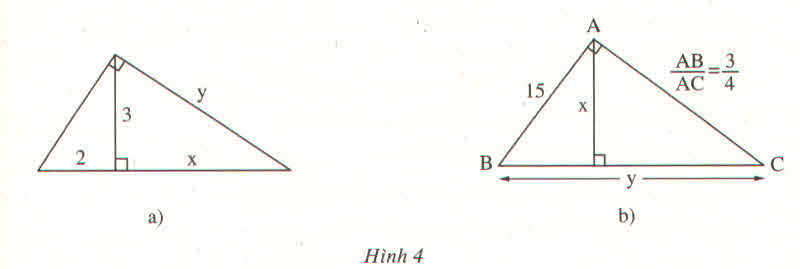
a) Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông⇒32=2x⇒x=\(\dfrac{9}{2}=4,5\)
Áp dụng định lý Pi-ta-go⇒y2=32+x2=9+20,25=29,25⇒\(y=\dfrac{3\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
b) Ta có \(\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Rightarrow AC=\dfrac{4}{3}.AB=\dfrac{4}{3}.15=20\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông ⇒\(\dfrac{1}{x^2}=\dfrac{1}{AB^2}+\dfrac{1}{AC^2}=\dfrac{1}{225}+\dfrac{1}{400}=\dfrac{1}{144}\Rightarrow x^2=144\Rightarrow x=12\)Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông ⇒AB.AC=x.y⇒\(y=\dfrac{AB.AC}{x}=\dfrac{15.20}{12}=25\)









\(1,\\ a,=\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)^2}}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}\right)^2}{\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}}}=\sqrt{\sqrt{a}-\sqrt{b}}\\ b,=\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{3}\right)}}{\sqrt{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{3}}}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{3}}}\\ =\sqrt{3}\\ c,=2y^2\cdot\dfrac{x^2}{\left|2y\right|}=\dfrac{2x^2y^2}{-2y}=-x^2y\\ d,=5xy\cdot\dfrac{\left|5x\right|}{y^2}=\dfrac{-25x^2y}{y^2}=\dfrac{-25x^2}{y}\)
Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(A=\left(3\sqrt{18}+2\sqrt{50}-4\sqrt{72}\right):8\sqrt{2}\)
\(=\left(9\sqrt{2}+10\sqrt{2}-24\sqrt{2}\right):8\sqrt{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-5\sqrt{2}}{8\sqrt{2}}=-\dfrac{5}{8}\)
b: Ta có: \(B=\left(-4\sqrt{20}+5\sqrt{500}-3\sqrt{45}\right):\sqrt{5}\)
\(=\left(-8\sqrt{5}+50\sqrt{5}-9\sqrt{5}\right):\sqrt{5}\)
\(=49\)