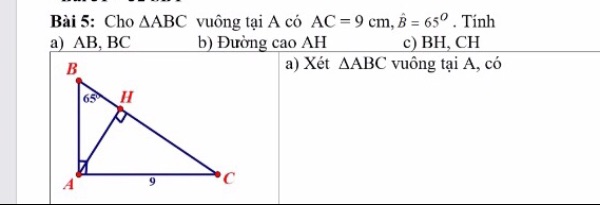
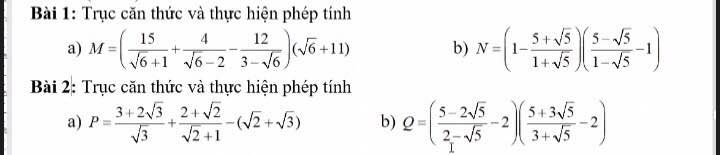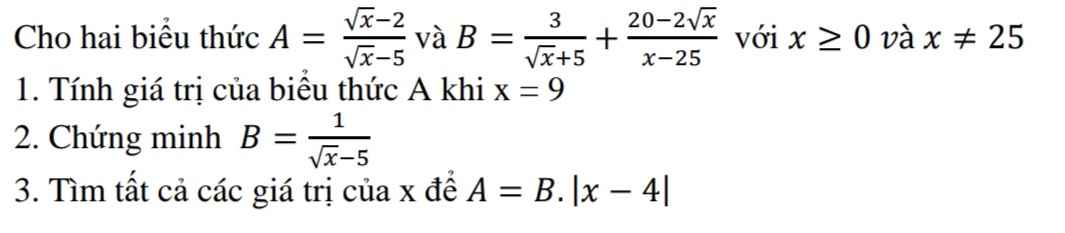Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



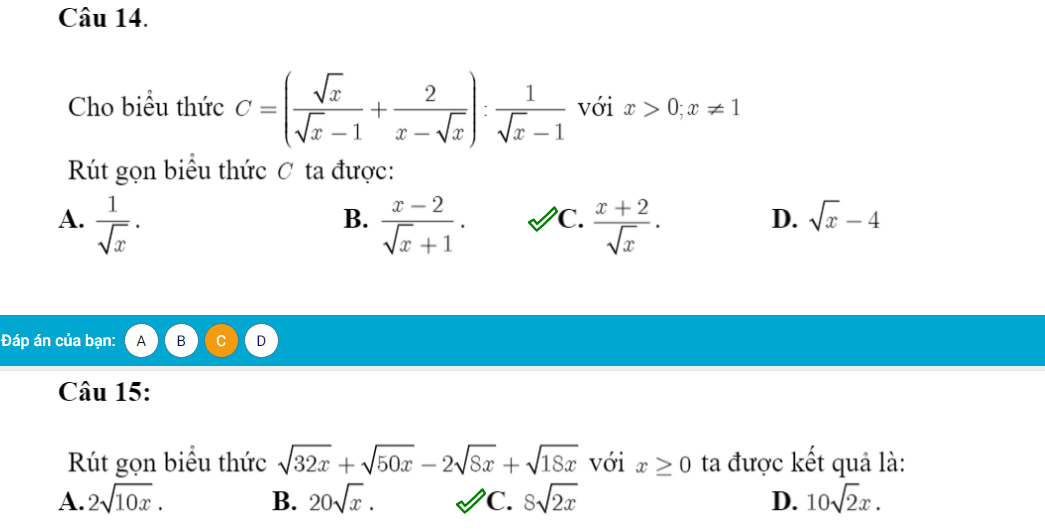
Câu 15:
Ta có: \(\sqrt{32x}+\sqrt{50x}-2\sqrt{8x}+\sqrt{18x}\)
\(=4\sqrt{2x}+5\sqrt{2x}-4\sqrt{2x}+3\sqrt{2x}\)
\(=8\sqrt{2x}\)

Câu 14 : \(C=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{2}{x-\sqrt{x}}\right):\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\) với x >0 ; x≠0
\(C=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\right):\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(C=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}.\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\right):\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(C=\dfrac{x+2}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{1}\)
\(C=\dfrac{x+2}{\sqrt{x}}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt


a, Thay tọa độ điểm ( 2;5 ) vào hàm số ta được ;
\(2\left(2m-1\right)+m-3=5\)
\(\Rightarrow m=2\)
b, - Gọi điểm cố định hàm số đi qua là M (x0; y0 ) ta được :
\(\left(2m-1\right)x_0+m-3=y_0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2mx_0-x_0+m-3-y_0=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(2x_0+1\right)-x_0-y_0-3=0\)
- Để hàm số luôn đi qua điểm cố định \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x_0+1=0\\x_0+y_0+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy điểm cố định mà hàm số đi qua là : M ( -1/2; -5/2 )
c, - Thay điểm có hoành độ là \(\sqrt{2}-1\) vào hàm số ta được :
\(\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)\left(2m-1\right)+m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{6+5\sqrt{2}}{7}\)
Vậy ...

3: Ta có: A=B|x-4|
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-5}:\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-5}=\left|x-4\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-4\right|=\sqrt{x}-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=\sqrt{x}-2\left(x\ge4;x\ne25\right)\\x-4=2-\sqrt{x}\left(0< x< 4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{x}-2=0\\x+\sqrt{x}-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\left(nhận\right)\\x=4\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
1: Thay x=9 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{3-2}{3-5}=\dfrac{-1}{-2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2: Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+5}+\dfrac{20-2\sqrt{x}}{x-25}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}-15+20-2\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+5\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-5}\)


Đặt \(a=\dfrac{x}{2};b=\dfrac{y}{2};c=\dfrac{z}{2}\). Khi đó \(xyz=1\).
Bất đẳng thức cần chứng minh trở thành:
\(\sum\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{8x^3+1}}\ge1\)
Ta có: \(\sum\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{8x^3+1}}=\sum\sqrt{\dfrac{b^3c^3}{8+b^3c^3}}=\sum\dfrac{b^2c^2}{\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}}\ge\dfrac{\left(ab+bc+ca\right)^2}{\sum\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}}=\dfrac{\sum b^2c^2+2\sum a}{\sum\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}}\ge\dfrac{\sum b^2c^2+6}{\sum\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}}\)
Phép chứng minh sẽ hoàn tất nếu ta chứng minh được:
\(\sum b^2c^2+6\ge\sum\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}\left(\cdot\right)\)
Để ý rằng, nếu ta chứng minh được \(b^2c^2+2\ge\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}\left(1\right)\) thì ta sẽ chứng minh được (*).
Thật vậy, bằng phép biến đổi tương đương, ta có:
\(b^2c^2+2\ge\sqrt{8bc+b^4c^4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b^4c^4+4b^2c^2+4\ge8bc+b^4c^4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(bc-1\right)^2\ge0\) (luôn đúng).
Vậy nhận xét (1) là đúng. Từ đây ta có điều phải chứng minh.
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(a=b=c=2\)
Đặt \(A=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a^3+1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{b^3+1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{c^3+1}}\)
\(\sqrt{a^3+1}=\sqrt{\left(a+1\right)\left(a^2-a+1\right)}\)
=>\(\sqrt{a^3+1}< =\dfrac{a+1+a^2-a+1}{2}=\dfrac{a^2+2}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a^3+1}}>=\dfrac{2}{a^2+2}\)
Chứng minh tương tự, ta được:
\(\sqrt{b^3+1}< =\dfrac{b^2+2}{2}\) và \(\sqrt{c^3+1}< =\dfrac{c^2+2}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{b^3+1}}>=\dfrac{2}{b^2+2};\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{c^3+1}}>=\dfrac{2}{c^2+2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{a^3+1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{b^3+1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{c^3+1}}>=\dfrac{2}{a^2+2}+\dfrac{2}{b^2+2}+\dfrac{2}{c^2+2}\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2}{a^2+2}+\dfrac{2}{b^2+2}+\dfrac{2}{c^2+2}\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2\left(b^2+2\right)\left(c^2+2\right)+2\left(a^2+2\right)\left(c^2+2\right)+2\left(b^2+2\right)\left(a^2+2\right)}{\left(a^2+2\right)\left(c^2+2\right)\left(b^2+2\right)}\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2\left(b^2c^2+2c^2+2b^2+4+a^2c^2+2a^2+2c^2+4+a^2b^2+2b^2+2a^2+4\right)}{\left(a^2+2\right)\left(b^2+2\right)\left(c^2+2\right)}\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2\left(a^2b^2+b^2c^2+c^2a^2\right)+8\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+24}{\left(a^2+2\right)\left(b^2+2\right)\left(c^2+2\right)}\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2\left(a^2b^2+b^2c^2+a^2c^2\right)+4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+24+4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)}{2\left(a^2b^2+b^2c^2+a^2c^2\right)+4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+8+8^2}\)(Vì abc=8)
Ta lại có: \(a^2+b^2+c^2>=3\sqrt[3]{a^2b^2c^2}=3\cdot\sqrt[3]{8^2}=12\)
=>\(4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)>=48\)
=>\(A>=\dfrac{2\left(a^2b^2+b^2c^2+a^2c^2\right)+4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+24+48}{2\left(a^2b^2+b^2c^2+a^2c^2\right)+4\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)+8+64}\)
=>A>=1(ĐPCM)