
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



\(B=\sqrt{14+2\sqrt{10}+2\sqrt{14}+2\sqrt{35}}\)
\(=\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{7}\)

\(\left(m-1\right)x^2-2mx+m-4=0\)
Theo Vi - ét , ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{2m}{m-1}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{m-4}{m-1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(A=3\left(x_1+x_2\right)+2x_1x_2-8\)
\(=3\left(\dfrac{2m}{m-1}\right)+2\left(\dfrac{m-4}{m-1}\right)-8\)
\(=\dfrac{6m}{m-1}+\dfrac{2m-8}{m-1}-8\)
\(=\dfrac{6m+2m-8}{m-1}-8\)
\(=\dfrac{8m-8}{m-1}-8\)
\(=\dfrac{8\left(m-1\right)}{m-1}-8\)
\(=8-8\)
\(=0\)
Vậy biểu thức A không phụ thuộc giá trị m

Câu 2:
a: Xét ΔCKE và ΔCDH có
\(\widehat{CEK}=\widehat{CHD}\)
\(\widehat{C}\) chung
Do đó: ΔCKE\(\sim\)ΔCDH
Suy ra: CK/CD=CE/CH
hay \(CK\cdot CH=CD\cdot CE\)
b: Xét ΔIAD và ΔICB có
\(\widehat{IAD}=\widehat{ICB}\)
\(\widehat{AID}=\widehat{CIB}\)
Do đó: ΔIAD\(\sim\)ΔICB
Suy ra: IA/IC=ID/IB
hay \(IA\cdot IB=IC\cdot ID\)


a) \(\sqrt{4x}+\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{49x}=6\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{7}{2}\sqrt{x}=6\Rightarrow6\sqrt{x}=6\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}=1\Rightarrow x=1\)
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{18x-9}-0,5\sqrt{2x-1}+\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{25\left(2x-1\right)}+\sqrt{49\left(2x-1\right)}=24\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{9\left(2x-1\right)}-0,5\sqrt{2x-1}+\dfrac{5}{2}\sqrt{2x-1}+7\sqrt{2x-1}=24\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{2x-1}-0,5\sqrt{2x-1}+\dfrac{5}{2}\sqrt{2x-1}+7\sqrt{2x-1}=24\)
\(\Rightarrow12\sqrt{2x-1}=24\Rightarrow\sqrt{2x-1}=2\Rightarrow2x-1=4\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
c) \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}-7=0\Rightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}=7\Rightarrow\left|x-1\right|=7\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=7\\x-1=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{49x}{x+2}}-3\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{4x+8}}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-\sqrt{5}=0\left(\dfrac{x}{x+2}\ge0,x\ne-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-3\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{4\left(x+2\right)}}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow0=\sqrt{5}\) (vô lý) \(\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
a) \(\sqrt{4x}+\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{49x}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{2}+\dfrac{7}{2}\sqrt{x}=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}\left(2+\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\6\sqrt{x}=6\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)
b) \(\sqrt{18x-9}-0.5\sqrt{2x-1}+\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{25\left(2x-1\right)}+\sqrt{49\left(2x-1\right)}=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\sqrt{2x-1}-0,5\sqrt{2x-1}+\dfrac{5}{2}\sqrt{2x-1}+7\sqrt{2x-1}=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1\ge0\\\sqrt{2x-1}\left(3-0.5+\dfrac{5}{2}+7\right)=49\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\12\sqrt{2x-1}=24\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\\sqrt{2x-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\2x-1=4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)
c) \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}-7=0\) (*)
Ta có \(x^2-2x+1=\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) \(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-2x+1}\ge0\forall x\)
(*) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{8\right\}\)
\(\)d) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{49x}{x+2}}-3\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{4x+8}}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-\sqrt{5}=0\) (**)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-\dfrac{3}{2}\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}=\sqrt{5}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\dfrac{x}{x+2}\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x+2>0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\x+2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x>-2\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)
(**) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}\left(\dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{3}{2}-2\right)=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0\sqrt{\dfrac{x}{x+2}}=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0=\sqrt{5}\) ( vô lý )
Vậy phương trình trên vô nghiệm

a) nhân ra thôi b
\(=\frac{\left(2\sqrt{10}-5\right)\left(9+\sqrt{10}\right)}{71}=\frac{18\sqrt{10}-45+20-5\sqrt{10}}{71}=\frac{-25+13\sqrt{10}}{71}.\)
b)cách khác nhé !\(\frac{9-2\sqrt{3}}{3\sqrt{6}-2\sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}\left(3\sqrt{3}-2\right)}{\sqrt{2}\left(3\sqrt{3}-2\right)}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{6}}{2}.\)

\(\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}+\sqrt{x^2+5}=9-2x\left(đk:x\le\dfrac{9}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+4+x^2+5+2\sqrt{\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\left(x^2+5\right)}=81-36x+4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\left(x^2+5\right)}=2x^2-34x+72\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\left(x^2+5\right)=4x^4+1156x^2+5184-136x^3+288x^2-4896x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^4-8x^3+36x^2-40x+80=4x^4-136x^3+1444x^2-4896x+5184\)
\(\Leftrightarrow128x^3-1408x^2+4856x-5104=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow128x^2\left(x-2\right)-1152x\left(x-2\right)+2552\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(128x^2-1152x+2552\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)(do \(128x^2-1152x+2552>0\))

1.2 với \(x\ge0,x\in Z\)
A=\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+7}{\sqrt{x}+2}=2+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\in Z< =>\sqrt{x}+2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left(\pm1;\pm3\right)\)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=1=>\sqrt{x}=-1\)(vô lí)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-1=>\sqrt{x}=-3\)(vô lí
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=3=>x=1\)(TM)
*\(\sqrt{x}+2=-3=\sqrt{x}=-5\)(vô lí)
vậy x=1 thì A\(\in Z\)
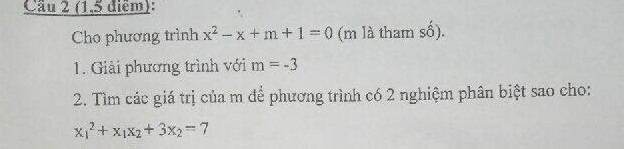





Lời giải:
1. Với $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow $x=2$ hoặc $x=-1$
2.
Để pt có 2 nghiệm pb thì $\Delta=1-4(m+1)>0$
$\Leftrightarrow m< \frac{-3}{4}$
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet:
$x_1+x_2=1$
$x_1x_2=m+1$
Khi đó:
$x_1^2+x_1x_2+3x_2=7$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1(x_1+x_2)+3x_2=7$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1+3x_2=7$
Kết hợp với $x_1+x_2=1$ thì $x_1=-2; x_2=3$
$m+1=x_1x_2=(-2).3=-6$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-7$ (tm)