Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 2:
Ta có: \(3n^3+10n^2-5⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n^3+n^2+9n^2+3n-3n-1-4⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n\in\left\{0;-3;3\right\}\)
hay \(n\in\left\{0;-1;1\right\}\)

MK..........................................................................................ngu hóa


a)
\(=\frac{8^3}{\left(-8\right)^{-5}}=\frac{8^3}{-\frac{1}{8^5}}=8^3.-\left(8\right)^5=-8^8\)
b)
\(=\frac{15x^2y^2}{5xy^2}=3x\)

a) \(\left(x+2\right)^3-x^2.\left(x+6\right)\)
\(=x^3+6x^2+12x+8-x^3-6x^2\)
\(=12x+8\)
b) \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+1\right)^3-2x.\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(=x^2-4-x^3-3x^2-3x-1-2x^3+4x^2-2x\)
\(=-3x^3+2x^2-5x-5\)

Bài 1:
a) (2x+5)(x-6)=2x2+5x-12x-30=2x2-7x-30
b) (2x-1)(x2-4x+3)=2x3-8x2+6x-x2+4x-3=2x3-9x2+10x-3
c) x2-2x-(x-7)(x+2)=x2-2x-x2+7x-2x+14=3x+14
d) 3x-(x+2)(x+4)=3x-x2-2x-4x-8=-x2-3x-8
Bài 2:
a) 2(x+1)=x-1
⇒2x+2=x-1
⇒2x+2-x+1=0
⇒x+3=0
⇒x=-3
b) x(x+2)-x2=1
⇒x2+2x-x2=1
⇒2x=1
⇒x=0,5
c) 3x(x-2)=(3x-1)(x-1)-5
⇒3x2-6x=3x2-x-3x+1-5
⇒3x2-6x-3x2+x+3x-1+5=0
⇒-2x+4=0
⇒-2x=-4
⇒x=2
d) 6(x-1)(x-2)-6x(x+3)=2x
⇒6(x2-x-2x+2)-6x2-18x-2x=0
⇒6x2-6x-12x+12-6x2-18x-2x=0
⇒-38x+12=0
⇒-38x=-12
⇒x=\(\dfrac{6}{19}\)

a) Phương trình phản ứng hóa học :
S + O2 →→ SO2
b) Số mol lưu huỳnh tham gia phản ứng :
nS=3,232=0,1(mol)nS=3,232=0,1(mol)
Theo phương trình, ta có : nSO2 = nS = nO2 = 0,1 mol
=> Thể tích khí sunfurơ sinh ra ở đktc là :
VO2 = 22,4.0,1 = 2,24 (l)
Tương tự thể tích khí oxi cần dùng ở đktc là :
VO2 = 22,4.0,1 = 2,24 (l)
Vì khí oxi chiếm 20% về thể tích của không khí nên thể tích không khí cần dùng là :
Vkk = 5.VO2 = 5.2,24 = 11,2 (l)

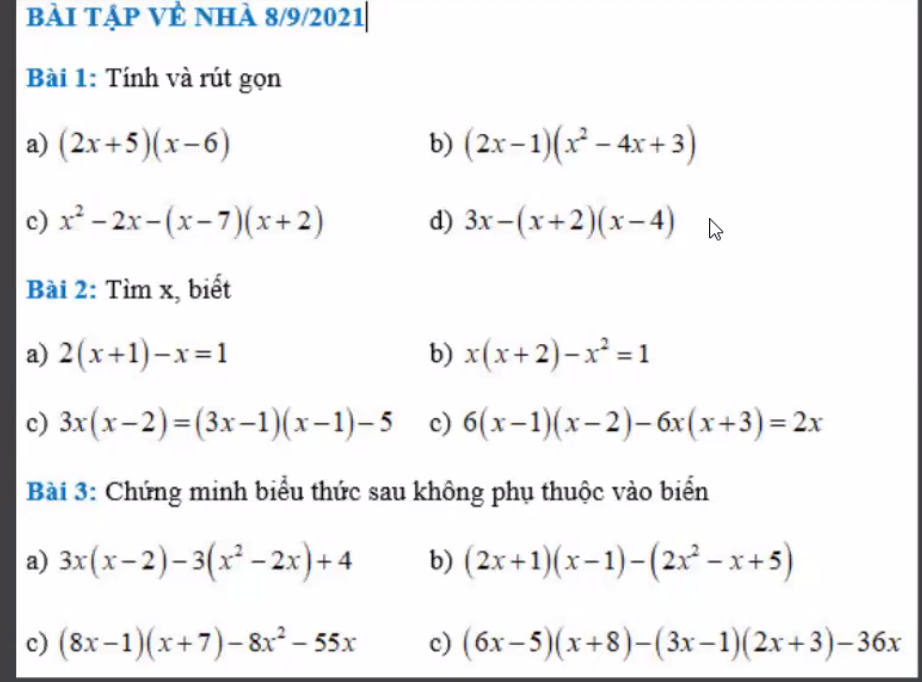
1: \(\Leftrightarrow x-2-7x+7=-1\)
=>-6x+5=-1
hay x=1(loại)
3: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x+3\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2-x^2-4x-3=4\)
=>-3x=9
hay x=-3(loại)
4: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1=3x\cdot\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=\dfrac{6x}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+4x-6x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-2x=0\)
=>2x(2x-1)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{0;\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)