
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left|x+\frac{1}{x}\right|=3x-1\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{1}{x}=3x-1\\-x-\frac{1}{x}=3x-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{1}{x}-3x+1=0\\-x-\frac{1}{x}-3x+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}-2x+\frac{1}{x}+1=0\\-4x-\frac{1}{x}+1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}-2x^2+1+x=0\\-4x^2-1+x=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-\frac{1}{2};x=1\\x=\frac{1-\sqrt{15t}}{8}\end{cases}}\)
| x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)| = 3x - 1
\(\Rightarrow\)x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)= \(\pm\)( 3x - 1 )
TH1 : x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)= 3x - 1
\(\Rightarrow\)2x = \(\frac{4}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
TH2 : x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)= - 3x + 1
\(\Rightarrow\)4x = \(\frac{2}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)x = \(\frac{1}{6}\)

\(a,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AC=AD\\\widehat{ACE}=\widehat{DCE}\left(CE.là.p/g\right)\\CE.chung\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\Delta ACE=\Delta DCE\left(c.g.c\right)\\ \Rightarrow AE=ED\\ b,\Delta ACE=\Delta DCE\Rightarrow\widehat{BAC}=\widehat{CED}=90^0\\ \Rightarrow BC\perp DE\\ \Rightarrow\widehat{BED}+\widehat{B}=90^0\)
Mà \(\widehat{ACB}+\widehat{B}=90^0\left(\Delta ABC\perp A\right)\)
Vậy \(\widehat{BED}=\widehat{ACB}\)
\(c,\) Gọi giao của phân giác \(\widehat{BED}\) và BC là F
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{FED}=\dfrac{1}{2}\widehat{BED}\)
Lại có \(\Delta ACE=\Delta DCE\Rightarrow\widehat{AEC}=\widehat{CED}\)
Mà \(\widehat{AEC}+\widehat{CED}=\widehat{AED}\Rightarrow\widehat{CED}=\dfrac{1}{2}\widehat{AED}\)
Ta có \(\widehat{CEF}=\widehat{CED}+\widehat{FED}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\widehat{AED}+\widehat{DEB}\right)\)
Mà \(\widehat{AED}+\widehat{DEB}=180^0\)
Do đó \(\widehat{CEF}=90^0\Rightarrow CE\perp EF\)
Suy ra cái đề

XIN LỖI MK K BT VẼ HÌNH TRÊN NÀY : |_ là vuông góc nhé bạn
Vì AB |_ CD tại O
=>AOD=AOC=DOB=BOC=90 độ
Mà OM là tia pg của góc BOC
=>COM =BOM=45 độ
Ta có góc AOM = AOC +COM
=>GÓC AOM= 90 độ +45 độ=135 độ
mk nhé!

a) Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=2x^2\left(x-1\right)-5\left(x+2\right)-2x\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=2x^3-2x^2-5x-10-2x^2+4x\)
\(=2x^3-4x^2-x-10\)
Bậc là 3
Ta có: \(g\left(x\right)=x^2\left(2x-3\right)-x\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\)
\(=2x^3-3x^2-x^2-x-3x+2\)
\(=2x^3-4x^2-4x+2\)
b) Ta có: h(x)=f(x)-g(x)
\(=2x^3-4x^2-x-10-2x^3+4x^2+4x-2\)
\(=3x-12\)
Đặt h(x)=0
nên 3x-12=0
hay x=4


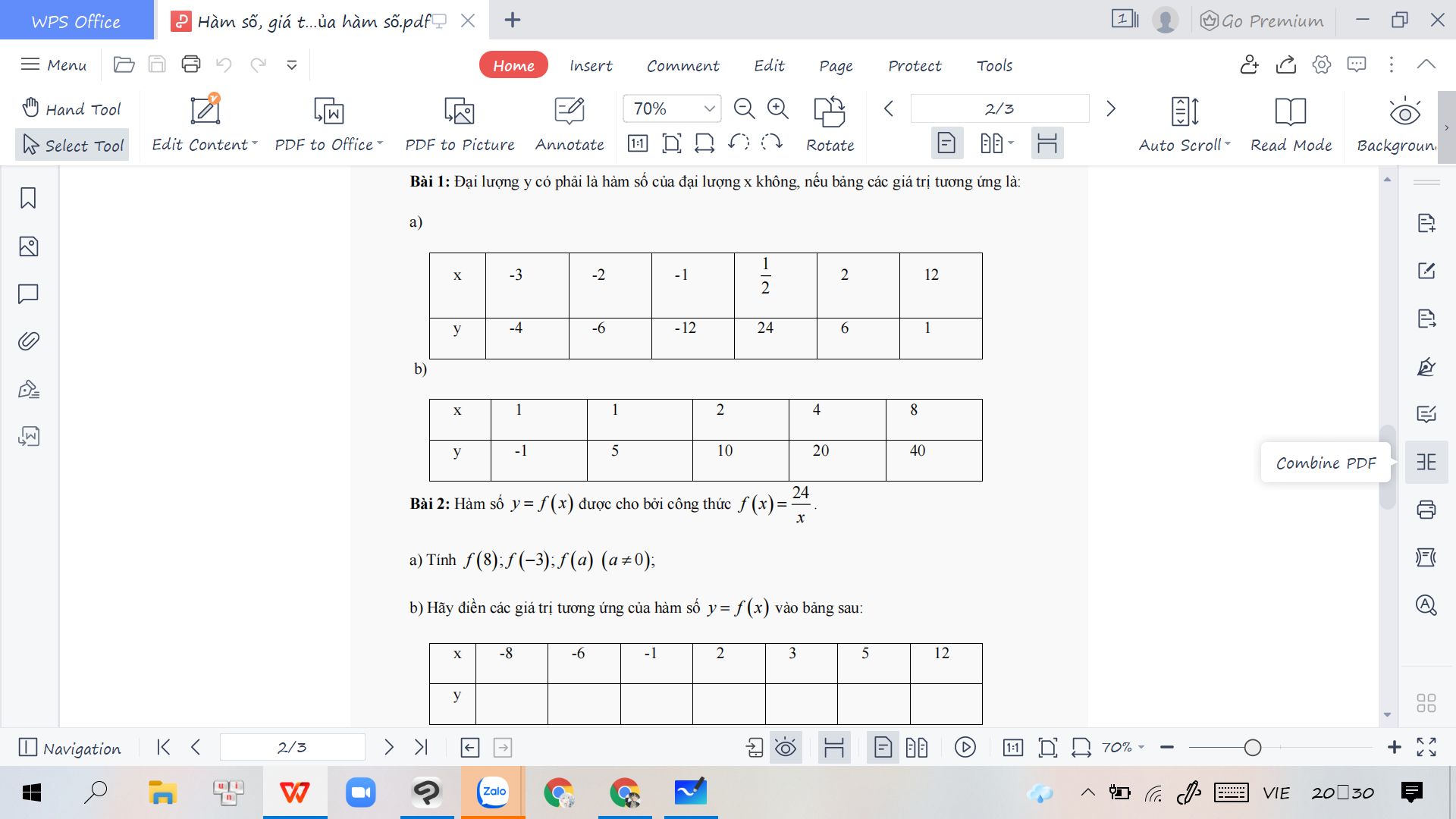


 CÁC BẠN GIÚP MÌNH VỚI 😥🥺
CÁC BẠN GIÚP MÌNH VỚI 😥🥺
Bài gì đâu bạn?
bài đâu