
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Mình nghĩ là không tồn tại , số chính phương hay ta có thể gọi nó là lũy thừa căn bậc 2 của 1 số , mà đây ta có các chữ số đều giống nhau , không thể thực hiên .
Các chữ số giống nhau nên nếu a có tồn tại thì a sẽ là các chữ số từ 1 - 9 ( a không thể là 0 )
mà các số đều dư khi sử dụng căn bậc \(\sqrt{ }\)
nên không có bất cứ số a nào thỏa mãn đề bài

2x-3 lướn hơn hoặc bằng 0
=>2x lớn hơn hoặc bằng 3
=>x lớn hơn hoặc bằng 3/2
mình nha!!!
\(\sqrt{2x-3}=0\Leftrightarrow2x-3=0\Rightarrow2x=3\Rightarrow x=1,5\)

a: \(P=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-9-x+9}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x+2\sqrt{x}+2x-4\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
b: Để P<1 thì P-1<0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}-3}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-3< 0\)
hay x<9
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: 0<=x<9 và x<>4
c: Để P<1 thì 0<=x<9 và x<>4
mà x là số nguyên
nên \(x\in\left\{0;1;2;3;5;6;7;8\right\}\)

2:
1+cot^2a=1/sin^2a
=>1/sin^2a=1681/81
=>sin^2a=81/1681
=>sin a=9/41
=>cosa=40/41
tan a=1:40/9=9/40

P = ( x + 9 + 6cănx - 6cănx - 18 + 25 ) / (cănx + 3)
áp dụng bđt Côsi suy ra min P = 4 khi x = 4

\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
Biểu thức \(A\) có nghĩa khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}+1\ne0;\text{ }x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}-1\ne0\end{cases}}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
Ta có:
\(A=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}-1}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)-2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)-2\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(A=\frac{x+\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}+2-2\sqrt{x}-2}{x-1}=\frac{x-3\sqrt{x}}{x-1}\)
Vậy, \(A=\frac{x-3\sqrt{x}}{x-1}\)
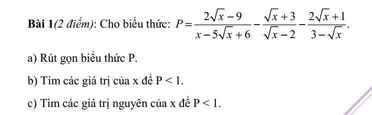
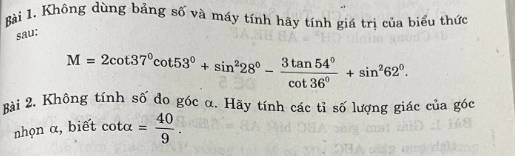
\(48,\sqrt{23+2.2\sqrt{5}\sqrt{3}}\)
\(\sqrt{20+2.2\sqrt{5}\sqrt{3}+3}\)
\(\sqrt{\left(2\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3}\right)^2}\)
\(\left|2\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3}\right|=2\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3}\)
\(50,\sqrt{14-6\sqrt{5}}\)
\(\sqrt{3^2-6\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{5}^2}\)
\(\sqrt{\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)^2}\)
\(3>\sqrt{5}< =>\left|3-\sqrt{5}\right|=3-\sqrt{5}\)
\(\)