
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


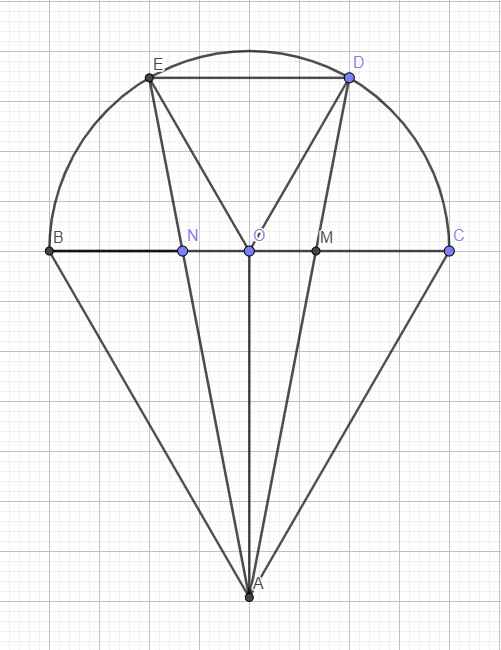
Gọi O là tâm đường tròn \(\Rightarrow\) O là trung điểm BC
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{ED}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow\widehat{BOE}=\widehat{EOD}=\widehat{DOC}=\dfrac{180^0}{3}=60^0\)
Mà \(OD=OE=R\Rightarrow\Delta ODE\) đều
\(\Rightarrow ED=R\)
\(BN=NM=MC=\dfrac{2R}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{NM}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\stackrel\frown{BE}=\stackrel\frown{DC}\Rightarrow ED||BC\)
Áp dụng định lý talet:
\(\dfrac{AN}{AE}=\dfrac{MN}{ED}=\dfrac{2}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{OB-BN}{BN}=\dfrac{R-\dfrac{2R}{3}}{\dfrac{2R}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{EN}{AN}=\dfrac{ON}{BN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) và \(\widehat{ENO}=\widehat{ANB}\) (đối đỉnh)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ENO\sim ANB\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{NBA}=\widehat{NOE}=60^0\)
Hoàn toàn tương tự, ta có \(\Delta MDO\sim\Delta MAC\Rightarrow\widehat{MCA}=\widehat{MOD}=60^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta ABC\) đều



Bài 1:
Kẻ \(OM\perp AB\), \(OM\)cắt \(CD\)tại \(N\).
Khi đó \(MN=8cm\).
TH1: \(AB,CD\)nằm cùng phía đối với \(O\).
\(R^2=OC^2=ON^2+CN^2=h^2+\left(\frac{25}{2}\right)^2\)(\(h=CN\)) (1)
\(R^2=OA^2=OM^2+AM^2=\left(h+8\right)^2+\left(\frac{15}{2}\right)^2\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(R=\frac{\sqrt{2581}}{4},h=\frac{9}{4}\).
TH2: \(AB,CD\)nằm khác phía với \(O\).
\(R^2=OC^2=ON^2+CN^2=h^2+\left(\frac{25}{2}\right)^2\)(\(h=CN\)) (3)
\(R^2=OA^2=OM^2+AM^2=\left(8-h\right)^2+\left(\frac{15}{2}\right)^2\)(4)
Từ (3) và (4) suy ra \(R=\frac{\sqrt{2581}}{4},h=\frac{-9}{4}\)(loại).
Bài 3:
Lấy \(A'\)đối xứng với \(A\)qua \(Ox\), khi đó \(A'\)có tọa độ là \(\left(1,-2\right)\).
\(MA+MB=MA'+MB\ge A'B\)
Dấu \(=\)xảy ra khi \(M\)là giao điểm của \(A'B\)với trục \(Ox\).
Suy ra \(M\left(\frac{5}{3},0\right)\).


1.3 Giải phương trình:
a) \(\sqrt{2x+3}=1+\sqrt{2}\)(ĐK: \(x\ge-\frac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=\left(1+\sqrt{2}\right)^2=3+2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\)(tm)
b) \(\sqrt{x+1}=\sqrt{5}+3\)(ĐK: \(x\ge-1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=\left(\sqrt{5}+3\right)^2=14+6\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=13+6\sqrt{5}\)(tm)
c) \(\sqrt{3x-2}=2-\sqrt{3}\)(ĐK: \(x\ge\frac{2}{3}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2=\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)^2=7-4\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{9-4\sqrt{3}}{3}\)(tm)
1.4: Phân tích thành nhân tử:
a) \(ab+b\sqrt{a}+\sqrt{a}+1=b\sqrt{a}\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)+\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)=\left(b\sqrt{a}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{a}+1\right)\)
b) \(\sqrt{x^3}-\sqrt{y^3}+\sqrt{x^2y}-\sqrt{xy^2}=x\sqrt{x}-y\sqrt{y}+x\sqrt{y}-y\sqrt{x}\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}\right)\)


Áp dụng BĐT \(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\ge\dfrac{4}{x+y}\)(Tự chứng minh BĐT này )
\(B\ge\dfrac{4}{\left(a+b\right)^2+1}\)
![]() cảm ơn Định đã trả lời giúp mk . Nhưng bn làm sai rồi vì nếu làm như vậy sẽ ko tìm ra a, b
cảm ơn Định đã trả lời giúp mk . Nhưng bn làm sai rồi vì nếu làm như vậy sẽ ko tìm ra a, b

Gọi số ngày hoàn thành công việc nếu làm riêng của người thứ nhất là x, người thứ 2 là y(ngày),(x,y>0)
1 ngày người thứ nhất làm được:\(\frac{1}{x}\)
1 ngày người thứ hai làm được:\(\frac{1}{y}\)
=> 1 ngày cả người làm được:\(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{12}\)(1)
3 ngày người thứ nhất làm được:\(\frac{3}{x}\)
Vì sau 3 ngày, người thứ 2 làm nốt 15 ngày nên: Số ngày người thứ 2 làm là 15+3=18
18 ngày người thứ hai làm được \(\frac{18}{x}\)
Do đó, ta được:\(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{18}{y}=1\)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) , ta có hệ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{12}\\\frac{3}{x}+\frac{18}{y}=1\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(\frac{1}{x}\)= a, \(\frac{1}{y}\)= b, ta được
\(\hept{\begin{cases}a+b=\frac{1}{12}\\3a+18b=1\end{cases}}\)<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}a=\frac{1}{30}\\b=\frac{1}{20}\end{cases}}\)<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=30\\y=20\end{cases}}\). Vậy......










Để hệ pt có nghiệm duy nhât \(\dfrac{a+1}{1}\ne\dfrac{-1}{a-1}\Leftrightarrow a^2-1\ne-1\Leftrightarrow a^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow a\ne0\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(a^2-1\right)x-\left(a-1\right)y=a^2-1\\x+\left(a-1\right)y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a^2x=a^2+1\\y=\dfrac{2-x}{a-1}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{a^2+1}{a^2}\\y=\dfrac{2-\dfrac{a^2+1}{a^2}}{a-1}=\dfrac{\dfrac{a^2-1}{a^2}}{a-1}=\dfrac{\left(a^2-1\right)\left(a-1\right)}{a^2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(\dfrac{a^2+1}{a^2}-\dfrac{\left(a^2-1\right)\left(a-1\right)}{a^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+1-a^3+a^2+a-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-a^3+2a^2+a=0\Leftrightarrow a^2-2a-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)^2-2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(a-1+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow a=1\pm\sqrt{2}\)