
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a: Xét tứ giác DIHK có
góc DIH=góc DKH=góc KDI=90 độ
nên DIHK là hình chữ nhật
b: Xét tứ giác IHAK có
IH//AK
IH=AK
Do đó: IHAK là hình bình hành
=>B là trung điểm chung của IA và HK
Xét ΔIKA có IC/IK=IB/IA
nên BC//KA
Xét ΔIDA có IB/IA=IM/ID
nên BM//DA
=>B,C,M thẳng hàng

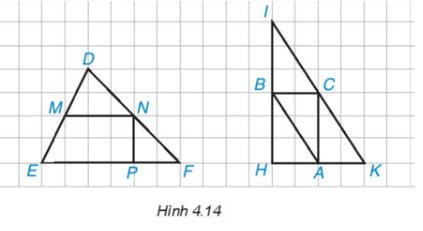
Đường trung bình trong tam giác DEF là: cạnh MN.
Đường trung bình trong tam giác HIK là: cạnh BC, CA, AB.
Quan sát Hình 4.14, ta thấy:
* Xét ∆DEF có M là trung điểm của cạnh DE; N là trung điểm của cạnh DF nên MN là đường trung bình của ∆DEF.
* Xét ∆IHK có:
• B là trung điểm của cạnh IH; C là trung điểm của cạnh IK nên BC là đường trung bình của ∆DEF.
• B là trung điểm của cạnh IH; A là trung điểm của cạnh HK nên AB là đường trung bình của ∆DEF.
• A là trung điểm của cạnh HK; C là trung điểm của cạnh IK nên AC là đường trung bình của ∆DEF.
Vậy đường trung bình của ∆DEF là MN; các đường trung bình của ∆IHK là AB, BC, AC.

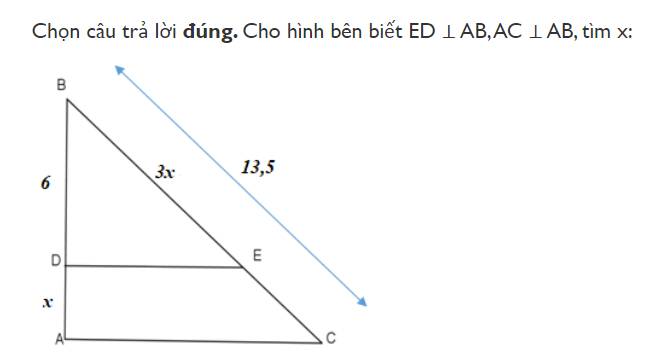
Ta có: DE//AC (cùng vuông góc với AB)
Áp dụng định lý Ta-lét ta có:
\(\dfrac{BD}{AD}=\dfrac{BE}{CE}\Rightarrow\dfrac{BD}{AD}=\dfrac{BE}{BC-BE}\Rightarrow\dfrac{6}{x}=\dfrac{3x}{13,5-3x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6\left(13,5-3x\right)=x\cdot3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow81-18x=3x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow27-6x=x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+6x-27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+9x-27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+9\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(tm\right)\\x=-9\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: `x=3`

a) Xét tứ giác ABCD ta có:
\(\widehat{A}+\widehat{B}+\widehat{C}+\widehat{D}=360^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{D}=360^o-102^o-102^o-102^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{D}=54^o\)
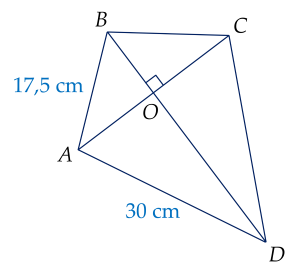
b) Xét tam giác vuông AOD ta có:
\(AD^2=OD^2+OA^2\)
\(\Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{AD^2-OD^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow OA=\sqrt{30^2-26,7^2}\approx13,7\left(cm\right)\)
Xét tam giác vuông AOB ta có:
\(AB^2=OA^2+OB^2\)
\(\Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{AB^2-OA^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow OB=\sqrt{17,5^2-13,7^2}\approx10,9\left(cm\right)\)
Độ dài đường chéo BD là:
\(BD=OB+OD=26,7+10,9\approx37,6\left(cm\right)\)
a) Số đo góc \(D\) ở đuôi chiếc diều là: \(\hat{D} = 36 0^{\circ} - \left(\right. \hat{A} + \hat{B} + \hat{C} \left.\right) = 36 0^{\circ} - \left(\right. 10 2^{\circ} + 10 2^{\circ} + 10 2^{\circ} \&\text{nbsp}; \left.\right) = 5 4^{\circ} .\)
b) Xét \(\Delta O A D\) vuông tại \(O\), theo định lí Pythagore ta có:
\(O A^{2} = A D^{2} - O D^{2} = 30^{2} - 26 , 7^{2} = 187 , 11\)
Xét \(\Delta O A B\) vuông tại \(O ,\) theo định lí Pythagore ta có:
\(O B^{2} = A B^{2} - O A^{2} = 17 , 5^{2} - 187 , 11 = 119 , 14\)
Do đó \(O B = \sqrt{119 , 14} \approx 10 , 9\) (cm).
Suy ra \(B D = O B + O D = 10 , 9 + 26 , 7 = 37 , 6\) (cm).

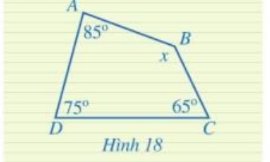
Xét tứ giác ABCD có:
\(\begin{array}{l} \widehat A + \widehat B + \widehat C + \widehat D = {360^0}\\{85^0} + x + {65^0} + {75^0} = {360^0}\\x = {360^0} - {85^0} - {65^0} - {75^0} = {135^0}\end{array}\)

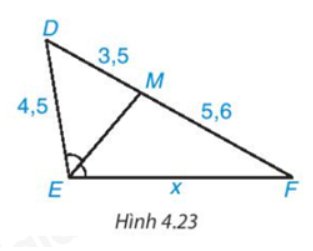
Trong Hình 4.23 có \(\widehat {DME} = \widehat {MEF}\) nên EM là tia phân giác của \(\widehat {{\rm{DEF}}}\).
Áp dụng tính chất đường phân giác của tam giác, ta có:
\(\dfrac{{E{\rm{D}}}}{{EF}} = \dfrac{{M{\rm{D}}}}{{MF}}\) hay \(\dfrac{{4,5}}{x} = \dfrac{{3,5}}{{5,6}}\)
Suy ra: \(x = \dfrac{{5,6.4,5}}{{3,5}} = 7,2\)(đvđd)
Vậy x = 7,2 (đvđd).






 Trả lời lẹ giúp em đi ạ
Trả lời lẹ giúp em đi ạ
a: MNPQ là hình bình hành
=>MQ//NP
=>MQ//IP
Xét tứ giác MIPQ có IP//MQ
nên MIPQ là hình thang
b: ΔMNP vuông cân tại N
=>MN=NP và \(\widehat{MNP}=90^0\)
Hình bình hành MNPQ có \(\widehat{MNP}=90^0\)
nên MNPQ là hình chữ nhật
=>\(\widehat{Q}=\widehat{P}=90^0\)
Xét ΔMNI vuông tại N có \(sinNMI=\dfrac{NI}{MN}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
nên \(\widehat{NMI}\simeq42^0\)
\(\widehat{NMI}+\widehat{QMI}=\widehat{NMQ}=90^0\)
=>\(\widehat{QMI}+42^0=90^0\)
=>\(\widehat{QMI}=48^0\)
IP//MQ
=>\(\widehat{QMI}+\widehat{MIP}=180^0\)(hai góc trong cùng phía)
=>\(\widehat{MIP}+48^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{MIP}=132^0\)