
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b, \(\left(4x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+2=0\) (Vì \(x^2+1>0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(x=\frac{-1}{2}.\)
c, \(\left(x^2-4\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(5-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\5-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{2;5\right\}\).
d, \(3x^2+2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+3x-x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-1;\frac{1}{3}\right\}\).

1/ \(3x^2-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\frac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy .....................
2/ \(4x^2-4x+\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Delta=b'^2-ac=2^2-\frac{4.1}{2}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{4}\\x_2=\frac{2-\sqrt{2}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ........................
3/ \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+5x-2\right)-\left(x^3-1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+5x-2\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1\right)\left(4x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\frac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ......................
a) Ta có: \(3x^2+2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\3x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\frac{-2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(x\in\left\{0;\frac{-2}{3}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(4x^2-4x+\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2-\frac{1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}\\2x-1=-\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}+1\\2x=-\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}+1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{2+\sqrt{2}}{4}\\x=\frac{2-\sqrt{2}}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(x=\frac{2\pm\sqrt{2}}{4}\)

a)(x2-2x+1)-4=0
⇔(x-1)2-4=0
⇔(x-1-2)(x-1+2)=0
⇔(x-3)(x+1)=0
⇔x-3=0 hoặc x+1=0
1.x-3=0⇔x=3
2.x+1=0⇔x=-1
vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm:x=3 và x=-1

1/ \(3x^2+2x-1=0\)
Nhận thấy: a-b+c=1 nên pt có nghiệm \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy .............
2/ \(3x^2+4x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(3x-2\right)+2\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(3x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=\frac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ....................
3/ \(x^2+\left(x+2\right)\left(11x-7\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2+11x^2+15x-14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2+15x-14=0\)
\(\Delta=15^2-4.12.\left(-14\right)=897\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{-15+\sqrt{897}}{24}\\x=\frac{-15-\sqrt{897}}{24}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ................
3x^2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> 2x^2 + 2x + x^2 - 1 = 0
=> 2x. (x + 1) + (x + 1).(x - 1) = 0
=> ( x+1). ( 3x - 1) = 0
TH1: x+1=0 => x = - 1
TH2: 3x - 1 =0 => x =1/3
Vậy.....

\(\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)^2\\\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x-1\right)^2\\\Leftrightarrow \left(x+1\right)^2-4\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left(x+1\right)^2-\left(2x-2\right)^2=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left[\left(x+1\right)+\left(2x-2\right)\right]\left[\left(x+1\right)-\left(2x-2\right)\right] =0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1+2x-2\right)\left(x+1-2x+2\right)=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left(3x-1\right)\left(3-x\right)=0\\\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=0\\3-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{1}{3}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right. \)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{\frac{1}{3};3\right\}\)
\(\left(2x+7\right)^2=9\left(x+2\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+7\right)^2-9\left(x+2\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+7\right)^2-\left(3x+6\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(2x+7\right)+\left(3x+6\right)\right]\left[\left(2x+7\right)-\left(3x+6\right)\right]=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+7+3x+6\right)\left(2x+7-3x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(5x+13\right)\left(1-x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x+13=0\\1-x=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{-13}{5}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{\frac{-13}{5};1\right\}\)
\(4\left(2x+7\right)^2=9\left(x+3\right)^2\\\Leftrightarrow 4\left(2x+7\right)^2-9\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(4x+14\right)^2-\left(3x+9\right)^2=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left[\left(4x+14\right)+\left(3x+9\right)\right]\left[\left(4x+14\right)-\left(3x+9\right)\right]=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left(4x+14+3x+9\right)\left(4x+14-3x-9\right)=0\\\Leftrightarrow \left(7x+23\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\\\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}7x+23=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{-23}{7}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right. \)
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{\frac{-23}{7};-5\right\}\)

a, ĐKXĐ : \(x^2+1\ne0\) ( luôn đúng với mọi x )
Ta có : \(\frac{4x-8+\left(4-2x\right)}{x^2+1}=0\)
=> \(4x-8+4-2x=0\)
=> \(2x-4=0\)
=> \(x=2\)
Vậy phương trình trên có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{2\right\}\)
b, ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne0\)
Ta có : \(\frac{x^2\left(x-3\right)}{x}=0\)
=> \(x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình trên có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{0,3\right\}\)
c, ĐKXĐ : \(x^2-x+1\ne0\) ( luôn đúng với mọi x )
Ta có : \(\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)-x-2}{x^2-x+1}=0\)
=> \(\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)-x-2=0\)
=> \(2x^2+4x-x-2-x-2=0\)
=> \(2x^2+2x-4=0\)
=> \(x^2+x-2=0\)
=> \(\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2-\frac{9}{4}=0\)
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{3}{2}\\x+\frac{1}{2}=-\frac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình trên có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{-2,1\right\}\)

(x2 + x + 1)(6 - 2x) = 0
<=> 6 - 2x = 0 (do x2 + x + 1 > 0)
<=> 2x = 6
<=> x = 3
Vậy S = {3}
(8x - 4)(x2 + 2x + 2) = 0
<=> 8x - 4 = 0 (vì x2 + 2x + 2 > 0)
<=> 8x = 4
<=> x = 1/2
Vậy S = {1/2}
x3 - 7x + 6 = 0
<=> x3 - x - 6x + 6 = 0
<=> x(x2 - 1) - 6(x - 1) = 0
<=> x(x - 1)(x + 1) - 6(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + x - 6)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + 3x - 2x - 6)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x + 3)(x - 2)(x - 1) = 0
<=> x + 3 = 0
hoặc x - 2 = 0
hoặc x - 1 = 0
<=> x = -3
hoặc x = 2
hoặc x = 1
Vậy S = {-3; 1; 2}
x5 - 5x3 + 4x = 0
<=> x(x4 - 5x2 + 4) = 0
<=> x(x4 - x2 - 4x2 + 4) = 0
<=> x[x2(x2 - 1) - 4(x2 - 1)] = 0
<=> x(x - 2)(x + 2)(x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0 hoặc x - 1 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 2 hoặc x = -2 hoặc x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Vậy S = {-2; -1; 0; 1; 2}
+ Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right).\left(6-2x\right)=0\)
- Ta lại có: \(x^2+x+1=\left(x^2+x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
- Vì \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)mà \(\left(x^2+x+1\right).\left(6-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow6-2x=0\Leftrightarrow-2x=-6\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(\left(8x-4\right).\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
- Ta lại có: \(x^2+2x+2=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+1=\left(x+1\right)^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
- Vì \(x^2+2x+2>0\forall x\)mà \(\left(8x-4\right).\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow8x-4=0\Leftrightarrow8x=4\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(x^3-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^2\right)+\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(6x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x^2+x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left[\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(3x-6\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x-2\right).\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-3;1;2\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(x^5-5x^3+4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left[\left(x^4-x^2\right)-\left(4x^2-4\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left[x^2.\left(x^2-1\right)-4.\left(x^2-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x^2-1\right).\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(TM\right)\)
hoặc \(x^2-1=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x=\pm1\left(TM\right)\)
hoặc \(x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=4\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-2;-1;0;1;2\right\}\)
!!@@# ^_^ Chúc bạn hok tốt ^_^#@@!!

\(a,2x+7\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x\ge-7\Rightarrow x\ge\dfrac{-7}{2}\)
\(b,5-2x\le0\Leftrightarrow-2x\le-5\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(c,\dfrac{x+2}{x^2+1}\ge0\Leftrightarrow x+2\ge x^2+1\Leftrightarrow x+2-x^2-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow x-x^2+1\ge0\)\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{5}{4}\ge0\Leftrightarrow-\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge-\dfrac{5}{4}\Rightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge\dfrac{5}{4}\)\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{1}{2}\ge\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}\\x-\dfrac{1}{2}\ge-\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\\x\ge-\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{4}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(d,\dfrac{x^2+3}{2-x}< 0\Leftrightarrow x^2+3< 2-x\Leftrightarrow x^2+3-2+x\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge\dfrac{-3}{4}\)( vô lí )
Vậy : BPT trên vô nghiệm

a)Ta có: \(\frac{4x-17}{2x^2+5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-17=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{17}{4}\)
Vậy: \(x=\frac{17}{4}\)
b) ĐKXĐ: x≠-2
Ta có: \(\frac{\left(x^2-2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x+2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-6x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-6\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=6\end{matrix}\right.\)(tm)
Vậy: x∈{-1;6}
c) ĐKXĐ: x≠3
Ta có: \(\frac{x^2-x-6}{x-3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(loại\right)\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: x=-2
d) ĐKXĐ: x≠-5
Ta có: \(\frac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\)
⇔\(\frac{2x-5}{x+5}-3=0\)
⇔\(\frac{2x-5}{x+5}-\frac{3\left(x+5\right)}{x+5}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5-3\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5-3x-15=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x-20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x+20\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-20\)(tm)
Vậy: x=-20
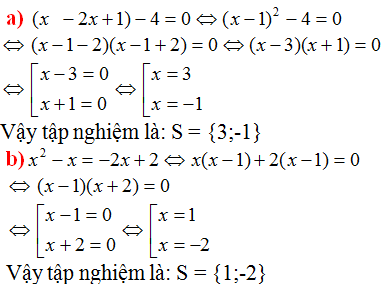
Em mới học lớp 6 thôi . Đợi hai năm nữa em giải cho !
ta co |x+1| =x+1 khi x lon hon hoac bang -1 ; |x+1|= - (x+1) khi x nho hon -1 th1 : x lon hon hoac bang 1 thi x^2+2x+2x+2-2=0 suy ra x=0 hoac x=-4 th2: x nho hon -1 thi x^2+2x-2x-2-2=0 suy ra x=2 hoac x=-2