
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


(x2 + x + 1)(6 - 2x) = 0
<=> 6 - 2x = 0 (do x2 + x + 1 > 0)
<=> 2x = 6
<=> x = 3
Vậy S = {3}
(8x - 4)(x2 + 2x + 2) = 0
<=> 8x - 4 = 0 (vì x2 + 2x + 2 > 0)
<=> 8x = 4
<=> x = 1/2
Vậy S = {1/2}
x3 - 7x + 6 = 0
<=> x3 - x - 6x + 6 = 0
<=> x(x2 - 1) - 6(x - 1) = 0
<=> x(x - 1)(x + 1) - 6(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + x - 6)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x2 + 3x - 2x - 6)(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x + 3)(x - 2)(x - 1) = 0
<=> x + 3 = 0
hoặc x - 2 = 0
hoặc x - 1 = 0
<=> x = -3
hoặc x = 2
hoặc x = 1
Vậy S = {-3; 1; 2}
x5 - 5x3 + 4x = 0
<=> x(x4 - 5x2 + 4) = 0
<=> x(x4 - x2 - 4x2 + 4) = 0
<=> x[x2(x2 - 1) - 4(x2 - 1)] = 0
<=> x(x - 2)(x + 2)(x - 1)(x + 1) = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x - 2 = 0 hoặc x + 2 = 0 hoặc x - 1 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 2 hoặc x = -2 hoặc x = 1 hoặc x = -1
Vậy S = {-2; -1; 0; 1; 2}
+ Ta có: \(\left(x^2+x+1\right).\left(6-2x\right)=0\)
- Ta lại có: \(x^2+x+1=\left(x^2+x+\frac{1}{4}\right)+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ge\frac{3}{4}>0\forall x\)
- Vì \(x^2+x+1>0\forall x\)mà \(\left(x^2+x+1\right).\left(6-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow6-2x=0\Leftrightarrow-2x=-6\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(\left(8x-4\right).\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
- Ta lại có: \(x^2+2x+2=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+1=\left(x+1\right)^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
- Vì \(x^2+2x+2>0\forall x\)mà \(\left(8x-4\right).\left(x^2+2x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow8x-4=0\Leftrightarrow8x=4\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(x^3-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3-x^2\right)+\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(6x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x^2+x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left[\left(x^2-2x\right)+\left(3x-6\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right).\left(x-2\right).\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-3;1;2\right\}\)
+ Ta có: \(x^5-5x^3+4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left[\left(x^4-x^2\right)-\left(4x^2-4\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left[x^2.\left(x^2-1\right)-4.\left(x^2-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x.\left(x^2-1\right).\left(x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(TM\right)\)
hoặc \(x^2-1=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x=\pm1\left(TM\right)\)
hoặc \(x^2-4=0\Leftrightarrow x^2=4\Leftrightarrow x=\pm2\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-2;-1;0;1;2\right\}\)
!!@@# ^_^ Chúc bạn hok tốt ^_^#@@!!

Bài làm
~ Bạn Thủy bên dưới có vẻ bị Lag mạnh, bài dễ như này mà cũng dùng denta với đen tiếc. Đéo biết làm thì đừng làm chứ đéo phải làm cái kiểu mà lớp 8 chưa học nhé bạn >.<, câu c dòng thứ hai với dòng thứ 3 không phải là thừa sao? đã vậy câu c làm sai đề nữa, bên trên là 1 - 5x. bên dưới là 1 + 5x . câu cuối cũng sai hằng đẳng thức, phải là +16x chứ hông phỉa -16x.~
a) 2x + 5 = 20 - 3x
<=> 2x + 3x = 20 + 5
<=> 5x = 25
<=> x = 5
Vậy x = 5 là nghiệm phương trình.
b) 4x2 + 5x = 0
<=> x( 4x + 5 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\4x+5=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-\frac{5}{4}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy S = { 0; -5/4 }
c) \(\left(x-2\right)^2=1-5x\)
<=> \(x^2-4x+4=1-5x\)
<=> x2 - 4x + 5x - 1 + 4 = 0
<=> x2 + x + 3 = 0
<=> \(x^2+x.2.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{11}{4}=0\)
<=> \(\left(x^2+x+\frac{1}{4}\right)=-\frac{11}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=-\frac{11}{4}\)( vô lí )
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
d) x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
<=> x2 + 2x + 3x + 6 = 0
<=> x( x + 2 ) + 3( x + 2 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 3 )( x + 2 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+3=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=-2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm phương trình S = { -3; -2 }
e) x4 - 5x2 + 4 = 0
<=> x4 - x2 - 4x2 + 4 = 0
<=> x2( x2 - 1 ) - 4( x2 - 1 ) = 0
<=> ( x2 - 1 )( x2 - 4 ) = 0
<=> ( x - 1 )( x + 1 )( x - 2 )( x + 2 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-1\end{cases}}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x+2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm phương trình S = { 1; -1; 2; -2 }
f) 5( x2 - 3x ) = ( 4x + 2 )2 + 1
<=> 5x2 - 15x = 16x2 + 16x + 4 + 1
<=> 5x2 - 16x2 - 15x - 16x - 4 - 1 = 0
<=> -11x2 - 31x - 5 = 0
<=> -( 11x2 + 31x + 5 ) = 0
Ta có:( 11x2 + 31x + 5 ) > 0 V x
=> -( 11x2 + 31x + 5 ) < 0 V x
=> -( 11x2 + 31x + 5 ) = 0 ( vô lí )
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
a, \(2x+5=20-3x\)
\(2x+5-20+3x=0\)
\(5x-15=0\Leftrightarrow5x=15\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
b, \(4x^2+5x=0\)
\(x\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(x=0\)
\(4x+5=0\Leftrightarrow4x=-5\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{5}{4}\)
c, \(\left(x-2\right)^2=1-5x\)
\(\left(x-2\right)=\pm\sqrt{1-5x}\)
\(x-2=\sqrt{1+5x}\)
\(x^2-4x+4=1+5x\)
\(x^2-4x+4-1-5x=0\)
\(x^2-9x+3=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-9\right)^2-4.3.1=81-12=69>0\)
Nên pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(x_1=\frac{9-\sqrt{69}}{2.1}=\frac{9-\sqrt{69}}{2}\)
\(x_2=\frac{9+\sqrt{69}}{2.1}=\frac{9+\sqrt{69}}{2}\)

a)<=>\(\left(x^3+x^2-2x\right)+\left(3x^2+3x-6\right)=0\)
<=>\(x\left(x^2+x-2\right)+3\left(x^2+x-2\right)=0\)
<=>\(\left(x^2+x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Phương trình trên bạn tự bấm máy tính nha
<=>\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
Đến đây tự làm đc rồi
Vậy x=1 hoặc -2 hoặc -3
b)<=>\(\left(x^3-4x^2+4x\right)+\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
<=>\(x\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
<=>\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
<=>\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
<=>\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=2\end{cases}}\)
c)Câu c mik chưa làm đc
Đáp án câu C:
\(x^3-4x^2+5x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2-4x^2+5x\right)=0\)
\(Tacó:x^2-4x+5=x^2-4x+2^2+1\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2+1\)
\(Mà\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\)
\(Nên\left(x-2\right)^2+1\ge1\)
\(Khiđó:x\left(x^2-4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)

a)(x2-2x+1)-4=0
⇔(x-1)2-4=0
⇔(x-1-2)(x-1+2)=0
⇔(x-3)(x+1)=0
⇔x-3=0 hoặc x+1=0
1.x-3=0⇔x=3
2.x+1=0⇔x=-1
vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm:x=3 và x=-1

a, \(x^4-6x^3+11x^2-6x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2-3x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pm\sqrt{5}+3}{2}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt
\(x^4-\left(6x^2-2x^2\right)+\left(9x^2-6x+1\right)=0\)
\(x^4-2x^2\left(3x-1\right)+\left(3x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\left(x^2-3x+1\right)^2=0\)
tự làm
B) \(\left(6x^4-18x^3\right)+\left(13x^{^3}-39x^2\right)+\left(x-3x\right)-\left(2x-6\right)=0\)
\(6x^3\left(x-3\right)+13x^2\left(x-3\right)+x\left(x-3\right)-2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(6x^3+13x^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(6x^3+12x^2+x^2+2x-x-2\right)\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left\{6x^2\left(x+2\right)+x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)\right\}\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(6x^2-x-1\right)\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(6x^2-3x+2x-1\right)\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(3x\left(2x-1\right)+\left(2x-1\right)\right)\)
\(\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)=0\)
câu C nghĩ đã

a) Khai triển bình phương ròii giải như bình thường
b) <=>(x+2)(x2-2x+1)=0
sau đó tiếp tục giải phương trình tích là ra
c) <=>x (2x2-5x-7)=0
<=> x=0
hoặc 2x2-5x-7=0
bn đọc tự giải^^
#hoctốt
#plsss...k☺

\(a,x^2-x-6=0\)
\(x^2-3x+2x-6=0\)
\(x\left(x-3\right)+2\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
\(b,x^2+5x+6=0\)
\(x^2+2x+3x+6=0\)
\(x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\left(x+3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-3\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)

\(x^2-5x+6=\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=0\\x-2=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)
1, <=>x^2-x-2 = x^2-4
<=>x^2-4-x^2+x+2 = 0
<=> x-2 = 0
<=> x=2
2, <=> (x-2).(x-3)=0
<=> x-2 = 0 hoặc x-3 = 0
<=> x=2 hoặc x=3
Giải các phương trình:
\(a,\left(x^2-5x\right)^2+10\left(x^2-5x\right)+24=0\)
\(b,x^4-30x^2+31x-30=0\)

a, Đặt \(x^2-5x=a\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(a^2+10a+24=0\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2+4a+6a+24=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(a+4\right)\left(a+6\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a+4=0\\a+6=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-5x+4=0\left(1\right)\\x^2-5x+6=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}}\)
Giải pt (1) ta có : \(x^2-5x+4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-4x-x+4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=4\end{cases}}\)
Giải pt (2) ta có : \(x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{1;2;3;4\right\}\)
\(x^4-30x^2+31x-30=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^4-30x^2+x+30x-30=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^4+x\right)-\left(30x^2-30x+30\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x^3+1\right)-30\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-30\left(x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x^2+x-30\right)=0\)
Mà \(x^2-x+1>0\)với \(\forall\)\(x\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+x-30=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-5x+6x-30=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-5\right)+6\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=5\\x=-6\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{5;-6\right\}\)

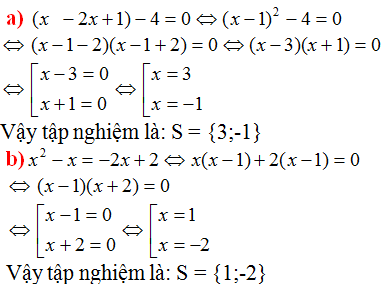
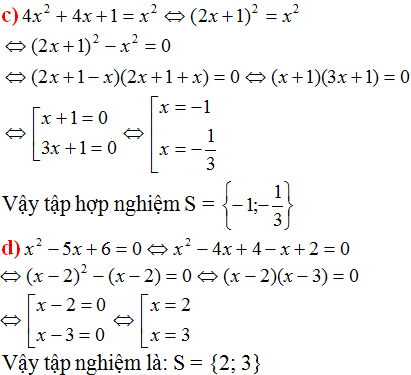
x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
⇔ x2 – 2x – 3x + 6 = 0
(Tách để xuất hiện nhân tử chung)
⇔ (x2 – 2x) – (3x – 6) = 0
⇔ x(x – 2) – 3(x – 2) = 0
⇔(x – 3)(x – 2) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 2 = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {2; 3}.