
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(3x^4+x^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^4-3x^2+4x^2-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2\cdot\left(x^2-1\right)+4\cdot\left(x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(3x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-1=0\\3x^2+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm1\\x^2=-\dfrac{4}{3}\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(S=\left\{\pm1\right\}\)
Đặt `x^2=t(t>=0)`
Ta có PT: `3t^2+t-4=0`
`3+1-4=0`
`=> t_1 = 1 ; t_2 = -4/3 (L)`
`=> x^2=1`
`<=> x=\pm 1`
Vậy `S={\pm 1}`.

\(\Leftrightarrow3^{x^2}.4^{x+1}=3^{-x}\)
Lấy logarit cơ số 3 hai vế:
\(\Rightarrow log_3\left(3^{x^2}.4^{x+1}\right)=log_3\left(3^{-x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+\left(x+1\right)log_34=-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+\left(x+1\right)log_34=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)log_34=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+log_34\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-log_34=-2log_32\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đáp án A
Phương pháp:
Đặt ẩn phụ, đưa về phương trình bậc hai một ẩn. Giải phương trình và suy ra ẩn t.
Cách giải:
![]()
![]()
Phương trình đã cho trở thành
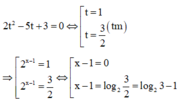
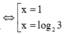
![]()

Đặt t = e x (t > 0), ta có phương trình t 2 − 3t – 4 + 12/t = 0 hay
t 3 − 3 t 2 − 4t + 12 = 0
⇔ (t − 2)(t + 2)(t − 3) = 0
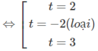
Do đó
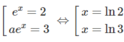

Toàn bộ nghiệm của 3 pt này đều là nghiệm thực, không có nghiệm phức nào
a. \(x^2-3x-2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b. \(x^4-5x^2+6=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2=2\\x^2=3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\sqrt{2}\\x=\pm\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c. \(-x^2+4x+5=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)

1: \(2^x=64\)
=>\(x=log_264=6\)
2: \(2^x\cdot3^x\cdot5^x=7\)
=>\(\left(2\cdot3\cdot5\right)^x=7\)
=>\(30^x=7\)
=>\(x=log_{30}7\)
3: \(4^x+2\cdot2^x-3=0\)
=>\(\left(2^x\right)^2+2\cdot2^x-3=0\)
=>\(\left(2^x\right)^2+3\cdot2^x-2^x-3=0\)
=>\(\left(2^x+3\right)\left(2^x-1\right)=0\)
=>\(2^x-1=0\)
=>\(2^x=1\)
=>x=0
4: \(9^x-4\cdot3^x+3=0\)
=>\(\left(3^x\right)^2-4\cdot3^x+3=0\)
Đặt \(a=3^x\left(a>0\right)\)
Phương trình sẽ trở thành:
\(a^2-4a+3=0\)
=>(a-1)(a-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a-1=0\\a-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\left(nhận\right)\\a=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3^x=1\\3^x=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
5: \(3^{2\left(x+1\right)}+3^{x+1}=6\)
=>\(\left[3^{x+1}\right]^2+3^{x+1}-6=0\)
=>\(\left(3^{x+1}\right)^2+3\cdot3^{x+1}-2\cdot3^{x+1}-6=0\)
=>\(3^{x+1}\left(3^{x+1}+3\right)-2\left(3^{x+1}+3\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(3^{x+1}+3\right)\left(3^{x+1}-2\right)=0\)
=>\(3^{x+1}-2=0\)
=>\(3^{x+1}=2\)
=>\(x+1=log_32\)
=>\(x=-1+log_32\)
6: \(\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)^x+\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x=2\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{1}{2+\sqrt{3}}\right)^x+\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x}+\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x=2\)
Đặt \(b=\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x\left(b>0\right)\)
Phương trình sẽ trở thành:
\(\dfrac{1}{b}+b=2\)
=>\(b^2+1=2b\)
=>\(b^2-2b+1=0\)
=>(b-1)2=0
=>b-1=0
=>b=1
=>\(\left(2+\sqrt{3}\right)^x=1\)
=>x=0
7: ĐKXĐ: \(x^2+3x>0\)
=>x(x+3)>0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x< -3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_4\left(x^2+3x\right)=1\)
=>\(x^2+3x=4^1=4\)
=>\(x^2+3x-4=0\)
=>(x+4)(x-1)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-4\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

-log22 x2_ log2x2- 20=0
↔ pt này vô ng bạn ơi!!! xem lại đầu bài.
Bài này phương trình có tận 4 nghiệm chứ không phải vô nghiệm đâu bạn Đỗ đại học nhé
Điều kiện \(x\ne0\)
Ta có từ phương trình ban đầu cho \(\Leftrightarrow4\log_2^2\left|x\right|-2\log_2\left|x\right|-20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\log_2^2\left|x\right|-\log_2\left|x\right|-10=0\)
Đặt \(t=\log_2\left|x\right|\) ta được phương trình \(2t^2-t-10=0\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}t=-2\\t=\frac{5}{2}\end{cases}\)
Với \(t=2\Rightarrow\log_2\left|x\right|=-2\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|=\frac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\frac{1}{4}\)
Với \(t=\frac{5}{2}\Rightarrow\log_2\left|x\right|=\frac{5}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|=\sqrt{32}\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{32}\)
Vậy phương trình có 4 nghiệm : \(x=\frac{1}{4};x=-\frac{1}{4};x=\sqrt{32};x=-\sqrt{32}\)

Đặt \(t=2^x\left(t>0\right)\) thì phương trình trở thành
\(4t^2-2t.4-\left(t^4+2t^3\right)=0\)
Bây giờ coi 4=u là một ẩn của phương trình, còn t là số đã biết. Phương trình trở thành phương trình bậc 2 đối với ẩn u. Tính \(\Delta'\)
ta có :
\(\Delta'=\left(-t\right)^2+\left(t^4+2t^3\right)=\left(t^2+t\right)^2\)
Do đó :
\(\begin{cases}u=t-t\left(t+1\right)\\u=t+t\left(t+1\right)\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}4=-t^2\\4=t^2+2t\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow t^2+2t-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}t=-1-\sqrt{5}\\t=-1+\sqrt{5}\end{cases}\)
Suy ra \(2^x=\sqrt{5}-1\Leftrightarrow x=\log_2\left(\sqrt{5}+1\right)\)
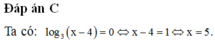
Đặt \(2^x=t>0\) ta được:
\(t^2-5t+4=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2^x=1\\2^x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)