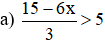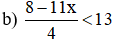Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


2x(6x – 1) > (3x – 2)(4x + 3)
⇔ 12x2 – 2x > 12x2 – 8x + 9x – 6
⇔ 12x2 – 2x – 12x2 + 8x – 9x > -6 (Chuyển vế, đổi dấu)
⇔ -3x > -6
⇔ x < 2 (Chia cả hai vế cho -3 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm x < 2.

a) \(\dfrac{15-6x}{3}>5\Leftrightarrow15-6x>15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x>0\Leftrightarrow x< 0\) (vì \(-6< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x< 0\right\}\)
b) \(\dfrac{8-11x}{4}< 13\Leftrightarrow8-11x< 52\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-11x< -44\Leftrightarrow x>4\) (vì \(-11< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x>4\right\}\)
c) \(8x+3\left(x+1\right)>5x-\left(2x-6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x+3x+1>5x-2x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x+3x-5x+2x>6-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x>5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{5}{8}\) (vì \(8>0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x>\dfrac{5}{8}\right\}\)
d) \(2x\left(6x-1\right)>\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x>12x^2+9x-8x-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x-12x^2-9x+8x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x>-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 2\) (vì \(-3< 0\))
\(S=\left\{x|x< 2\right\}\)
a) \(\dfrac{15-6x}{3}>5\) <=> \(15-6x>15\) <=> \(6x< 0\) <=> \(x< 0\)
b) \(\dfrac{8-11x}{4}< 13\) <=> \(8-11x< 52\) <=> \(11x>-44\)<=> \(x>-4\)
c) \(8x+3\left(x+1\right)>5x-\left(2x-6\right)\)
<=> 8x + 3x + 3 - 5x + 2x - 6 > 0
<=> 8x > 3
<=> x > 3/8
d) 2x(6x - 1) > (3x - 2)(4x + 3)
<=> 12x2 - 2x > 12x2 + x - 6
<=> 12x2 - 2x - 12x2 - x > -6
<=> -3x > -6
<=> x < 2

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-1;0\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{x-2}{x}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+3\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+3x+x^2-3x+2=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2-2x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=-2\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-7;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x-2}{x+7}=\dfrac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(6x+1\right)\left(x+7\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-9x-4x+6=6x^2+42x+x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-13x+6-6x^2-43x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-56x=1\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{56}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{56}\right\}\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-3x+4x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-6x+7x-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x\left(x-1\right)+7\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(6x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\6x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\6x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-\dfrac{7}{6}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{1;-\dfrac{7}{6}\right\}\)
d) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\dfrac{2}{7}\)
Ta có: \(\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)=\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8}{2-7x}+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)-\left(x-5\right)\left(\dfrac{3x+8+2-7x}{2-7x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+3-x+5\right)\cdot\dfrac{-4x+6}{2-7x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+8\right)\cdot\left(-4x+6\right)=0\)(Vì \(2-7x\ne0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+8=0\\-4x+6=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\\-4x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-8\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-8;\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)

a/ x.(x + 1)(x2 + x + 1) = 42
=> (x2 + x)(x2 + x + 1) = 42
Đặt a = x2 + x ta đc:
a.(a + 1) = 42
=> a2 + a - 42 = 0
=> (a - 6)(a + 7) = 0
=> a = 6 hoặc a = -7
Với a = 6 => x2 + x = 6 => x2 + x - 6 = 0 => (x - 2)(x + 3) = 0 => x = 2 hoặc x = -3
Với a = -7 => x2 + x = -7 => x2 + x + 7 = 0 , mà x2 + x + 7 > 0 => pt vô nghiệm
Vậy x = 2 , x = -3
b/ (3x - 1)2 - 5(2x + 1)2 + (6x - 3)(2x + 1) = (x - 1)2
=> 9x2 - 6x + 1 - 5.(4x2 + 4x + 1) + (12x2 - 3) = x2 - 2x + 1
=> 9x2 - 6x + 1 - 20x2 - 20x - 5 + 12x2 - 3 - x2 + 2x - 1 = 0
=> - 24x - 8 = 0
=> -24x = 8
=> x = -1/3
Vậy x = -1/3

\(\frac{3x-2}{x+7}=\frac{6x+1}{2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left(3x-2\right)\left(2x-3\right)=\left(x+7\right)\left(6x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(6x^2-13x+6=6x^2+43x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(-56x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x=\frac{-1}{56}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(S=\left\{-\frac{1}{56}\right\}\)
Study well !

\(\frac{4}{x^2-3x+2}-\frac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
<=> \(\frac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
<=> 4(2x2 - 6x + 1) - 3(x - 1)(x - 2) + (x - 1)(x - 2)(2x2 - 6x + 1) = 0
<=> 28x2 - 30x + 2x4 - 12x3 = 0
<=> 2x(14x - 15 + x2 - 6x2) = 0
<=> 2x(x2 - 3x + 5)(x - 3) = 0
vì x2 - 3x + 5 khác 0 nên:
<=> 2x = 0 hoặc x - 3 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 3
\(\frac{4}{x^2-3x+2}-\frac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^4-12x^3+28x^2-30x}{2x^4-12x^3+28x^2-15x+2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^4-12x^3+28x^2-30x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-3x+5\) khác 0
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=3\end{cases}}\)


1: \(\Leftrightarrow6\left(3x-1\right)+3\left(6x-2\right)=4\left(1-3x\right)\)
=>18x-6+18x-6=4-12x
=>36x-12=4-12x
=>48x=16
hay x=1/3
2: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-1+x-3\right)=0\)
=>(2x-1)(3x-4)=0
=>x=1/2 hoặc x=4/3