
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(M\left(2;6\right)\in y=ax+5\Leftrightarrow6=a\cdot2+5\Rightarrow a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(\text{Δ}=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot\left(2m+1\right)\)
=9-8m-4=-8m+5
Để phương trình có nghiệm kép thì -8m+5=0
hay m=5/8
Pt trở thành \(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}=0\)
hay x=3/2

\(b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }3x-1=x+2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{7}{2}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{3}{2};\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(\dfrac{3}{2};\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\text{ là giao 2 đths}\\ c,\left(D_2\right)\text{//}\left(D\right);B\left(1;0\right)\in\left(D_2\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=0\\a=3;b\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=3\\b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(D_2\right):y=3x-3\)

a: \(P=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-9-x+9}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}+\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x+2\sqrt{x}+2x-4\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
b: Để P<1 thì P-1<0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}-3}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-3< 0\)
hay x<9
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: 0<=x<9 và x<>4
c: Để P<1 thì 0<=x<9 và x<>4
mà x là số nguyên
nên \(x\in\left\{0;1;2;3;5;6;7;8\right\}\)

c: Xét tứ giác AEDF có
\(\widehat{AED}=\widehat{AFD}=\widehat{FAE}=90^0\)
Do đó: AEDF là hình chữ nhật
mà AD là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{DAE}\)
nên AEDF là hình vuông

Thay \(t=7,82\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{15d}=7,82:\dfrac{1}{7}=54,74\\ \Rightarrow15d=2996,4676\\ \Rightarrow d\approx200\left(m\right)\)

a: Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=3\\x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=3\\2x+4y=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-5y=-5\\x+2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=1\\x=4-2y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-5y=3\\3x-y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}12x-15y=9\\12x-4y=24\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-11y=-15\\3x-y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{15}{11}\\3x=y+6=\dfrac{81}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{27}{11}\\y=\dfrac{15}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y=-6\\-2x+y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x-2y=-6\\-4x+2y=6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0y=0\\-2x+y=3\end{matrix}\right.\left(luônđúng\right)\)
d: Ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+3y=6\\4x+2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\2x=4-y=6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Bạn ơi, làm như vậy thì quá ngắn rồi ạ, với lại bạn làm thiếu mất đề bài của mình rồi

\(x=\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\\ \Rightarrow x^3=\left(\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}\right)^3+\left(\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\right)^3+3\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\left(\sqrt[3]{9+4\sqrt{5}}+\sqrt[3]{9-4\sqrt{5}}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3=9+4\sqrt{5}+9-4\sqrt{5}+3.x\\ \Rightarrow x^3=18+3x\)
\(y=\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}+\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\)
\(y^3=\left(\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}\right)^3+\left(\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\right)^3+3\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\left(\sqrt[3]{3+2\sqrt{2}}+\sqrt[3]{3-2\sqrt{2}}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3=3+2\sqrt{2}+3-2\sqrt{2}+3y\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3=6+3y\)
\(P=x^3+y^3-3\left(x+y\right)+1993\)
\(P=18+3x+6+3y-3\left(x+y\right)+1993\)
\(P=2017+3\left(x+y\right)-3\left(x+y\right)\)
\(P=2017\)




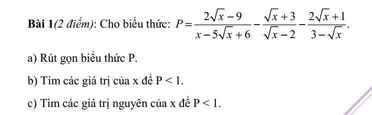





a) Âp dụng định lý Py-ta-go trong\(\Delta ABC\) vuông tại A có đường cao AH:
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\)
\(\Rightarrow AB+\sqrt{BC^2-AC^2}=\sqrt{29^2-20^2}=\sqrt{441}=21\left(cm\right)\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng cho \(\Delta ABC\) vuông tại A có đường cao AH
\(AH.BC=AB.AC\Rightarrow AH=\dfrac{AB.AC}{BC}=\dfrac{21.20}{29}=\dfrac{420}{29}\left(cm\right)\)
b)\(AC^2=CH.CB\Rightarrow CH=\dfrac{AC^2}{CB}=\dfrac{20^2}{29}=\dfrac{400}{29}\left(cm\right)\)
xét tam giác AHC có AD là Phân giác của \(\widehat{HAC}\) ta có:
\(\dfrac{DC}{DH}=\dfrac{AC}{AH}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{DC}{AC}=\dfrac{DH}{AH}=\dfrac{DC+DH}{AC+AH}=\dfrac{CH}{AC+AH}=\dfrac{400}{\dfrac{29}{20+\dfrac{420}{29}}}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow DC=\dfrac{2}{5}AC=\dfrac{2}{5}20=8\left(cm\right)\)
\(S_{ADC}=\dfrac{CD.AH}{2}=\dfrac{8.\dfrac{420}{29}}{2}=\dfrac{2680}{2}\left(cm^2\right)\)
\(S_{ADC}=\dfrac{1680}{2}\left(cm^2\right)\)