
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
Vận tốc cano khi dòng nước lặng là: $25-2=23$ (km/h)
Bài 2:
Đổi 1 giờ 48 phút = 1,8 giờ
Độ dài quãng đường AB: $1,8\times 25=45$ (km)
Vận tốc ngược dòng là: $25-2,5-2,5=20$ (km/h)
Cano ngược dòng từ B về A hết:
$45:20=2,25$ giờ = 2 giờ 15 phút.

Bài 1:
a.
$a^3-a^2c+a^2b-abc=a^2(a-c)+ab(a-c)$
$=(a-c)(a^2+ab)=(a-c)a(a+b)=a(a-c)(a+b)$
b.
$(x^2+1)^2-4x^2=(x^2+1)^2-(2x)^2=(x^2+1-2x)(x^2+1+2x)$
$=(x-1)^2(x+1)^2$
c.
$x^2-10x-9y^2+25=(x^2-10x+25)-9y^2$
$=(x-5)^2-(3y)^2=(x-5-3y)(x-5+3y)$
d.
$4x^2-36x+56=4(x^2-9x+14)=4(x^2-2x-7x+14)$
$=4[x(x-2)-7(x-2)]=4(x-2)(x-7)$
Bài 2:
a. $(3x+4)^2-(3x-1)(3x+1)=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-[(3x)^2-1]=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-(3x)^2=48$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4-3x)(3x+4+3x)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(6x+4)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x+4=12$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x=8$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$
b. $x^2-4x+4=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-2-9)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-11)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x-11=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=11$
c.
$x^2-25=3x-15$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)=3(x-5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-5=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=5$ hoặc $x=-2$

a)tam giác BHA có BI là phân giác(góc ABI=góc HBI) nên \(\dfrac{AI}{IH}=\dfrac{AB}{BH}\Rightarrow AI\cdot BH=AB\cdot IH\)
b)xét tam giác BHA và tam giác BAC có:
góc ABC chung
góc BHA=góc BAC=90 độ
\(\Rightarrow\Delta BHA\infty\Delta BAC\left(g.g\right)\\ \Rightarrow\dfrac{BH}{AB}=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\Rightarrow AB^2=BH\cdot BC\)
c)ta có:
theo câu a) \(\dfrac{AI}{IH}=\dfrac{AB}{BH}\Rightarrow\dfrac{IH}{AI}=\dfrac{BH}{AB}\left(1\right)\)
theo câu b) \(\dfrac{BH}{AB}=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\)
ta lại có BD là phân giác góc ABC nên \(\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{AD}{DC}\Rightarrow\dfrac{AD}{DC}=\dfrac{BH}{AB}\)(2)
từ (1) và (2)\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{IH}{IA}=\dfrac{AD}{DC}\left(=\dfrac{BH}{AB}\right)\)



Xét tứ giác ABEC có
AB//EC
AC//BE
Do đó: ABEC là hình bình hành
Suy ra: AC=BE
mà AC=BD
nên BE=BD
hay ΔBED cân tại B

Câu 4:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x^2-25\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
c: Để A=-3 thì x-1=-6
hay x=-5(loại)
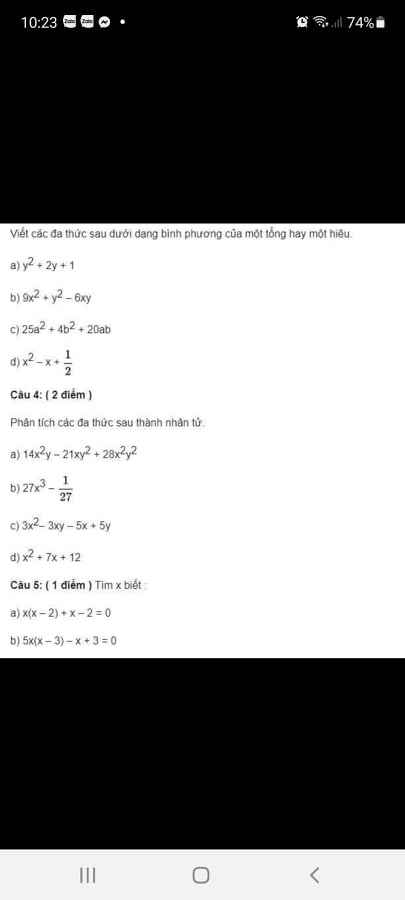




 giúp mk nha mờn nhìu ạk
giúp mk nha mờn nhìu ạk cac
cac



 giúp mik với nha!
giúp mik với nha!


Câu 3:
a. $y^2+2y+1=(y+1)^2$
b. $9x^2+y^2-6xy=(3x)^2-2.3x.y+y^2=(3x-y)^2$
c. $25a^2+4b^2+20ab=(5a)^2+2.5a.2b+(2b)^2$
$=(5a+2b)^2$
d. Sửa đề:
$x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}=x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+(\frac{1}{2})^2$
$=(x-\frac{1}{2})^2$
Câu 5:
a. $x(x-2)+x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(x-2)+(x-2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=-1$
b.
$5x(x-3)-x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x(x-3)-(x-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-3)(5x-1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-3=0$ hoặc $5x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=3$ hoặc $x=\frac{1}{5}$