
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Hệ số biến dạng theo mỗi trục đo O'x', O'y', O'z' lần lượt là:
p=O'A'OA=22=1�=�'�'��=22=1;
q=O'B'OB=13�=�'�'��=13;
r=O'C'OC=46=23�=�'�'��=46=23.


\(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{6}+\frac{k\pi}{2}\)


a)

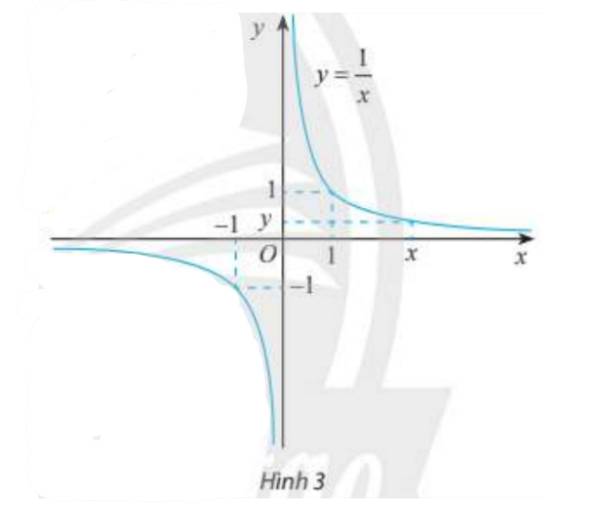
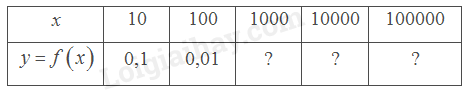
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng lớn (dần tới \( + \infty \)).
b)
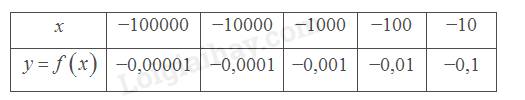
Giá trị \(f\left( x \right)\) dần về 0 khi \(x\) càng bé (dần tới \( - \infty \)).

cau 12:
gọi E là trung điểm AB \(\Rightarrow\)MẸ//BC ; và EN// AC do do ME=BD/2 ;NE= AC/2
\(\Rightarrow\left[\widehat{BD;AC}\right]=\left[\widehat{ME;EN}\right]=90^0\)
\(\Delta MEN\)vuông tại E\(\Rightarrow MN^2=ME^2+NE^2=\left(\dfrac{3a}{2}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{a}{2}\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{10a^2}{4}\right)\Rightarrow MN=\dfrac{a\sqrt{10}}{2}\)
chọn đáp án A
vẽ hình ở ngoài rồi dán vào ko biết tại sao nó lại thụt xuống dưới![]()

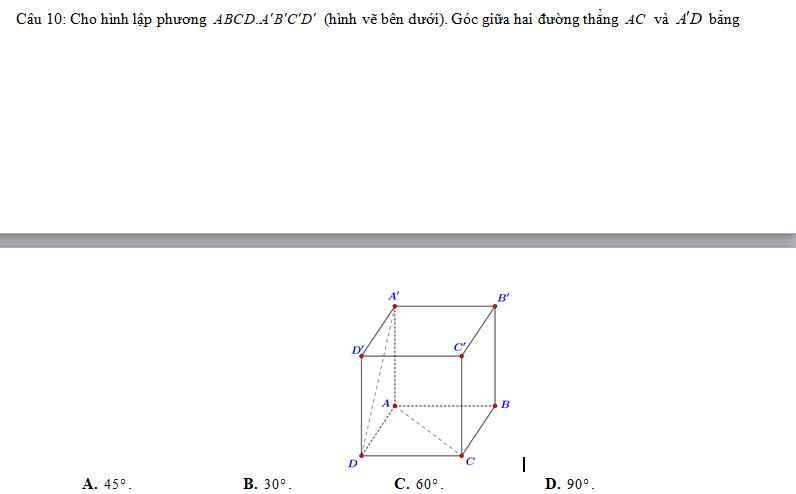
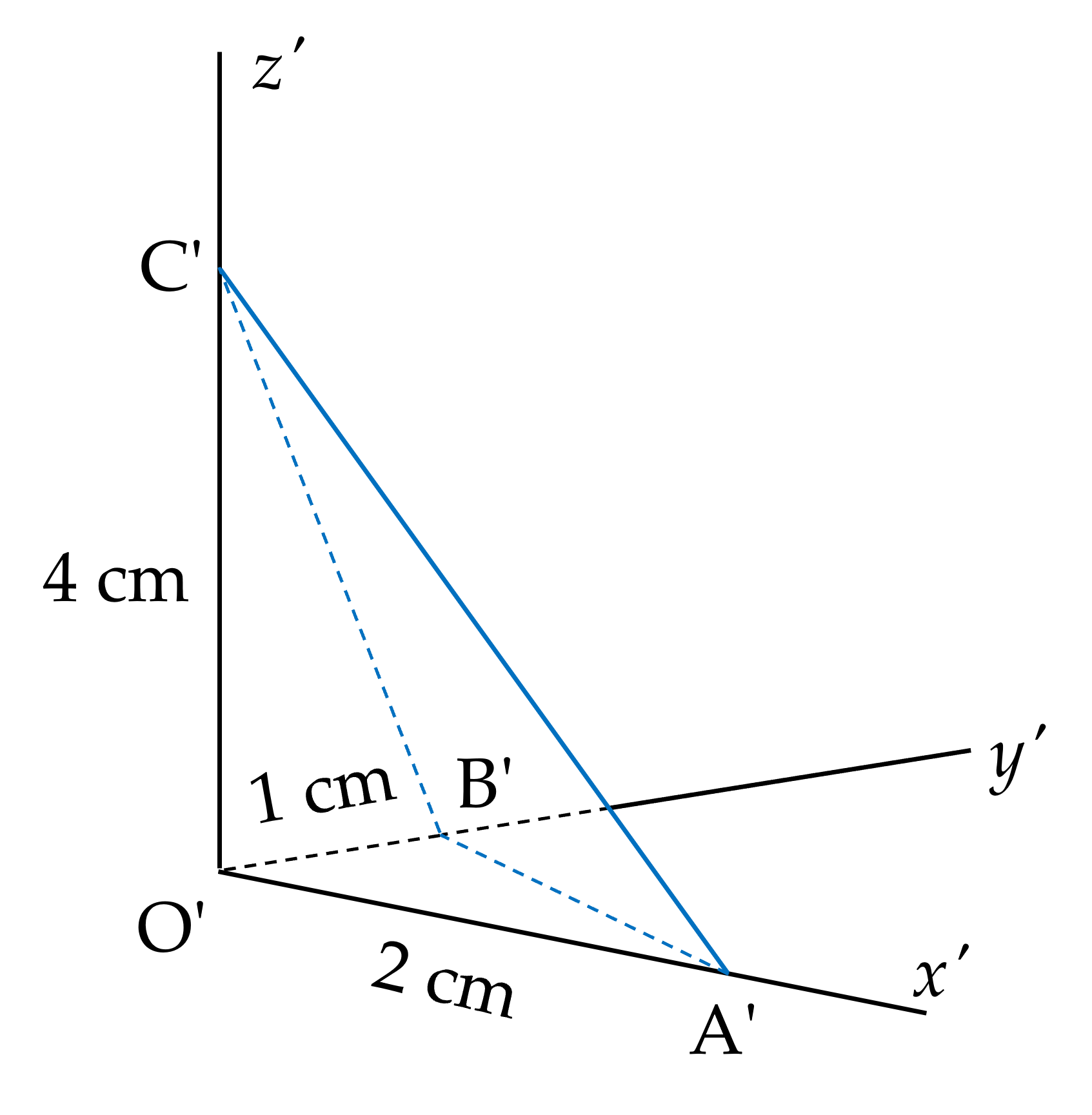

 Ai giải chi tiết cái này hộ mình với
Ai giải chi tiết cái này hộ mình với


 :
:
Có \(9.10.10.10.10=90000\) số có 5 chữ số (không gian mẫu)
Có \(\dfrac{99994-10013}{17}+1=5294\) số có 5 chữ số chia hết 17
Xác suất: \(P=\dfrac{5294}{90000}=...\)