Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu c;d giải \(\Delta\)
Các câu còn lại là phương trình trùng phương, mình chỉ làm 1 câu thôi. Các câu sau tương tự
a/ \(x^4-2x^2-8=0\left(1\right)\)
Đặt: \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\Rightarrow t^2-2t-8=0\)
( a = 1; b = -2; c = -8 )
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=\left(-2\right)^2-4.1.\left(-8\right)\)
\(=36>0\)
\(\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{36}=6\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(t_1=\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2-6}{2.1}=-2\left(l\right)\)
\(t_2=\frac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2+6}{2.1}=4\left(n\right)\Rightarrow x^2=4\Leftrightarrow x=2hayx=-2\)
Vậy: S = {-2;2}

a). Đặt \(x^2=y\) \(\left(y\ge0\right)\) ta có ;
\(3y^2-12y+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2-4y+3=0\)
Nhận xét : \(a+b+c=1+\left(-4\right)+3=0\)
\(\Rightarrow y_1=1\) (TM \(y\ge0\))
\(y_2=\dfrac{3}{1}=3\)
Với \(y=y_1=1\Rightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x_1=1;x_2=-1\)
Với \(y=y_2=3\Rightarrow x^2=3\Leftrightarrow x_3=\sqrt{3};x_4=-\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy \(x_1=1;x_2=-1;x_3=\sqrt{3};x_4=-\sqrt{3}\) là các giá trị cần tìm
b) . Đặt \(x^2=y\) \(\left(y\ge0\right)\) ta có ;
\(2y^2+3y-2=0\)
\(\Delta_y=3^2-4\cdot2\cdot\left(-2\right)=9+16=25\) \(\left(\sqrt{\Delta}=5\right)\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\) nên pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Rightarrow\)\(y_1=\dfrac{-3+5}{2\cdot2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) (TM \(y\ge0\) )
\(y_2=\dfrac{-3-5}{2\cdot2}=-2\) (KTM \(y\ge0\) )
Với \(y=y_1=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x^2=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x_1=\dfrac{1}{4};x_2=-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Vậy \(x_1=\dfrac{1}{4};x_2=-\dfrac{1}{4}\) là các giá trị cần tìm
c) Đặt \(x^2=y\) \(\left(y\ge0\right)\) ta có ;
\(y^2+5y+1=0\)
\(\Delta_y=5^2-4\cdot1\cdot1=25-4=21\)
Vì \(\Delta>0\) nên pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Rightarrow y_1=\dfrac{-5+\sqrt{21}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{-5+\sqrt{21}}{2}\) (KTM \(y\ge0\))
\(y_2=\dfrac{-5-\sqrt{21}}{2\cdot1}=\dfrac{-5-\sqrt{21}}{2}\) (KTM \(y\ge0\))
Vậy pt đã cho vô nghiệm
phần b sai rồi
b, 2x4+3x2-2=0
Đặt x2=t (t>0) ta có
2t2 + 3t-2=0
\(\Delta\)=32-4.2.(-2)=25 \(\Rightarrow\)\(\sqrt{\Delta}\)=5
vì \(\Delta\)>0 nên PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
t1=\(\dfrac{-3+5}{2.2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\) (thỏa mãn)
t2=\(\dfrac{-3-5}{2.2}=-2\) (loại)
với t1=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) => x2=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) => x1=\(\pm\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\) =>x1=\(\pm\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
vậy PT đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt là x1=\(-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\) ;x2=\(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)

a) x4 – 5x2+ 4 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: t2 – 5t + 4 = 0; t1 = 1, t2 = 4
Nên: x1 = -1, x2 = 1, x3 = -2, x4 = 2.
b) 2x4 – 3x2 – 2 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: 2t2 – 3t – 2 = 0; t1 = 2, t2 = (loại)
Vậy: x1 = √2; x2 = -√2
c) 3x4 + 10x2 + 3 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: 3t2 + 10t + 3 = 0; t1 = -3(loại), t2 = (loại)
Phương trình vô nghiệm.
a) x4 – 5x2+ 4 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: t2 – 5t + 4 = 0; t1 = 1, t2 = 4
Nên: x1 = -1, x2 = 1, x3 = -2, x4 = 2.
b) 2x4 – 3x2 – 2 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: 2t2 – 3t – 2 = 0; t1 = 2, t2 = (loại)
Vậy: x1 = √2; x2 = -√2
c) 3x4 + 10x2 + 3 = 0.
Đặt x2 = t ≥ 0, ta có: 3t2 + 10t + 3 = 0; t1 = -3(loại), t2 = (loại)
Phương trình vô nghiệm.
nhớ like


\(\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-8\right)\left(x-10\right)=72x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-8\right)\left(x-10\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-14x+40\right)\left(x^2-13x+40\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40-0,5x\right)\left(x^2-13,5x+40+0,5x\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40\right)^2-\left(0,5x\right)^2-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40\right)^2-72,25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40+8,5x\right)\left(x^2-13,5x+40-8,5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-5x+40\right)\left(x^2-22x+40\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-5x+40=0\left(VN\right)\\x^2-22x+40=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=20\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Câu a,c xem lại đề, cách làm giống câu b, còn câu e giống câu d
b) \(2x^4+5x^3+x^2+5x+2=0\)
Ta nhận thấy x=0 không phải là 1 nghiệm của phương trình, chia cả 2 vế của phương trình cho \(x^2\ne0\), ta được:
\(2x^2+5x+1+\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{2}{x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)+5\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+1=0\)
Đặt \(y=x+\dfrac{1}{x}\Rightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}=y^2-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(y^2-2\right)+5y+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2+5y-3=0\)
PT đơn giản, tự giải nha, ta được nghiệm y=1/2 và y=-3
Với y=1/2 thì không tìm được x
Với y=-3 thì tìm được 2 nghiệm, tự giải
a) (3x2 – 5x + 1)(x2 – 4) = 0
=> 3x2 – 5x + 1 = 0 => x =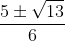
hoặc x2 – 4 = 0 => x = ±2.
b) (2x2 + x – 4)2 – (2x – 1)2 = 0
⇔ (2x2 + x – 4 + 2x – 1)(2x2 + x – 4 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x2 + 3x – 5)(2x2 – x – 3) = 0
=> 2x2 + 3x – 5 = 0 hoặc 2x2 – x – 3 = 0
X1 = 1; x2 = -2,5; x3 = -1; x4 = 1,5
a) (3x2 – 5x + 1)(x2 – 4) = 0
=> 3x2 – 5x + 1 = 0 => x =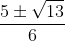
hoặc x2 – 4 = 0 => x = ±2.
b) (2x2 + x – 4)2 – (2x – 1)2 = 0
⇔ (2x2 + x – 4 + 2x – 1)(2x2 + x – 4 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (2x2 + 3x – 5)(2x2 – x – 3) = 0
=> 2x2 + 3x – 5 = 0 hoặc 2x2 – x – 3 = 0
X1 = 1; x2 = -2,5; x3 = -1; x4 = 1,5
Nhớ like nha
please