Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải:
a)
\(3x^2-5x+1=2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-5x+1-2x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-7x+4=0\) (\(a=3; b=-7; c=4)\)
b)
\(\frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3=3x+\frac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3-3x-\frac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-7x-\frac{10}{3}=0(a=\frac{3}{5};b=-7; c=\frac{-10}{3})\)
c)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+x-5-\sqrt{3}x-\sqrt{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+(1-\sqrt{3})x-(5+\sqrt{2})=0\)
(\(a=-\sqrt{3}; b=1-\sqrt{3}; c=-(5+\sqrt{2}))\)
d)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5(m+1)x+m^2-2=0\)
(\(a=1;b=-5(m+1); c=m^2-2)\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-3x+7=0\)
a=4; b=-3; c=7
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{5}x^2-x^2+5x-3-3x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\cdot\left(\sqrt{5}-1\right)+2x+1=0\)
\(a=\sqrt{5}-1;b=2;c=1\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow mx^2-x^2-3x+mx+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(m-1\right)+x\left(m-3\right)+5=0\)
a=m-1; b=m-3; c=5
d: \(\Leftrightarrow m^2x^2-x^2+x+m-mx-m-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(m^2-1\right)+x\left(1-m\right)-2=0\)
\(a=m^2-1;b=1-m;c=-2\)

1) Đk: x khác -3
x khác 1
Biểu thức \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-x}{x^2+2x-3}+\dfrac{2x+6}{x^2+2x-3}=\dfrac{12}{x^2+2x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+2x+6=12\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
kl: x thuộc {-3;2}

c: =>3x^2+3y^2=39 và 3x^2-2y^2=-6
=>5y^2=45 và x^2=13-y^2
=>y^2=9 và x^2=4
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\in\left\{2;-2\right\}\\y\in\left\{3;-3\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5\sqrt{x}=5\\\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{y}=-\dfrac{11}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\\sqrt{y}=1+\dfrac{11}{2}=\dfrac{13}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=1 và y=169/4
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x+3-3}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y+4}=4\\\dfrac{2x+2-2}{x+1}-\dfrac{5}{y+4}=9\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{3}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y+4}=4-3=1\\-\dfrac{2}{x+1}-\dfrac{5}{y+4}=9-2=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x+1=11/9 và y+4=-11/19
=>x=2/9 và y=-87/19

7.
ĐKXĐ: ...
\(\Leftrightarrow10\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=3\left(x^2+2\right)\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=a>0\\\sqrt{x+1}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow10ab=3\left(a^2+b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3a^2-10ab+3b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-3b\right)\left(3b-a\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=3b\\3a=b\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=3\sqrt{x+1}\\3\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=\sqrt{x-1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x+1=9x+9\\9x^2-9x+9=x-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-10x-8=0\\9x^2-10x+10=0\end{matrix}\right.\) (casio)
6.
ĐKXĐ: ...
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4=3\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=a>0\\\sqrt{x+1}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2+2b^2=3ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2-3ab+2b^2=0\)
Phương trình vô nghiệm (vế phải là \(5\sqrt{x^3+1}\) sẽ hợp lý hơn)

a) Vì biểu thức \(\sqrt{\dfrac{-5}{x^2+6}}\)có -5<0 nên làm cho cả phân số âm
Từ đó suy ra căn thức vô nghiệm
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x để biểu thức trên xác định
b) \(\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
Để biểu thức trên xác định thì chia ra 4 TH (vì để xác định thì cả x-1 và x-3 cùng dương hoặc cùng âm)
\(\left[\begin {array} {} \begin{cases} x-1\geq0\\ x-3\geq0 \end{cases} \Leftrightarrow \begin{cases} x\geq1\\ x\geq3 \end{cases} \Rightarrow x\geq3 \\ \begin{cases} x-1\leq0\\ x-3\leq0 \end{cases} \Leftrightarrow \begin{cases} x\leq1\\ x\leq3 \end{cases} \Rightarrow x\leq1 \end{array} \right.\)
c) \(\sqrt{x^2-4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
Rồi làm như câu b
d) \(\sqrt{\dfrac{2-x}{x+3}}\)
Để biểu thức trên xác định thì
\(\begin{cases}2-x\ge0\\x+3>0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x\ge2\\x>-3\end{cases}\) \(\Rightarrow\) \(x\ge2\) hoặc \(x>-3\)
e) Ở các biểu thức sau này nếu chỉ có căn thức có ẩn và + (hoặc trừ) với 1 số thì chỉ cần biến đổi cái có ẩn còn cái số thì kệ xác nó đi ![]() )
)
\(\sqrt{x^2-3x}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x\left(x-3\right)}\)
Để biểu thức trên xác định thì \(x\ge0\) và \(x-3\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge3\)
Bữa sau mình làm tiếp
a) 5x2 + 2x = 4 – x ⇔ 5x2 + 3x – 4 = 0; a = 5, b = 3, c = -4
b) x2 + 2x – 7 = 3x +
x2 + 2x – 7 = 3x +  ⇔
⇔  x2 – x -
x2 – x - 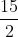 = 0, a =
= 0, a =  , b = -1, c = -
, b = -1, c = -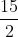
c) 2x2 + x - √3 = √3 . x + 1 ⇔ 2x2 + (1 - √3)x – 1 - √3 = 0
Với a = 2, b = 1 - √3, c = -1 - √3
d) 2x2 + m2 = 2(m – 1)x ⇔ 2x2 - 2(m – 1)x + m2 = 0; a = 2, b = - 2(m – 1), c = m2