Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

D=sin(pi+x)+sinx+cot(pi-x)+tan(pi/2-x)
=-sinx+sinx-cotx+cotx=0

điều kiện : cosx\(\ne\)\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)=> x\(\ne\)\(\pm\)\(\frac{\pi}{4}\)+2k\(\pi\), k\(\in\)Z
pt<=> tử số =0
<=>cos2x-sin(3x-\(\frac{\pi}{4}\)+x+\(\frac{3\pi}{4}\))-sin(3x-\(\frac{\pi}{4}\)-x-\(\frac{3\pi}{4}\))-2=0
<=> cos2x-sin(x+\(\frac{\pi}{2}\))-sin(2x-\(\pi\))-2=0
<=> cos2x-cosx+sin2x-2sin2x-2cos2x=0
<=>-cos2x-coxs+2sinx.cosx-2sin2x=0
đến đây bạn nhóm lại ra nghiệm rồi kiểm tra đk là xong


\(1-2cos^2x-sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-2\left(1-sin^2x\right)-sinx=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x-sinx-1=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=1\\sinx=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{7\pi}{6}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\left\{\dfrac{\pi}{2};\dfrac{7\pi}{6};\dfrac{11\pi}{6};\dfrac{5\pi}{2}\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sum x=6\pi\)

Lê Huy Hoàng:
a) ĐK: $x\in\mathbb{R}\setminus \left\{k\pi\right\}$ với $k$ nguyên
PT $\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x-4\tan x+5=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-2)^2+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-2)^2=-1< 0$ (vô lý)
Do đó pt vô nghiệm.
c)
ĐK:.............
PT $\Leftrightarrow 1+\frac{\sin ^2x}{\cos ^2x}-1+\tan x-\sqrt{3}(\tan x+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x+\tan x-\sqrt{3}(\tan x+1)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x+(1-\sqrt{3})\tan x-\sqrt{3}=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan x=\sqrt{3}$ hoặc $\tan x=-1$
$\Rightarrow x=\pi (k-\frac{1}{4})$ hoặc $x=\pi (k+\frac{1}{3})$ với $k$ nguyên
d)
ĐK:.......
PT $\Leftrightarrow \tan x-\frac{2}{\tan x}+1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \tan ^2x+\tan x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (\tan x-1)(\tan x+2)=0$
$\Rightarrow \tan x=1$ hoặc $\tan x=-2$
$\Rightarrow x=k\pi +\frac{\pi}{4}$ hoặc $x=k\pi +\tan ^{-2}(-2)$ với $k$ nguyên.

Quan sát đồ thị hàm số y = tan x trên đoạn [-π; 3π/2].
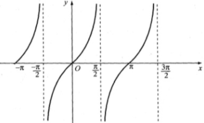
a. tan x = 0 tại các giá trị x = -π; 0; π.
(Các điểm trục hoành cắt đồ thị hàm số y = tanx).
b. tan x = 1 tại các giá trị x = -3π/4; π/4; 5π/4.
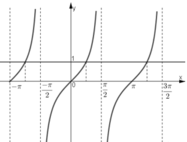
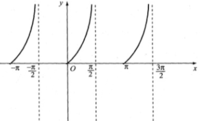
c. tan x > 0 với x ∈ (-π; -π/2) ∪ (0; π/2) ∪ (π; 3π/2).
(Quan sát hình dưới)
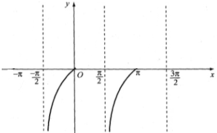
d. tan x < 0 khi x ∈ [-π/2; 0) ∪ [π/2; π)
(Quan sát hình dưới).

Ta có:
(1)\(cos\left(x\right)-sin\left(x\right)=\sqrt{2}.\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(cos\left(x\right)-sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}.cos\left(x\right)-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}.sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.\left(sin\dfrac{\pi}{4}cos\left(x\right)-cos\dfrac{\pi}{4}.sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-x\right)\)
(2) \(cos\left(x\right)+sin\left(x\right)=\sqrt{2}.\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(cos\left(x\right)+sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}.cos\left(x\right)+\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}.sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.\left(cos\dfrac{\pi}{4}cos\left(x\right)+sin\dfrac{\pi}{4}.sin\left(x\right)\right)\\ =\sqrt{2}.cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
ADCT trên ta được:
\(sin\left(x\right)+\sqrt{2}.sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x\right)=\sqrt{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow sin\left(x\right)+\sqrt{2}.sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\right)=\sqrt{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow sin\left(x\right)+cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)-sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\sqrt{2}\\ \sqrt{2}sin\left(x\right)+\sqrt{2}cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)+\sqrt{2}sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-x\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(x\right)+cos\left(x\right)+sin\left(x\right)+cos\left(x\right)-sin\left(x\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}sin\left(x\right)+2cos\left(x\right)=2\)
Đến đây lại dùng cách trong sgk giải pt: a.sin(x) + b.cos(x) = c tìm ra x để thay nhá
pi<x<3/2pi
=>cosx<0
pi<x<3/2pi
=>pi/2<1/2x<3/4pi
=>cos(x/2)<0
1+tan^2x=1/cos^2x
=>1/cos^2x=1+8=9
=>cosx=-1/3
\(cosx=2\cdot cos^2\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)-1\)
=>\(2\cdot cos^2\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(cos^2\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>cos(x/2)=1/căn 3