Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1. Theo hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\x_1.x_2=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(C=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2-x_1+x_2^2-x_2}{x_1x_2-x_1-x_2+1}=\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2-2.\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)}{\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)+1}=\dfrac{\dfrac{22}{9}}{\dfrac{8}{3}}=\dfrac{11}{12}\)
\(1,3x^2+4x+1=0\)
Do pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\) nên theo đ/l Vi-ét ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=-\dfrac{4}{3}\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(C=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_2-1\right)\left(x_1-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2-x_1+x_2^2-x_2}{x_1x_2-x_2-x_1+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{S^2-2P-S}{P-S+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)^2-2.\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)}{\dfrac{1}{3}-\left(-\dfrac{4}{3}\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{11}{12}\)
Vậy \(C=\dfrac{11}{12}\)

\(F=x_1^2-3x_2-2013\)
Áp dụng Viét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-3\\x_1x_2=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(x_1\) là nghiệm của PT nên \(x_1^2+3x_1-7=0\Leftrightarrow x_1^2=7-3x_1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow F=7-3x_1-3x_2-2013\\ F=-2006-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)=-2006-3\left(-3\right)=-1997\)

Vì \(x_1\) là nghiệm PT nên \(x_1^2+3x_1-7=0\Leftrightarrow x_1^2=7-3x_1\)
\(F=x_1^2-3x_2-2013=7-3x_1-3x_2-2013\\ F=-3\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2006\)
Mà theo Viét ta có \(x_1+x_2=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow F=\left(-3\right)\left(-3\right)-2006=-1997\)
cho PT 2x^2-3x-1=0. x1, x2 là 2 nghiệm của PT, không giải PT hãy tính A = x1^4 + x2^4. B = I x1-x2 I


a)
5x2+ 12x- 30= 0
x( 5x +12- 30)= 0
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\5x+12-30=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\5x+12=30\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\5x=30-12\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\5x=18\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=18:5\end{cases}}\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=\frac{18}{5}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy PT có tập nghiệm là T={18/5;0}
P/s: chị nhớ thêm dấu tương đương vào PT nhé :)

Vì P = 6 / -2 = -3 < 0
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm trái dấu
Áp dụng định lí Viet ta có:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1x_2=\frac{6}{-2}\\x_1+x_2=\frac{3}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Ta có: \(\left|x_1-x_2\right|^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)^2-4\left(\frac{6}{-2}\right)=\frac{57}{4}\)
=> \(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=\frac{\sqrt{57}}{2}\)

\(x^2 - 4x - 3 = 0\) có 1.(-3) < 0
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et có \(x_1 + x_2 = 4\) \(; x_1x_2 = -3\)
Mà \(A = \dfrac{x_1^2}{x_2} + \dfrac{x_2^2}{x_1}\)
\(= \dfrac{x_1^3 + x_2^3}{x_1x_2}\)
\(= \dfrac{(x_1 + x_2)(x_1^2 - x_1x_2 + x_2^2)}{x_1x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{(x_1+x_2)[(x_1 +x_2)^2 - 3x_1x_2]}{x_1x_2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4.[4^2 - 3.(-3)]}{-3}\)
\(= \dfrac{-100}{3}\)
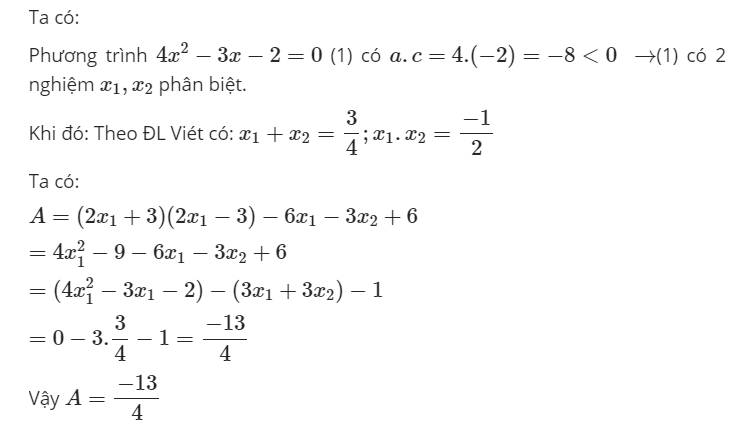
Do \(\Delta=5^2+4\cdot3\cdot4=25+48=73>0\) nên PT có 2 nghiệm phân biệt.
Khi đó: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\frac{-b}{a}=\frac{-\left(-5\right)}{3}=\frac{5}{3}\\x_1x_2=\frac{c}{a}=\frac{-4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ đây, ta suy ra:
\(A=x_1^3x_2+x_1x_2^3\\ =x_1x_2\left(x_1^2+x^2_2\right)\\ =x_1x_2\left(x_1^2+2x_1x_2+x^2_2-2x_1x_2\right)\\ =x_1x_2\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]\\ =\frac{-4}{3}\cdot\left[\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)^2-\frac{-4\cdot2}{3}\right]\\ =\frac{-4}{3}\cdot\frac{25-\left(-8\cdot3\right)}{9}\\ =\frac{-4}{3}\cdot\frac{25+24}{9}\\ =\frac{-4}{3}\cdot\frac{49}{9}=\frac{-196}{27}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt nha .
.
Ta có:
A = x1x2(x12 + x22) = x1x2[(x1 + x2)2 - 2x1x2]
Ta có: \(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4.3.\left(-4\right)=25+48>0\)
Áp dụng định lý Vi-ét với phương trình 3x2 - 5x - 4 ta có:
x1 + x2 = \(\frac{-\left(-5\right)}{3}=\frac{5}{3}\)
x1x2 = \(\frac{-4}{3}\)
Thay vào A ta được:
A = \(\frac{-4}{3}\left[\left(\frac{5}{3}\right)^2-2.\frac{-4}{3}\right]=\frac{-4}{3}.\left(\frac{25}{9}+\frac{8}{3}\right)=\frac{-4}{3}.\frac{49}{3}=\frac{-196}{3}\)
(P/s: CÓ thể SAI)