Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a/ A=\(\frac{x\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=\frac{x}{3x-1}\)
A xác định khi 3x-1 #0 <=> x khác 1/3
b/ x=8 => A=\(\frac{8}{3.8-1}=\frac{8}{23}\)
c/ A\(\le0\)Khi:
+/\(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\3x-1\le0\end{cases}}< =>0\le x\le\frac{1}{3}\)
+/ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\le0\\3x-1\ge0\end{cases}}\)Không có giá trị x phù hợp
Vậy để A<0 <=> \(0\le x\le\frac{1}{3}\)
a,\(\frac{3x^2-x}{9x^2-6x+1}=\frac{x\left(3x-1\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)^2}=\frac{x}{3x-1}\)
Vậy đk xác định của phân thức là \(x\ne\frac{1}{3}\)
b, Ta thay x=8
\(\frac{x}{3x-1}=\frac{8}{3.8-1}=\frac{8}{23}\)
c, x<0
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x}{3x-1}=-1\Leftrightarrow x=0,25\)

Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45

a) phân thức xác định khi \(x^3+8\ne0\Leftrightarrow x^3\ne-8\Leftrightarrow x\ne-2\)
b)\(\frac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}=\frac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=\frac{2}{x+2}\)
c) \(\frac{2}{x+2}=\frac{2}{2+2}=\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\)
d)\(\frac{2}{x+2}=2\Leftrightarrow x+2=1\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)

Đặt phân thức đã cho là A
\(ĐKXĐ:x^2-x\ne0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\ne0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
a) \(A=\frac{2x-2}{x^2-x}=\frac{2\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{2}{x}\)
Với \(x=3\)( thoả mãn ĐKXĐ ) \(\Rightarrow A=\frac{2}{3}\)
Với \(x=0\)( không khoả mãn ĐKXĐ ) \(\Rightarrow\)Không tìm được giá trị của A
b) \(A=2\)\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x}=2\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)( không thoả mãn ĐKXĐ )
Vậy không tìm được giá trị của x để \(A=2\)
c) A có giá trị nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x}\inℤ\)\(\Leftrightarrow2⋮x\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
So sánh với ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x=1\)không thoả mãn
Vậy A nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2;-1;2\right\}\)
ĐKXĐ:
----------->x khác 0
---------->(x-1) khác 0 ----------> x khác 1
VẠY ĐKXĐ LÀ X khác 0 và 1.
Bạn tự rút gọn nha
a, 2x-2\ x^2-x= 2\x
Thay x=3 vào biểu thức có:
-----> = 2\3
Vậy nếu thay x=3 vào biểu thức thì = 2\3
thay x=0 vào biểu thức có
------> = 0 vì 2\0=0
VẬY nếu thay x=0 thì biểu thức thì =0
b,
theo đề bài ta có
2\x=2
-----> 2:x=2
Vậy x=1
Câu c mik ko chắc nên bn tự làm nha
mik rất sorry:(((((((

Đặt \(\frac{5x+5}{2x^2+2x}=A\)
a/ Để A xác định\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x+1\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
TXĐ:\(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)
b/ Với \(x\ne0;x\ne-1\)ta có \(A=\frac{5x+5}{2x^2+2x}\)
Để A=1\(\Leftrightarrow5x+5=2x^2+2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x+1\right)=2x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=2x\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{2}{5}\)( TM )

a, ĐỂ \(\frac{2x+4}{x\left(x+2\right)}\)xác định
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+2\ne0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-2\end{cases}}\)

Bài 3 :
a) Phân thức xác định \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\ne0\\x+1\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}}\)
Ta có :
\(A=\frac{3x+3}{x^2-1}=\frac{3\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{3}{x-1}\)
Để A có giá trị bằng -2 thì \(\frac{3}{x-1}=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3=-2x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}\)
b) Để A là số nguyên thì :
\(3⋮x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{1;3;-1;-3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;0;-2\right\}\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
Vậy...........
\(a,ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm1\)
Ta có : \(\frac{3x+3}{x^2-1}=\frac{3\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{3}{x-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3x+3}{x^2-1}=-2\Leftrightarrow\frac{3}{x-1}=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(x-1\right)=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+2=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}\)
\(b,\) Để phân thức \(\frac{3x+3}{x^2-1}\) có giá trị nguyên thì \(\frac{3}{x-1}\) có giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow3⋮x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;-2;4\right\}\)
Vậy \(x=-2;0;2;4\)

bài1 A=\(\left(\frac{3-x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(\left(-\frac{x-3\cdot\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)^2\cdot\left(x-3\right)}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(-\frac{x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x+3}{3x^2}=\frac{-1}{3x}\)
b) thế \(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)vào biểu thức A
\(-\frac{1}{3\cdot\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)}=\frac{2}{3}\)
c) A=\(-\frac{1}{3x}< 0\)
VÌ (-1) <0 nên 3x>0
x >0

Answer:
a. \(ĐKXĐ:x^2-9\ne0\Rightarrow x^2\ne9\Rightarrow x\ne\pm3\)
b. \(A=\frac{x^2-6x+9}{x^2-9}=\frac{\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right).\left(x+3\right)}=\frac{x-3}{x+3}\)
c. \(A=7\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x-3}{x+3}=7\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3=7.\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3=7x+21\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3-7x-21=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-6x-24=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-4\)
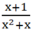
a) Ta có: x2 + x = x(x + 1)
Giá trị phân thức này được xác định với điều kiện x2 + x ≠ 0
⇒ x(x + 1) ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ 0 và x + 1 ≠ 0
⇒ x ≠ 0 và x ≠ -1
b) Vì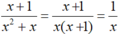 và x = 1 000 000 thỏa mãn điều kiện của biến nên có thể tính giá trị của phân thức đã cho bằng cách tính giá trị của phân thức rút gọn
và x = 1 000 000 thỏa mãn điều kiện của biến nên có thể tính giá trị của phân thức đã cho bằng cách tính giá trị của phân thức rút gọn 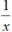
Vậy giá trị của phân thức đã cho tại x = 1 000 000 là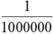
+ Tại x= -1 phân thức đã cho không được xác định.
Vậy không tồn tại giá trị của phân thức tại x = -1