Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a)\(\sin^2\alpha+\cos^2\alpha=1\Rightarrow\sin^2\alpha=1-\cos^2\alpha\)
\(\Rightarrow1-2^2=-3\) \(\Rightarrow\cos=-\sqrt{3}\left(0< \alpha< \dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\)
b) \(\tan\alpha\times\cot\alpha=1\Rightarrow\tan\alpha=\dfrac{1}{\cot\alpha}\Rightarrow\tan=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
a)Do \(0< \alpha< \dfrac{\pi}{2}\) nên các giá trị lượng giác của \(\alpha\) đều dương.
\(cos\alpha=2sin\alpha\)(1)
Nếu \(sin\alpha=0\Rightarrow cos\alpha\) (vô lý).
Vì vậy \(sin\alpha\ne0\) . Từ (1) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{cos\alpha}{sin\alpha}=2\)\(\Leftrightarrow cot\alpha=2\).
Suy ra: \(tan\alpha=\dfrac{1}{2}\).
\(sin\alpha=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{1+cot^2\alpha}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\).
\(cos\alpha=\sqrt{1-sin^2\alpha}=\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}\).

a) Do \(\pi< \alpha< \dfrac{3\pi}{2}\) nên \(sin\alpha< 0;cot\alpha>0;tan\alpha>0\).
Vì vậy: \(sin\alpha=-\sqrt{1-cos^2\alpha}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{15}}{4}\).
\(tan\alpha=\dfrac{sin\alpha}{cos\alpha}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{15}}{4}:\dfrac{-1}{4}=\sqrt{15}\).
\(cot\alpha=\dfrac{1}{tan\alpha}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{15}}\).
b) Do \(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< \alpha< \pi\) nên \(cos\alpha< 0;tan\alpha< 0;cot\alpha< 0\).
\(cos\alpha=-\sqrt{1-sin^2\alpha}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\);
\(tan\alpha=\dfrac{2}{3}:\dfrac{-\sqrt{5}}{3}=\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{5}}\); \(cot\alpha=1:tan\alpha=\dfrac{-\sqrt{5}}{2}\).
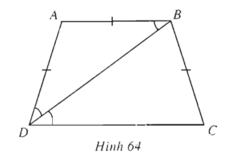
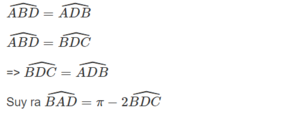
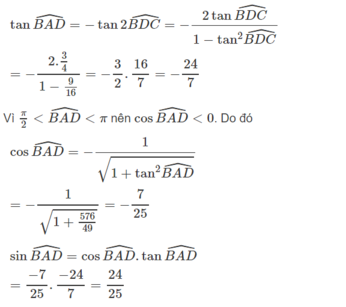

Ta có :
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{ADB}\)
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{BDC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{BDC}=\widehat{ADB}\)
Suy ra \(\widehat{BAD}=\pi-2\widehat{BDC}\)
Từ đó ta có :
\(\tan\widehat{BAD}=-\tan2\widehat{BDC}=-\dfrac{2\tan\widehat{BDC}}{1-\tan^2\widehat{BDC}}=-\dfrac{2.\dfrac{3}{4}}{1-9\cdot16}=-\dfrac{3}{2}.\dfrac{16}{7}=-\dfrac{24}{7}\)Vì \(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< \widehat{BAD}< \pi\) nên \(\cos\widehat{BAD}< 0\)
Do đó : \(\cos\widehat{BAD}=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\tan^2\widehat{BAD}}}=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\dfrac{576}{49}}}=-\dfrac{7}{25}\)
\(\sin\widehat{BAD}=\cos\widehat{BAD}\tan\widehat{BAD}=\dfrac{-7}{25}.\dfrac{-24}{7}=\dfrac{24}{25}\)