

Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




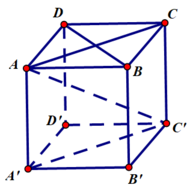
Tao có: \(\overrightarrow{BC}.\overrightarrow{AD}=\overrightarrow{BC}\left(\overrightarrow{DC}+\overrightarrow{CA}\right)=\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{CD}-\overrightarrow{CB}.\overrightarrow{CA}\)
\(=\frac{1}{2}\left(CB^2+CD^2-BD^2\right)-\frac{1}{2}\left(CB^2+CA^2-AB^2\right)\)
\(=\frac{1}{2}\left(AB^2+CD^2-BD^2-CA^2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\cos\left(\overrightarrow{BC},\overrightarrow{DA}\right)=\frac{1}{2}.\frac{c^2+c'^2-b^2-b'^2}{2aa'}\)

1/ \(\overrightarrow{AB}^2-\overrightarrow{AD}^2=\overrightarrow{BC}^2-\overrightarrow{CD}^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{AD}\right)=\left(\overrightarrow{BC}+\overrightarrow{CD}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{BC}-\overrightarrow{CD}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}\right).\overrightarrow{DB}=\overrightarrow{BD}\left(\overrightarrow{BC}-\overrightarrow{CD}\right)=\overrightarrow{DB}\left(\overrightarrow{CB}+\overrightarrow{CD}\right)\)
Gọi M là trung điểm BD
\(\Rightarrow2\overrightarrow{AM}.\overrightarrow{DB}=2\overrightarrow{CM}.\overrightarrow{DB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{DB}.\left(\overrightarrow{AM}-\overrightarrow{CM}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{BD}.\overrightarrow{AC}=0\)
2/ \(A=\left|\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right|\Rightarrow A^2=\overrightarrow{a}^2-2\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{b}^2\)
\(=a^2+b^2-2ab.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=4^2+5^2-2.4.5.cos120^0=61\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\sqrt{61}\)
b/ \(B=\left|2\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right|\Rightarrow B^2=4a^2+b^2+4\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}\)
\(=4a^2+b^2+4ab.cos120^0=49\)
\(\Rightarrow B=7\)
3/ \(\left|\overrightarrow{x}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{a}-2\overrightarrow{b}\right|\Rightarrow\left|\overrightarrow{x}\right|^2=a^2+4b^2-4\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=12\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|\overrightarrow{x}\right|=2\sqrt{3}\)
\(\left|\overrightarrow{y}\right|^2=a^2+b^2-2\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=5\Rightarrow\left|\overrightarrow{y}\right|=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\overrightarrow{x}.\overrightarrow{y}=\left(\overrightarrow{a}-2\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)=a^2+2b^2-3\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=4\)
\(\Rightarrow cos\alpha=\frac{\overrightarrow{x}.\overrightarrow{y}}{\left|\overrightarrow{x}\right|.\left|\overrightarrow{y}\right|}=\frac{4}{2\sqrt{15}}=\frac{2\sqrt{15}}{15}\)

a) Giả sử A'=(x'; y'). Khi đó \(T_{\overrightarrow{v}}\left(A\right)=A'\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x'=3-1=2\\y'=5+2=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do đó: A' = (2;7)
Tương tự B' =(-2;3)
b) Ta có: \(A=T_{\overrightarrow{v}}\left(C\right)\Leftrightarrow C=^T\overrightarrow{-v}\left(A\right)=\left(4;3\right)\)
c) Cách 1. Dùng biểu thức tọa độ của phép tịnh tiến
Gọi M(x;y), M' = \(^T\overrightarrow{v}\) =(x'; y'). Khi đó x' = x-1, y' = y + 2 hay x = x' +1, y= y' - 2. Ta có M ∈ d ⇔ x-2y +3 = 0 ⇔ (x'+1) - 2(y'-2)+3=0 ⇔ x' -2y' +8=0 ⇔ M' ∈ d' có phương trình x-2y+8=0. Vậy \(^T\overrightarrow{v}\) (d) = d'.
Cách 2. Dùng tính chất của phép tịnh tiến
Gọi \(^T\overrightarrow{v}\)(d) =d'. Khi đó d' song song hoặc trùng với d nên phương trình của nó có dạng x-2y+C=0. Lấy một điểm thuộc d chẳng hạn B(-1;1), khi đó \(^T\overrightarrow{v}\) (B) = (-2;3) thuộc d' nên -2 -2.3 +C =0. Từ đó suy ra C = 8.
a) Giả sử A'=(x'; y'). Khi đó
(A) = A' ⇔
Do đó: A' = (2;7)
Tương tự B' =(-2;3)
b) Ta có A = (C) ⇔ C=
(A) = (4;3)
c)Cách 1. Dùng biểu thức tọa độ của phép tịnh tiến
Gọi M(x;y), M' = =(x'; y'). Khi đó x' = x-1, y' = y + 2 hay x = x' +1, y= y' - 2. Ta có M ∈ d ⇔ x-2y +3 = 0 ⇔ (x'+1) - 2(y'-2)+3=0 ⇔ x' -2y' +8=0 ⇔ M' ∈ d' có phương trình x-2y+8=0. Vậy
(d) = d'
Cách 2. Dùng tính chất của phép tịnh tiến
Gọi (d) =d'. Khi đó d' song song hoặc trùng với d nên phương trình của nó có dạng x-2y+C=0. Lấy một điểm thuộc d chẳng hạn B(-1;1), khi đó
(B) = (-2;3) thuộc d' nên -2 -2.3 +C =0. Từ đó suy ra C = 8

Đường thẳng d nhận \(\left(1;2\right)\) là 1 vtcp
Phép tịnh trên theo \(\overrightarrow{v}\) biến d thành chính nó khi và chỉ khi \(\overrightarrow{v}\) cùng phương vecto chỉ phương của d
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{a+1}{1}=\frac{3a-4}{2}\Leftrightarrow a=6\)

a) Gọi M' (x₁' ; y₁' ), N' (x₂' ; y₂ )
* M' là ảnh của M qua phép F, nên toạ độ M' thoả:
{x₁' = x₁.cosα – y₁.sinα + a
{y₁' = x₁.sinα + y₁.cosα + b
* N' là ảnh của N qua phép F, nên toạ độ N' thoả:
{x₂' = x₂.cosα – y₂.sinα + a
{y₂' = x₂.sinα + y₂.cosα + b
b) * Khoảng cách d giữa M và N là:
d = MN = √ [(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
* Khoảng cách d' giữa M' và N' là:
d' = M'N' = √ [(x₂' - x₁' )² + (y₂' - y₁' )²]
= √ {[x₂.cosα – y₂.sinα + a - (x₁.cosα – y₁.sinα + a)]² + [x₂.sinα + y₂.cosα + b - (x₁.sinα + y₁.cosα + b)]²}
= √ {[cosα(x₂ - x₁) - sinα(y₂ - y₁)]² + [sinα(x₂ - x₁) + cosα(y₂ - y₁)]²}
= √ [(x₂ - x₁)².(cos²α + sin²α) + (y₂ - y₁)².(cos²α + sin²α)]
= √ [(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
c) Phép F là phép dời hình vì: MN = M'N' = √ [(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
d) Khi α = 0 ⇒ cosα = 1, sinα = 0
Suy ra:
{x' = x + a
{y' = y + b
Đây là biểu thức toạ độ của phép tịnh tiến. Vậy F là phép tịnh tiến