Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt \(t=cosx;t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Để hàm số có tập xác định R
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx^2-\left(2+m\right)cosx+2m\ge0;\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-\left(2+m\right)t+2m\ge0\) với mọi \(t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
Đặt \(f\left(t\right)=t^2-\left(2+m\right)t+2m\); \(I\left(\dfrac{2+m}{2};f\left(\dfrac{2+m}{2}\right)\right)\)
TH1: \(\dfrac{2+m}{2}< -1\) \(\Leftrightarrow m< -4\)
Để \(f\left(t\right)\ge0;\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)\(f\left(t\right)_{min}=f\left(-1\right)\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow3+3m\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge-1\)(ktm đk)
TH2: \(-1\le\dfrac{m+2}{2}\le1\)\(\Leftrightarrow-4\le m\le0\)
Để \(f\left(t\right)\ge0;\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\) \(\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)_{min}=f\left(\dfrac{2+m}{2}\right)\ge0\)\(\Leftrightarrow-m^2+4m-4\ge0\)\(\Leftrightarrow m=2\) (ktm đk)
TH3:\(\dfrac{m+2}{2}>1\) \(\Leftrightarrow m>0\)
Để \(f\left(t\right)\ge0;\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)_{min}=f\left(1\right)\ge0\)\(\Leftrightarrow m-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge1\)
Kết hợp cả ba TH \(\Rightarrow m\ge1\)
Vậy...
Đơn giản hơn:
\(t^2-\left(m+2\right)t+2m\ge0\) ; \(\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-2\right)-m\left(t-2\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-m\right)\left(t-2\right)\ge0\) (1)
Do \(t-2< 0\) ; \(\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\) nên (1) tương đương:
\(t-m\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge t\) ; \(\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge1\)

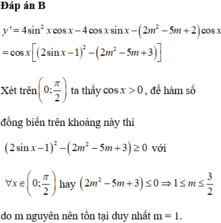
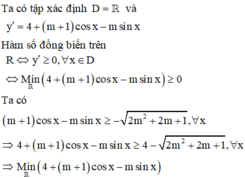
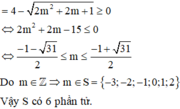

Hàm số xác định trên R khi và chỉ khi:
\(2cos^2x-m.sinx+1>0\) ;\(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2-2sin^2x-m.sinx+1>0\) ;\(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2sin^2x-m.sinx+3>0\)
Đặt \(sinx=t\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)=-2t^2-m.t+3>0\) ; \(\forall t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\min\limits_{\left[-1;1\right]}f\left(t\right)>0\)
Do \(a=-2< 0\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)_{min}\) luôn rơi vào 1 trong 2 đầu mút của đoạn
\(f\left(-1\right)=m+1\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=1-m\)
TH1: \(f\left(t\right)_{min}=m+1\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1>0\\1-m\ge m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>-1\\m\le0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow-1< m\le0\)
TH2: \(f\left(t\right)_{min}=1-m\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-m>0\\m+1\ge1-m\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow0\le m< 1\)
Vậy \(-1< m< 1\)
Có duy nhất 1 giá trị nguyên của m thỏa mãn (m=0)