Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(0\right)=5\Rightarrow0+0+5\Rightarrow c=5\\f\left(1\right)=0\Rightarrow a+b+5=0\\f\left(5\right)=0\Rightarrow25a+5b+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(1\right)\\\left(2\right)\\\left(3\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
tu (3) => b =-1-5a
tu (2) => a-1-5a+5 =0 => a =1 ;b =-6
y =x^2 -6x +5
y(-1) =1 +6 +5 khac 3 => loai
y(-1/2) =1/4 -6/2 +5 =1/4 +2 = 9/4 nhan
Q(1/2;9/4) thuoc dths

a) f(-1) = 2.(-1) = -2
f(-2) = 2.(-2) = -4
f(-4) = 2.(-4) = -8
b) Khi f(2) = 4
=> 2a = 4
=> a = 2
Vậy a = 2

3.
a) thay vào hàm số y=f(x)=-2x+3, ta đc:
f(-2)=-2.(-2)+3=7
f(-1)=-2.(-1)+3=5
f(0)=-2.0+3=3
\(f\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)=-2.\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)+3=4\)
\(f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=-2.\frac{1}{2}+3=2\)

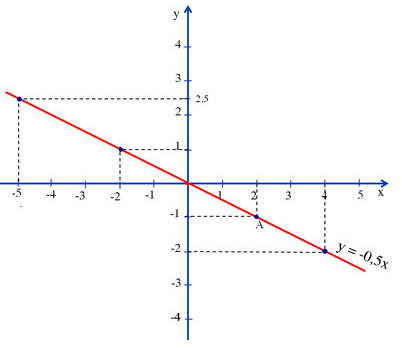
Cho x =2 được y =-2 =>A(2 ;-1) thuộc đồ thị. Vẽ đồ thị
a) Trên đồ thị ta thấy
f(2)=-1
f(-2) =1
f(4)=-2
f(0)=0;
b) Trên đồ thị ta thấy
y=-1 => x=2
y=0 => x=0
y=2,5 => x=-5
c) Khi y dương y > 0 ứng với phần đồ thị nằm trên trục hoành và bên trái trục tung nên x < 0.
Khi y âm : y < 0 ứng với phần đồ thị nằm trên trục hoành và bên phải trục tung nên x > 0

Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.
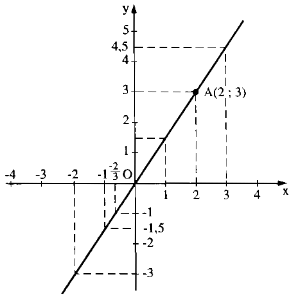
a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) =0
b)\(y=-1\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(y=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
\(y=4,5\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0
Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.

a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) = 0
b)y=−1⇒x=\(\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
b)y=0⇒x==\(\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
y=4,5⇒x=\(\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0