Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(y=3x+m\)(*)
1) a) Đồ thị hàm số (*) đi qua \(A\left(-1,3\right)\)nên \(3=3.\left(-1\right)+m\Leftrightarrow m=6\).
b) Đồ thị hàm số (*) đi qua \(B\left(-2,5\right)\)nên \(5=3.\left(-2\right)+m\Leftrightarrow m=11\).
2) Đồ thị hàm số (*) cắt trục hoành tại điểm có hoành độ \(3x+m=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{m}{3}\)
Suy ra \(-\frac{m}{3}=-3\Leftrightarrow m=9\).
3) Đồ thị hàm số (*) cắt trục tung tại điểm có tung độ \(y=3.0+m=m\)
suy ra \(m=-5\).

Tham khảo:


c. Giao điểm thứ hai của đồ thị có hoành độ bằng -3 và tung độ bằng 9. Ta có : B(-3 ; 9).

a) Hàm số đã cho là y = 2x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm A(1,5; 0) nên 0 = 2 . 1,5 + b. Suy ra b = -3.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = 2x - 3.
b) Hàm số đã cho là y = 3x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm A(2; 2) nên 2 = 3 . 2 + b. Suy ra b = -4.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = 3x - 4.
c) Vì đồ thị của hàm số đã cho song song với đường thẳng y = √3x nên nó có hệ số góc là a = √3. Do đó hàm số đã cho là y = √3x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm B(1; √3 + 5) nên √3 + 5 = √3 . 1 + b. Suy ra b = 5.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = √3x + 5.
Bài giải:
a) Hàm số đã cho là y = 2x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm A(1,5; 0) nên 0 = 2 . 1,5 + b. Suy ra b = -3.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = 2x - 3.
b) Hàm số đã cho là y = 3x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm A(2; 2) nên 2 = 3 . 2 + b. Suy ra b = -4.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = 3x - 4.
c) Vì đồ thị của hàm số đã cho song song với đường thẳng y = √3x nên nó có hệ số góc là a = √3. Do đó hàm số đã cho là y = √3x + b.
Vì đồ thị đi qua điểm B(1; √3 + 5) nên √3 + 5 = √3 . 1 + b. Suy ra b = 5.
Vậy hàm số đã cho là y = √3x + 5

Lời giải
a) A(-1;2)
=> y(-1) =2 <=> a.(-1)^2 =2 => a=2
hàm số được xác định y=2x^2
b) xác đinh tọa độ điểm B
2x^2 =8 => x =+-2
=>có 2 điểm B thỏa mãn
B(2,8) và B'(-2;8)
(d): y=a'x+b'
(d) đi qua A => 2=-a'+b' => b' =2+a'
hay d: y=a'(x+1)+2
(d) đi qua B(2,8) => 8=a'(2+1) +2 => a'=2
(d) đi qu B(-2,8) =>8=a'(-2+1) +2 => a' =-6
vậy
có hai đường thẳng thỏa mãn đầu bài là
d1: y=2x+4
d2:y=-6x-4
đồ thị

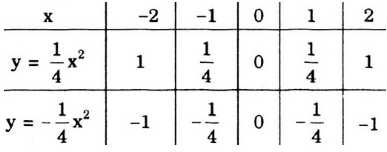
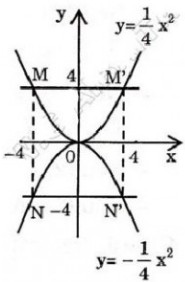


b: f(-2)=-1/2*(-2)^2=-1/2*4=-2
=>M(-2;-2)
f(1)=-1/2*1^2=-1/2
=>N(1;-1/2)
Gọi (d): y=ax+b là phương trình đường thẳng cần tìm
Theo đề, ta có hệ: -2a+b=-2 và a+b=-1/2
=>a=1/2 và b=-1
=>y=1/2x-1
c: (D)//y=1/2x-1 nên (D): y=1/2x+b
PTHĐGĐ là:
-1/2x^2-1/2x-b=0
=>x^2+x+2b=0
Δ=1^2-4*1*2b=-8b+1
Để (P) cắt (D) tại một điểm duy nhất thì -8b+1=0
=>b=1/8